Why Software Bugs Cost Companies Millions and How QA Saves the Day
Software bugs quietly drain billions from companies each year. Apart from financial losses, they result in broken features, lost customers, and halted growth.
But here’s the good news: most of these failures are preventable. All it takes is a smart QA strategy integrated into your development process from day one.
We’ve seen it firsthand at ThinkSys. Our QA experts help clients spot critical issues before they ever reach production. As a result, our clients see fewer emergencies, faster releases, and better software.
Let’s break down how high-impact QA protects your product and reputation and why cutting corners here can cost you everything.
Real-World Examples Where Software Bugs Cost Millions
In 2022 alone, U.S. businesses lost $2.41 trillion due to poor software quality. The Consortium for Information & Software Quality (CISQ) revealed this in a report. But the even more shocking part was a $330 billion increase from just two years prior. And the costs keep rising.

Downtime makes it even more painful. Gartner estimates the average outage costs $5,600 per minute. But for companies like Amazon, those numbers explode. A 13-minute outage once cost them $2.6 million—because every minute of peak downtime burns around $200,000.
Upon visiting their website, users saw this message.
The gaming industry is not immune either. The buggy launch of Cyberpunk 2077 forced CD Projekt Red to issue mass refunds and damage control, costing over $50 million in total.
In 2018, a botched system migration at TSB Bank locked 1.9 million customers out of their accounts. As a result, £330 million in losses, a £48.65 million fine, and a collapse in customer trust led to leadership resignations.
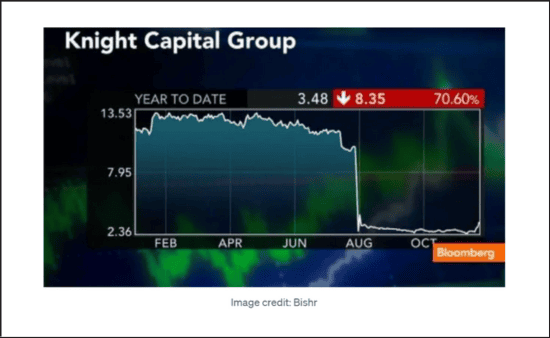
Other industries face even higher stakes. Toyota recalled millions of vehicles when a software flaw in its Electronic Throttle Control System raised safety concerns.
The CISQ report makes it clear that poor software quality doesn’t just cause downtime. It ends companies. We will cover this more in detail in later sections.
Why Software Failures Get More Expensive in the Long Run
Fixing a bug during design might cost you $100. Wait until production, and that same issue can explode to $10,000 or more, according to IBM’s Systems Science Institute.
Why the difference? The longer a bug stays hidden, the more systems it touches—and the harder it is to fix.
That’s why here’s a principle every developer (and product manager) should know:
The Rule of Ten:
- Catch it in design → $100
- Catch it in development → $1,000
- Catch it in production → $10,000+
The cost multiplies tenfold at every stage of the pipeline.
But why do costs explode like this?
Technical debt is a major factor. Quick fixes and rushed coding decisions create a snowball effect, making software increasingly difficult and expensive to maintain.
Martin Fowler's 'Technical Debt Quadrant' framework demonstrates that while some technical compromises are strategic, unplanned shortcuts often lead to expensive problems later.
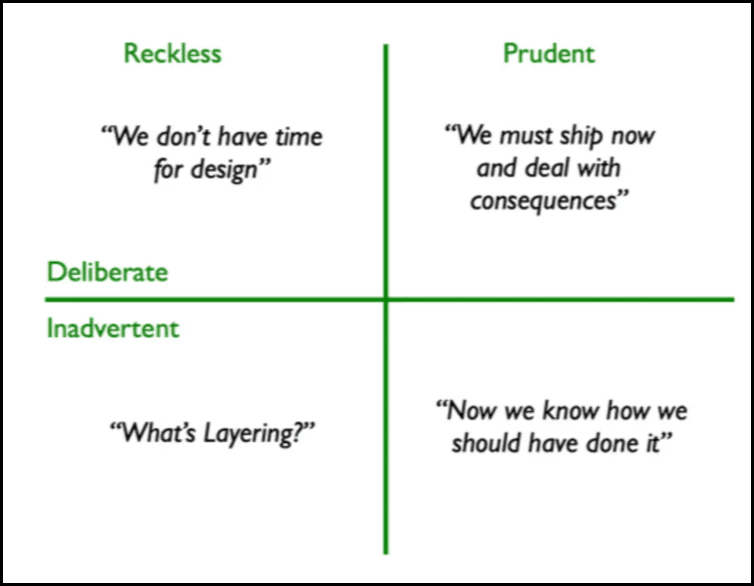
The stakes get higher in regulated industries and customer-facing applications.
Different sectors face different levels of risk. Financial services, healthcare, and aviation deal with strict regulations and high-stakes operations. A minor bug in a mobile game becomes a major crisis in banking software, potentially triggering massive losses and regulatory penalties.
So, how do the best teams prevent this?
They test early.
The State of DevOps Report 2016 stated that top-performing teams spend 22% less time on unplanned work and rework. This way, teams reclaim 29% more time to focus on new development. This efficiency comes from CI/CD and DevOps practices that emphasize early issue detection.
The core principle is that build your QA process to catch issues early, because fast fixes are only possible when problems surface early.
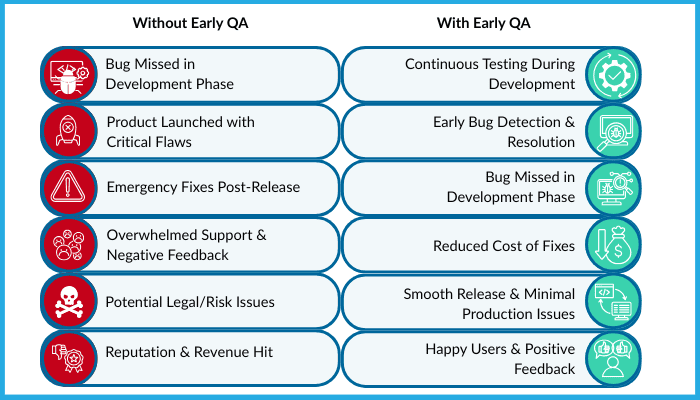
But the real cost of a bug goes far beyond finances.
The hidden costs are also involved, which are directly tied to trust, morale, and opportunity, and some companies never recover from them.
Let’s talk about those next.
Damages That Hurt More Than Financial Losses
When software fails, it cuts into trust, reputation, and sometimes even safety.
In sectors like healthcare or finance, a single flaw can put lives or livelihoods at risk. Even in less critical industries, the damage is often permanent and invisible until it’s too late.
Let’s say a company ships its product with a small bug in the authentication system. Internal testing misses it. After the launch, hackers exploit the flaw to access customer data - names, contact details, and payment information. Users write negative reviews on social media. The support team can't keep up. The company's reputation crumbles within days.
In today’s market, trust is currency. Lose it, and no patch, update, or apology will buy it back.
Some companies never recover. Not because the bug couldn’t be fixed, but because the trust never came back.
The internal damage is just as bad.
Engineering teams spend half their time fixing bugs instead of building new features. That leads to lost momentum, missed opportunities, and team burnout.
Perhaps the most tragic illustration of software failure comes from aviation.

In Boeing 737 MAX, a software flaw contributed to two fatal crashes, grounding the fleet worldwide. Consequently, the company lost Billions, earned a bad reputation, and took years of recovery time.
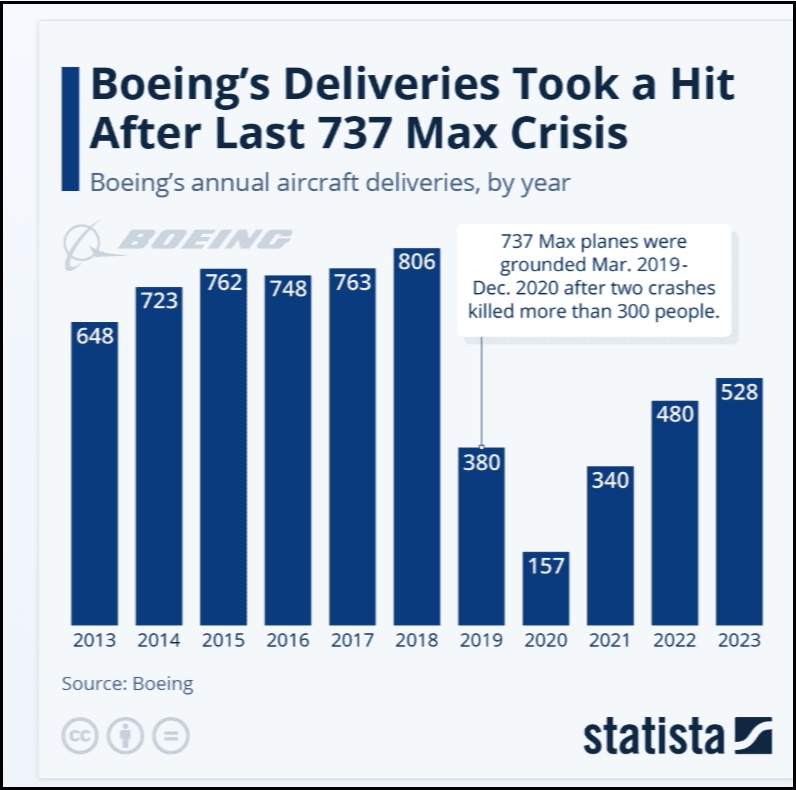
Software glitches stall your growth—and eventually, erode your identity.
Because once people stop believing in you, no amount of effort can bring them back.
How QA Saves You from Financial and Reputational Losses
One bad release can destroy trust, burn cash, and set your roadmap back months. QA exists to stop that from happening.
It stops bugs early, reduces emergency patching, and saves countless engineering hours. Studies show that every $1 invested in QA saves $5–$10 in downstream costs.
QA works because it’s proactive. It catches small issues before they become expensive emergencies—saving time, money, and customer trust.
Martin Fowler’s research on continuous testing proves it: catching bugs during development is dramatically cheaper than fixing them post-release. Wait until production, and you’re suddenly dealing with emergency patches, legal exposure, and lost users.
Must Read:- 16 Types of Bugs you must know
So what separates good QA from game-changing QA?
Three things: metrics, mindset, and modern practices. That means tracking the right numbers, building a culture of quality, and using tools that scale with speed.
High-performing teams ship software with:
- Low defect density
- High test coverage
- Minimal rollbacks
And the benefits compound when QA is built into the DevOps lifecycle.
Gene Kim, author of The Phoenix Project, puts it bluntly:
"When problems arise—and they always do—top teams fix them in under an hour. Others take days or weeks."
QA lets elite teams move fast with confidence.
Even Microsoft backs this up. Their research shows that early-stage testing improves quality and accelerates delivery.
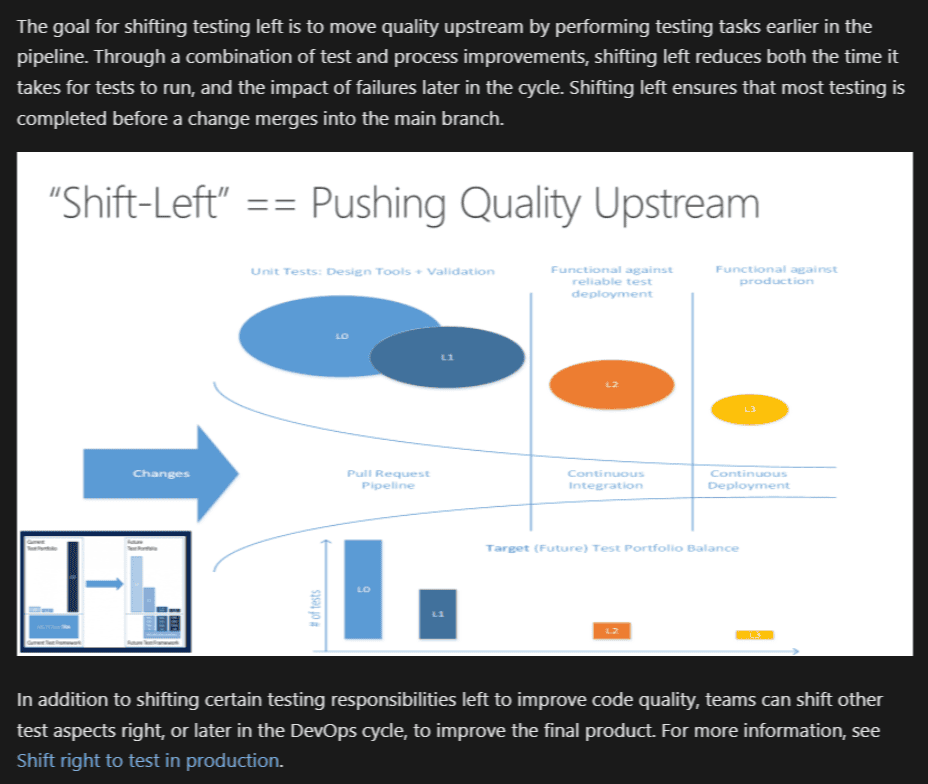
QA delivers the biggest impact when it starts at the very beginning.
James Bach, a pioneer in exploratory testing, warns that teams often trade quality for speed when rushing into Agile or DevOps. His advice is simple:
Start QA on day one.
Catch issues during planning, not post-launch. You’ll spend less, move faster, and avoid the fallout of broken trust.
QA is about risk prevention, brand protection, and productivity insurance. And the sooner it’s built into your pipeline, the stronger your product—and reputation—will be.
What High-Impact Quality Assurance Looks Like
Top-performing teams don’t guess when it comes to QA.
They follow proven systems, adapt their testing based on risk, and track metrics that actually improve product quality.
Let’s break down what high-impact QA looks like in practice—across industries, team sizes, and test types.
Start with Structure: The Testing Pyramid
Introduced by Mike Cohn in Succeeding with Agile, the Testing Pyramid remains the foundation of scalable, efficient QA:
The Testing Pyramid
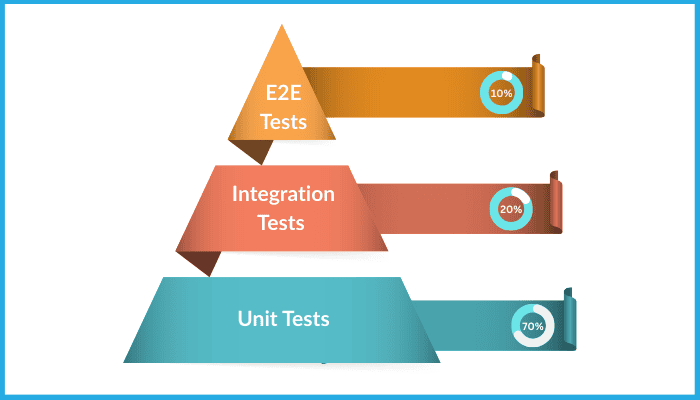
- 70% Unit Tests – Fast, isolated checks for components
- 20% Integration Tests – Ensures parts work together
- 10% End-to-End (E2E) Tests – Simulates full user journeys
This layered approach ensures fast feedback, low flakiness, and sustainable test coverage as you scale.
Customize for Your Industry
Different sectors face different risks, and your testing approach should reflect that.
Industry-Specific QA Focus:
- Finance & Healthcare: Security, compliance, traceability
- E-commerce: Frontend UX, checkout flows, performance under traffic
- Gaming: Speed, responsiveness, regression testing
- Enterprise SaaS: API stability, integrations, upgrade compatibility
Automate Strategically (Not Blindly)
Automation is essential—but it’s not everything.
Most teams aim to automate 70–90% of repetitive tests, using frameworks like Selenium, Cypress, or Playwright.
But some tests still require a human touch: exploratory testing, usability feedback, and behavior-based scenarios all benefit from manual review.
Tailor to Team Size
Your QA strategy should scale with your team:
- Small Teams – Start manual, automate core flows as you grow
- Mid-Size Teams – Use tools like Selenium or Cypress for broader coverage
- Enterprise Teams – Build comprehensive automation frameworks with QA specialists and real-time CI/CD integration
The ThinkSys Approach
At ThinkSys, we work with companies of all sizes across finance, healthcare, gaming, and SaaS. Whether you're scaling your first test suite or refining a mature QA pipeline, we help teams create smart, flexible QA strategies that fit their exact needs. So if you need to design a QA system for your organization, talk to our experts.
The Role of QA Tools in Ensuring Quality
The right QA tools catch bugs early, prevent costly rollbacks, and help teams ship with confidence.
Let’s break down the tools modern QA teams rely on to scale testing and reduce risk, without slowing down delivery.
Core Automation Frameworks
Three open-source tools dominate the test automation scenarios. Each offers different strengths:
- Selenium – Works across all major browsers and languages. Highly flexible but requires setup and strong coding skills (Java, Python).
- Cypress – Lightning-fast for frontend testing (especially Chrome/Edge). Ideal for JavaScript-heavy apps.
- Playwright – Supports all modern browsers out of the box, with a clean API and is great for async interactions. Still maturing but packed with modern features.
CI/CD Integration
Automation becomes powerful when plugged into your pipeline.
Whether you're using Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or CircleCI, these tools run your test suite automatically on every commit, so you catch issues before they hit production.
As a result, you see faster cycles, fewer surprises, and a tighter feedback loop between dev and QA.
Choosing the right tool depends on your app, your stack, and your team’s coding experience.
AI-Powered Testing
AI-based tools go beyond scripted testing. They analyze screenshots, DOM changes, and user behavior patterns to detect visual regressions, broken flows, and flaky tests—often before a human tester even notices.
Top AI-Powered Testing Platforms:
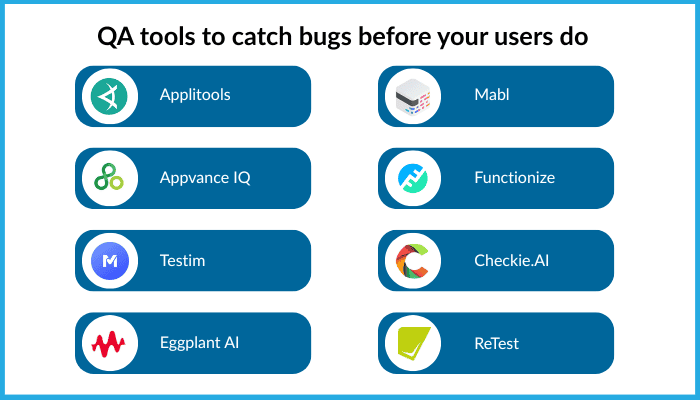
- Visual Testing: Applitools
- Enterprise Automation: Appvance IQ, Eggplant AI
- Low-Code / Fast Start: Mabl, Testim, Functionize
- Open / Experimental: Checkie.AI, ReTest
AI testing helps scale QA faster, especially for UI-rich apps, responsive layouts, or frequent deployments.
Sugguested Read:- How AI is revolutionizing testing?
Logging and Tracking Bugs
Automation is only half the battle. Once you catch a bug, you need a system to track and resolve it.
Most QA teams use tools like JIRA, Bugzilla, or Linear to connect test runs directly to issue tickets, so nothing falls through the cracks and everything is traceable.
Don’t Overlook Security Testing
Security is QA’s silent partner. Tools like OWASP ZAP and Snyk scan your codebase, packages, and APIs to uncover vulnerabilities early, before they become breaches.
Especially in regulated industries (finance, healthcare, govtech), this is non-negotiable.
These tools catch bugs by running scripts that mimic real users interacting with your product. They spot UI and functional problems before users ever see them.
Match Tools to Your Team
Different tools come with different learning curves:
Selenium is powerful, but requires strong coding.
Cypress is great for JS teams.
Playwright is newer, easier to onboard, but less battle-tested.
Choose what aligns with your current skills and what scales with your growth.
Yes, these tools take time to set up and learn.
But in return, they ensure faster cycles, fewer bugs, stronger launches, and happier customers.
That’s the power of the right QA tech stack.
Conclusion
Quality assurance is your first line of defense against broken releases, burnt-out teams, and customer churn.
When QA is integrated into your development process, it creates measurable value at every stage:
- Fewer bugs in production
- Faster feature delivery
- Higher customer trust
- Lower support and rework costs
Companies that invest in smart testing spend less time fixing problems and more time building the products customers love.
If your current QA process feels reactive, slow, or inconsistent, we can help.
At ThinkSys, we design quality strategies that scale with your team, your tech, and your timeline.
Frequently Asked Questions
Share This Article:



