Test Automation ROI Calculator: Is It Worth the Investment for Your Enterprise?
Finding and correcting a bug in the Requirements phase is the least expensive. But the price goes up quickly as bugs emerge in later stages, reaching 3 to 5 times more during Design, 10 times more during Coding, and an incredible 15 to 20 times more during Testing. The real surprise? Once a problem reaches Post-release or Production, it can cost 30 to 100 times more than the initial $1 baseline to fix it.
That's why more and more businesses are using test automation. However, before they begin using test automation, the primary concern is, "Is it worth the money?"
The answer isn’t as straightforward as adding numbers into a single equation. The ROI of test automation depends on multiple factors, including time saved, costs reduced, risks avoided, and strategic advantages such as faster time-to-market.
It's not as easy as just putting numbers into one equation to find the solution. The return on investment (ROI) of test automation depends on several factors, including the amount of time and money it saves, the number of risks it mitigates, and how it facilitates faster app releases.
In this article, you will get a detailed framework, backed by real data, multiple proven formulas, and practical examples, for calculating the ROI of test automation for your enterprise, allowing you to answer the question on your own.
What You Should Know about Test Automation ROI?
Before understanding the framework, it’s necessary to understand briefly about the test automation ROI. Test automation ROI is a crucial business indicator that demonstrates the value automated testing procedures bring to a company. By providing a numerical picture of the financial and operational gains from an automation strategy, it helps executives answer a crucial question: Is the investment in automation or manual testing truly worthwhile?
Beyond simple financial benefits, a detailed ROI analysis helps to predict future performance and provides a data-driven basis for decision-making and resource allocation. It shifts the discussion from a subjective opinion to one grounded in measurable metrics, ensuring every investment is strategic and impactful.
Framework for Calculating ROI of Test Automation
When it comes to measuring the value of test automation effectively, you can employ two primary calculation methods: financial ROI, which measures the monetary returns, and efficiency ROI, which quantifies time and resource savings.
For the most comprehensive analysis, this article will consider both.

1. The Financial ROI
Before investing money in something, every leader wants to examine the ROI from a financial perspective. That said, this part is about weighing the real monetary benefits of automation against its total expenses, which provides a way to make informed decisions. You can use the following formula for that:
Automation ROI %=Benefits from Automation-Automation CostsAutomation Costs×100
Now, the next question you might have is ‘how to calculate benefits from automation and automation costs?’ To help you answer this question, let’s break down the components.
| Mannual Testing | Automated Testing | |
| Test Cases | 200 | 200 |
| Time per Test | 30 Minutes | 5 Minutes |
| Total Execution Time | 625 Days | 100 Days |
- Savings (Benefits from Automation): Savings or direct benefits from automation refer to the monetary value gained by replacing manual testing with automation. It is calculated by quantifying the time saved per test run and translating that into a dollar value, and requires understanding three core components:
- Manual Testing Time: The total effort required to execute tests manually, measured per test case. This represents the baseline cost before the implementation of automation.
- Automation Testing Time: The time taken to execute the same tests using automation. Automated tests typically run faster and with minimal human intervention.
- Test Volume and Frequency: The number of test cases and the number of times each test is executed over a defined period.
Once you understand the components, you can use the following formula to quantify the savings:
Savings =Manual Testing Time -Automation Testing Time×Number of Tests ×Number of Test Runs
Let’s illustrate the calculation with an example. Assume that an organization has 200 test cases that take 30 minutes to execute manually. These can be automated and take only five minutes to complete. If these tests are run 50 times over the course of a year, where the per-hour cost of a QA engineer is $75, the savings would be:- Total manual testing time: 0.5 hours per test×200 tests×50 runs =5000 hours.
- Total automated time: ~0.08hours per test×200 tests×50 runs=800 hours.
- Total hours saved: 5000 hours-800 hours=4200 hours.
- Monetary Savings: 4200 hours×75=$315,000.
- Investments (Automation Costs): The investment in test automation showcases the total cost required to design, implement, and maintain an automated testing program. Estimating these costs accurately is critical for organizations to calculate ROI and align QA strategy with overall business goals. Automation investment can be categorized into four major components:
- One-Time Setup Costs: These include framework setup, tool licensing, infrastructure provisioning, and environment configuration.
- Labor Costs: QA engineer's time to code automated test scripts and configure tests.
- Ongoing Maintenance Costs: It involves updating or fixing tests as the application changes, effort for failed test cases, defect triage, and adapting to new releases.
- Indirect or Hidden Costs: Costs like training, knowledge transfer, tool integration, and occasional troubleshooting or consulting costs fall under this category.
- Calculating Investment Cost: The following formula will help you calculate your overall investment cost for automation testing.
Total Investment=(Setup costs+Labor Costs)×Hourly rate+Maintenance costs+Tool costs+Infrastructure costs+Training costs
Within this, the ongoing maintenance costs are a critical component and can be calculated using the following formula:
Maintenance costs=Maintenance Time Per Failed Test×% of Failed Tests Per Run×Number of Tests×Number of Runs×Hourly Rate
Using the same example, let’s calculate the investment. Let’s say that the initial framework setup takes 800 hours, and each of the 200 tests takes 2 hours to code. The coding and setup efforts will be:
Building and Coding Cost=(800+400)×75=$90,000
The next consideration is ongoing maintenance. In case each failed test requires 2 hours to fix, and the average failure rate is 5% per run across 200 tests executed 50 times a year, the total maintenance workload becomes 1,000 hours annually. This equates to:
Maintenance Costs=1000×75=$75,000
Finally, add indirect but essential costs such as annual tool licensing, infrastructure for cloud or server execution, and onboarding programs, which can cost $20,000, $10,000, and $5,000, respectively. Together, these additional costs equal $35,000. Adding all components, the total investment of implementing automation comes to:
Total Investment =90,000+75000+35000=$200,000
- Total ROI: The only thing left now is to combine the total savings and costs to calculate the final ROI percentage for the year. Just add the values to the initial ‘Automation ROI’ equation. For the above example, that would be:
Automation ROI %=$315,000-$200,000$200,000×100=57.5%
The above example shows 57.5% ROI during the first year of implementing automation testing in your enterprise. However, that’s an incomplete picture. The real ROI comes after the first year, as one-time expenses eat up the majority of the ROI.
Multi-Year ROI Projection
Let’s project the ROI over three years using our example:
- Annual Savings: $315,000 (remains constant for simplicity, though in reality it often grows as test coverage increases).
- Year 1 Investment: $200,000 (includes one-time setup of $90,000 plus $75,000 maintenance and $35,000 indirect/tooling costs).
- Year 2+ Investment: $110,000 annually (ongoing maintenance $75,000 + tools/infrastructure/training $35,000; no framework rebuild required).
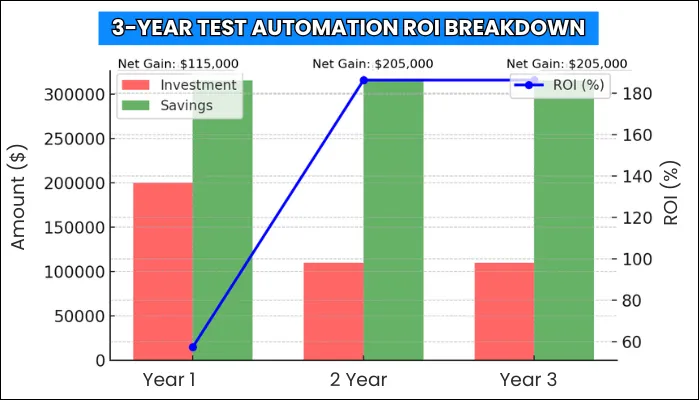
| Year | Savings | Investment | Net Gain | ROI (%) |
| 1 | $315,000 | $200,000 | $115,000 | 57.5% |
| 2 | $315,000 | $110,000 | $205,000 | 186.4% |
| 3 | $315,000 | $110,000 | $205,000 | 186.4% |
The aforementioned projection highlights how automation shifts from a moderate short-term return to a high-yield investment as one-time costs are absorbed. Over the course of three years, the enterprise generated $525,000 in excess of total expenses.
2. The Efficiency ROI: Quantifying Speed and Productivity
Even while financial returns are the most important thing to think about, you can't ignore the ROI based on time, effort, and resource efficiency, especially if your business works in an agile and DevOps setting.
This approach is all about saving time and speeding up the software delivery process, which is highly important for getting feedback quickly.
In the next part, you'll see a few formulas that compare the time it takes to do automated operations to the time it takes to execute the same tests manually.
This is because automated tests can run for much longer than a human tester can work in a day. The difference highlights how automated test runs can save a significant amount of time due to their continuous nature. With that in mind, let's break down the formulas:
- Automated test script development time:
Hourly automation time per test×Number of automated test cases8
Example: For our 200 test cases, this is (2 hours/test × 200 tests) / 8 hours/day = 50 days.
- Automated test script execution time:
Automated test execution time per test×Number of automated test cases×Period of RO18
Example: For our 200 tests run 50 times, this is (5 minutes/test × 200 tests × 50 runs) / (60 minutes/hour × 18 hours/day) = 46.3 days.
- Automated test analysis time:
Test analysis time×Period of ROI8
Example: Assuming a total of 200 hours is spent on test analysis over the year, this is (200 hours) / 8 hours/day = 25 days.
- Automated test maintenance time:
Maintenance time×Period of ROI8
Example: Based on our earlier calculation of 1,000 hours of maintenance, this is (1,000 hours) / 8 hours/day = 125 days.
- Manual execution time:
Manual test execution time×Number of manual test cases×Period of ROI8
Example: Based on our earlier calculation of 5,000 hours of manual execution, this is (5,000 hours) / 8 hours/day = 625 days.
While the financial model is essential for securing executive buy-in and justifying budgets, the efficiency model provides a more granular, day-to-day metric for agile teams focused on optimizing feedback loops and accelerating release velocity.
A truly comprehensive analysis requires calculating and presenting both to demonstrate the full scope of the business value.
The financial model is crucial for securing executive buy-in and justifying funding.
The efficiency model, on the other hand, provides agile teams with more detailed, day-to-day statistics to utilize when trying to expedite release times and improve feedback loops.
To fully demonstrate the value of the firm, a comprehensive study should encompass both calculations and presentations.
Benefits of Test Automation for Enterprise
One of the best ways to determine if the change will benefit your business is to calculate the ROI. But that's not the only thing that matters. The ROI encompasses much more than just spreadsheets and statistics.
It includes both measurable and intangible benefits, which, when combined, provide you with a strong and lasting edge over your competitors.
- Tangible Benefits: These are the benefits that can be directly measured and factored into an ROI calculation, demonstrating a clear financial impact.
- Cost Savings from Reduced Manual Hours: By automating redundant and high-frequency tasks, organizations can significantly reduce the time QA engineers spend on manual testing. Doing so frees up engineering capacity, allowing them to spend more time on strategic thinking.
- Quicker Releases: One of the main reasons why releases are delayed is that testing takes too long. Manual testing is still helpful in certain situations, but automation has largely replaced it for regression and smoke test suites, eliminating testing bottlenecks that slow down releases. The faster feedback loop enables development teams to add new features and updates frequently without compromising quality.
- Defect Prevention and Quality Gains: Fixing bugs found early on is much less expensive. Automating tests will identify flaws early on, making it cheaper to fix them. If you can prevent only two significant issues from entering production, you could save almost $10,000 per year, taking into account support, rework, and any damage to your reputation.
- Intangible Benefits: While you cannot directly relate them to monetary benefits, these are foundational to a high-performing software team and are often a prerequisite for achieving the full financial returns.
- Improved Team Morale and Retention: At first, the team may not notice it, but over time, performing the same manual regression tests repeatedly can lead QA engineers to burn out and lose interest in their work. Exploratory testing, strategic planning, and problem-solving are made easier by automating repetitive tasks, which boosts job satisfaction and talent retention.
- Consistent Release Cadence: As test automation suites grow, they provide more dependable and predictable feedback, especially when combined with AI. These kinds of features help teams maintain a consistent and predictable release schedule. With a high level of stability, you can scale the software delivery without linearly scaling the QA team.
- Faster Onboarding and Knowledge Sharing: Well-structured, reusable test cases serve as a form of living documentation for an app’s critical workflows, facilitating faster onboarding and knowledge sharing. New team members can use this information to quickly get up to speed, understand core functionalities, and begin contributing to the team’s goals sooner.
Read more: How to build a effective qa team?
Unmasking the Hidden Costs and Common Pitfalls
There is no denying the significant ROI from test automation. However, there have been times when many projects fail to attain the desired outcome.
Now, it's common to believe that the concept is flawed and success is guaranteed for limited enterprises.
However, the truth is that this failure is not caused by a flawed concept, but rather by a flawed implementation strategy that ignores critical hidden costs and common pitfalls.
- The Underestimated Cost of Maintenance: One of the commonest reasons for failure is the improper assumption of the ongoing maintenance cost of an automated test suite. Often referred to as test debt, the accumulated maintenance overhead of automated tests can quickly consume resources and slow down release cycles. Initial ROI calculations frequently underestimate this burden.
The truth is that the maintenance curve for every automation suite becomes steeper as it grows larger and more complex. Your staff may spend 15% to 40% of their time on maintenance.
Companies with significant test debt often spend up to 85% of their QA budget on maintenance rather than investing in new ideas. This hinders their growth and erodes their competitive edge. - Achieving 100% Test Automation: In theory, achieving 100% test automation sounds excellent. Not only does it lead to overworked teams, unnecessary frustration, and slow progress, but the entire goal is impractical. Automation testing is designed to automate repetitive tests, saving time. However, it was never intended to replace manual testing altogether.
Tests such as usability and exploratory should always be performed manually for better judgment and evaluation. Experts recommend implementing a balanced approach that combines automated and manual testing for the best ROI. - Flaky Tests: Poorly implemented automation can lead to tests that pass or fail unpredictably, even without any changes to the application code. Such tests are called flaky tests and carry significant hidden costs, including investigation overhead that can average $5.67 per incident in one study, along with an additional 1.3% of a developer's productive time spent on repair and monitoring.
How to Maximize and Sustain Your ROI
It's one thing to determine ROI, but it's a whole other thing to ensure it continues to deliver value every quarter. After the first wave of automated savings, teams often become thrilled, but then they see that efficiency stops.
You need more than just numbers to maintain a healthy and long-lasting ROI. To carry out the plan perfectly, you need a strategy, discipline, a clear roadmap, and professionals.
- Automate Slowly and Only What Matters: As mentioned above, automating every test case is a sure way to cause a disaster. You should keep in mind that not every test case should be automated.
In reality, teams occasionally fail at automation because they try to automate everything at once, including low-value scenarios. Instead, the best approach is to focus on test cases that occur frequently and are significant, as they cover the most ground with the least amount of effort. - Keep Test Suites Lean and Healthy: The primary reason for ROI loss is that test suites are often packed with outdated, broken, or non-functional scripts. If not managed well, test maintenance can take up the automation budget.
The solution to this problem is to conduct regular audits to eliminate tests that are no longer needed and to consolidate overlapping cases. You need to approach your automation suite like code because it also needs to be refactored, reviewed, and updated all the time. - Balance Speed with Stability: Undeniably, it’s tempting to aim for faster releases by aggressively pushing automation coverage.
However, brittle tests can slow you down more than manual testing ever did. Instead, you should focus on stable frameworks and robust test data strategies. A stable test may take a bit longer to design, but the payoff is a reduction in reruns and fewer false alarms. - Track ROI as an Ongoing Metric: Don’t treat ROI as a static number you calculate once. Just like revenue or churn, consider it a living metric and monitor it over time to spot trends and make adjustments.
Sometimes, an unnecessary tool license may be eating into savings, or maybe parallel execution is giving you a bigger boost than expected. All this can only be identified with continuous ROI tracking, allowing you to make smarter reinvestments.
Conclusion
Some believe test automation is about saving money, while others consider it a time-saving implementation.
However, the truth is that test automation is both an investment in efficiency and quality that delivers long-term value by reducing manual effort, accelerating test cycles, and improving test coverage and reliability.
While initial costs may be significant, the cumulative benefits in faster releases, early defect detection, and consistent test execution ultimately lead to cost savings, higher product quality, and a stronger competitive advantage.
With the rise of AI-driven test generation, self-healing scripts, predictive analytics, and no-code tools, the efficiency and accuracy of test automation are expected to continue growing.
For QA leaders, this means two things. First, automation will become smarter and more cost-effective. Second, staying updated requires continuous investment in the right tools, practices, and expertise.
Considering these facts, many businesses opt to partner with specialists rather than attempting to do it themselves. With expert guidance, you can align automation with business goals, adopt emerging technologies at the right pace, and see measurable ROI faster.
If you’re ready to future-proof your QA and turn test automation into a true growth driver, ThinkSys’s automation services can help you design, implement, and scale a strategy that delivers real business impact. Let’s connect and build the foundation for your next stage of growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Share This Article:






