Your 2025 QA Trends Report & Strategy Guide
Technology is changing fast, and businesses are under pressure to keep up. Many have already moved to digital platforms and adopted the latest tools. But that’s not enough anymore. Customers now expect software/apps that are not just fast—but also smart, secure, and built to last.
If you want to stay ahead of the competition and build real trust with users, your approach to quality needs to evolve too. Our QA Trends 2025 report breaks down what’s next in quality assurance—from smarter testing and automation to trends in different industries and regions. It’s a practical guide to help you build better, more reliable products in a fast-moving digital world.

What Do Customers Expect from Your Softwares/Applications in 2025?
After helping various industries with their QA strategy evolution, we have gained valuable insights. Customers now expect to interact with High-Performance, Intuitive,Bug-Free, Secure, and Sustainable applications. At ThinkSys, we call this the HIBS+ principle. Whether you are building applications for internal operations or offering them to end users, you need to follow this enhanced framework.
HIBS+ Principle Explained:
- High-Performance: Advanced AI-driven performance optimization, predictive scalability, and ensuring software/application availability during sudden traffic spikes with intelligent load balancing.
- Intuitive: Building hyper-personalized, adaptive user interfaces with intelligent UX anticipation that enhances navigational experience and compels users to spend more time.
- Bug-Free: Proactive defect prevention using autonomous and self-healing testing methodologies to fix inconsistencies before software/application release.
- Secure: Zero-trust security architecture with continuous, context-aware compliance ensuring customer data safety and privacy.
- +Sustainable:: Eco-friendly software development with energy-efficient testing practices and carbon-neutral development processes.
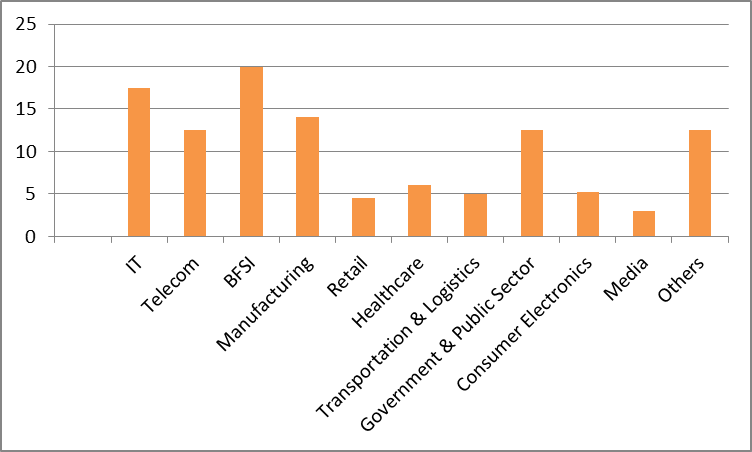
Industries that will invest heavily in Modern Quality Assurance (QA) Practices
Here are some industries that heavily invests in QA practices: Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, Healthcare Technology, Financial Services (BFSI), Manufacturing, Retail, Telecommunications, Transportation & Logistics, Government & Public Sector, Consumer Electronics, Media, Aerospace and Defense, Smart Cities and Urban Technologies, Quantum Computing, and Extended Reality (XR) Technologies and others.
Countries and Regions Emphasizing High-Quality,Cutting-Edge Digital Products
List of countries and regions that are increasing their emphasis on high quality, cutting edge digital products: U.S., Canada, Germany, UK, France, Italy, Spain, Russia, China, India, Japan, South Korea, Australia & New Zealand, Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, South Africa, Israel, Singapore, and United Arab Emirates.
Multiple Factors Leading to Wide Acceptance of Quality Assurance(QA) in Software Development
- As demand for intelligent consumer products like smart TVs, gaming consoles, and IoT devices continues rising exponentially, optimized performance with effortless connectivity becomes increasingly necessary.
- The automotive and transportation sectors are accelerating their transition to electric and autonomous vehicles, providing pathways for comprehensive digital transformation.
- To keep pace with rising demand for consumer electronics such as tablets, smartphones, wearables, and AR/VR devices, highly optimized and tested software solutions are essential.
- Due to incredible expansion of online shopping and digital commerce, retailers must upgrade applications to offer superior, personalized user experiences.
- Research and Development teams are revolutionizing industries by developing autonomous solutions for electric vehicles, quantum computing systems, and other advanced electronic devices.
The Evolving Strategic Role of Quality Assurance(QA) in 2025
Beyond specific technologies, the fundamental role and mindset of Quality Assurance are undergoing a significant transformation. QA is shifting from a distinct phase focused primarily on defect detection to a continuous, embedded practice integral to the entire software development lifecycle (SDLC). This evolution positions QA not merely as testers, but as strategic Quality Partners.
- Shift-Left & Shift-Right Integration: The emphasis is on involving QA earlier (Shift-Left) in the requirements analysis and design phases to prevent defects proactively, and extending QA involvement post-deployment (Shift-Right) through production monitoring, log analysis, and A/B testing feedback to ensure quality in real-world usage scenarios. This holistic view ensures quality is built-in and maintained throughout.
- QA as a Quality Partner: Modern QA professionals are expected to possess a deeper understanding of business goals, user experience, and technical architecture. They actively participate in planning, challenge requirements, guide automation strategy, contribute to risk assessment, and collaborate closely with development and product teams. This strategic partnership ensures quality considerations influence decisions from inception to delivery and beyond.
- Embedded Quality Mindset: Quality is increasingly viewed as a shared responsibility across the entire team, facilitated and championed by QA experts. This involves fostering a culture where developers, product owners, and operations personnel all contribute to and prioritize quality, supported by integrated processes and tools managed under the QA umbrella.
Latest Software Testing Trends 2025
The technological landscape continues to drive innovation in QA practices. Here are the key trends shaping software testing in 2025, incorporating the latest advancements and strategic shifts:
1. Generative AI-Powered Testing & Creation:
Artificial Intelligence, particularly Generative AI, is revolutionizing software testing beyond traditional automation:
- AI-Generated Test Cases & Data: Leveraging AI to automatically generate relevant test cases, test data, and even test scripts from requirements, user stories, or application models, ensuring broader coverage with real-time adaptability and continuous learning.
- Predictive Bug Detection: Utilizing advanced machine learning models and pattern recognition on historical data to predict potential defect hotspots and prioritize testing efforts.
- Autonomous Test Execution & Analysis: Moving towards systems where AI not only generates and executes tests but also analyzes results, identifies root causes, and suggests fixes with minimal human intervention.
- Intelligent Error Prediction & Prevention: Implementing mechanisms that anticipate potential failures based on code changes or environmental factors.
- Data Integrity is Crucial: Recognizing that the effectiveness of AI in QA heavily relies on structured, consistent, and context-rich data. Poor data integrity can lead to unreliable AI outputs, emphasizing the need for robust test management and data governance.
- Applicability: E-commerce, healthcare, banking, finance, manufacturing, retail, media, entertainment, travel.
2. TestOps and QA Orchestration:
TestOps helps connect testing with development and operations. It makes sure QA fits smoothly into the CI/CD pipeline, so teams can move faster without losing quality.
- Built-in QA pipelines let tests run automatically as part of builds and deployments.
- Centralized tools help teams manage test environments, run tests across locations, and track results—all in one place.
- Observability in testing means collecting data from test runs to spot issues, improve performance, and make testing more reliable.
- Easier environment setup uses containers and the cloud to create test environments quickly and consistently.
- Why it matters: It supports continuous testing, shortens feedback loops, and helps QA teams stay in control and aligned with the rest of the org.
- Applicability: E-commerce, healthcare, banking, finance, manufacturing, retail, media, entertainment, travel.
3. Low-Code/No-Code Test Automation:
Low-code and no-code tools are making test automation more accessible. You don’t need to be an engineer to build automated tests anymore.
- Visual tools let QA teams, business analysts, and even manual testers create tests using drag-and-drop interfaces or simple settings—no coding required.
- Faster test creation means teams can build and update test suites quickly.
- Easier access makes it possible for more people to contribute to automation, not just developers.
- Easier environment setup uses containers and the cloud to create test environments quickly and consistently.
- Why it matters: It helps QA move faster, improves the return on automation, and lets engineers focus on more complex problems.
4.Self-Healing Test Automation:
Self-healing automation solves the problem of fragile test scripts. When apps change, traditional tests often break. AI can now step in to fix that.
- AI detects changes in the app’s UI—like updated IDs or element X-paths,CSS selectors —that would normally cause tests to fail.
- Smart updates automatically fix or replace broken locators so the test keeps running without human help.
- Less manual work means teams spend less time fixing tests after every app update.
- Why it matters: It keeps automated testing stable, reduces interruptions, and makes it easier to scale your QA efforts.
5. Hyperautomation in QA:
Hyperautomation means automating more than just tests. It covers the entire QA process, from planning to reporting.
- It’s not just Test Execution: Automation now includes test design, data setup, environment provisioning, reporting, and analysis.
- It connects Smart Tools: AI, machine learning, RPA, low-code platforms, and process mining all work together in one system.
- It removes repetitive work: By automating routine tasks, teams save time and reduce mistakes. means teams spend less time fixing tests after every app update.
- Why it matters: You get wider automation coverage, smarter workflows, and more efficient QA from start to finish.
6. Quantum Computing Testing Frameworks:
Testing for the next generation of computing. As quantum computing evolves, QA has to evolve with it.
- New testing methods are needed for quantum algorithms and hybrid systems that combine quantum and classical computing.
- Resilience testing checks how well quantum systems handle errors and stay stable.
- Simulations let teams test performance before actual quantum hardware is available.
- Where it matters: Finance, cryptography, pharma, materials science, and advanced manufacturing.
7. Hyper-Personalized & Advanced Cybersecurity Testing:
Cybersecurity testing is getting smarter to keep up with smarter threats.
- Context-aware testing uses behavior and user profiles to simulate real-world attack scenarios.
- AI models threats in advance, helping teams spot and fix risks early.
- Zero-trust security is tested across cloud and edge systems to ensure it works everywhere.
- Continuous monitoring powered by AI helps detect issues in real time.
- Vulnerability management is automated—so threats are found and patched faster.
8. Sustainability-Driven QA (Green Testing):
QA is going green. Teams are now thinking about the environmental impact of how they test software.
- Energy-efficient testing helps cut down power use, both in test systems and in the apps being tested.
- Smarter resource use reduces hardware needs and lowers the carbon footprint.
- Sustainable SDLC means testing aligns with green development standards and regulations.
- Carbon-neutral practices support broader environmental goals in software teams.
- Why it matters: It’s essential for companies working toward ESG goals and meeting sustainability rules.
9. Extended Reality (XR) & Immersive Experience Testing:
Testing for AR, VR, and MR isn’t just about performance—it’s about the full user experience.
- Multi-sensory testing checks how users interact using sight, sound, touch, voice, and gestures.
- Cross-platform checks make sure the app runs well on different XR devices and platforms.
- User safety matters, so teams test for issues like motion sickness or mental fatigue.
- Accessibility testing ensures XR apps work for users with different abilities.
- Where it’s used: Gaming, healthcare, training, retail, education, and remote collaboration.
10. Autonomous Systems & Self-Healing Application Testing:
Autonomous systems need smarter testing. These systems are built to recover and fix themselves—so QA has to make sure that actually works.
- Self-diagnosis and repair features are tested to see if they can detect and fix issues on their own.
- Error correction is validated by checking if systems can learn from past problems and respond automatically.
- Predictive maintenance tools are tested to make sure they give early warnings before something fails.
- Adaptive recovery is about confirming that systems can adjust in real time when something goes wrong.
- Rollback checks ensure automatic recovery steps kick in during critical failures.
11. Edge Computing and IoT Advanced Testing:
Testing at the edge is different. These systems run in remote, low-power, or hard-to-reach places—so QA needs a different approach.
- Device testing checks how well apps run on edge hardware with limited memory, power, and battery.
- Network testing looks at how apps behave when connections are weak, unstable, or delayed—common in IoT setups.
- Security and compatibility testing ensures all the connected devices, gateways, and platforms work safely and together.
- Scalability testing checks if the system can handle data and connections from thousands (or millions) of devices.
12. Ethical AI and Bias Detection Testing:
AI systems must be fair, clear, and accountable. Testing helps make sure of that.
- Bias testing checks for unfair patterns in AI decisions—like bias based on race, gender, or age.
- Fairness validation makes sure AI treats different groups equally.
- Explainability tests check if AI systems can explain their decisions.
- Ongoing monitoring looks out for bias or discrimination in real-world use.
13. Advanced Blockchain and Decentralized Systems Testing:
Blockchain apps need extra-rigorous testing. They must be secure, reliable, and compliant.
- Smart contract testing checks logic and security using static and dynamic methods.
- DApp testing focuses on security and performance under real-world conditions.
- Interoperability tests make sure different blockchains can talk to each other.
- Consensus checks verify that the system’s core agreement process works properly.
- Compliance testing ensures blockchain solutions meet legal and industry rules.
14. Adaptive Compliance and Regulatory Testing:
Regulations change fast. Testing helps teams keep up.
- Flexible frameworks let teams adjust quickly to new rules like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA.
- Automated checks verify compliance across countries and industries.
- Real-time monitoring alerts teams to issues before they become risks.
- Privacy tests ensure data handling meets strict protection laws.
15. Microservices and Cloud-Native Testing Strategies:
Modern apps are made of many moving parts. Testing needs to keep up.
- Contract testing checks how services talk to each other—without needing full end-to-end setups.
- Container testing looks at how apps run inside Kubernetes and other platforms.
- Service mesh testing ensures secure, reliable communication between services.
- Chaos engineering simulates failures to test system resilience.
- API and integration testing focuses on connection points between services.
- Multi-cloud testing ensures apps run smoothly across different cloud providers.
16. Performance Engineering 2.0:
Performance testing is now continuous, not a one-time step.
- AI models predict performance issues before users notice.
- UX-focused tests measure what users actually feel—like load time and visual stability.
- Edge and 5G testing checks app behavior in high-speed, low-latency networks.
- Green performance metrics look at energy use and efficiency.
- Ongoing monitoring helps teams find and fix slowdowns fast.
17. Security Testing with Advanced DevSecOps Integration:
Security must be built into every stage of development.
- Shift-left testing means scanning code for security issues early in the pipeline.
- IaC testing checks infrastructure code (like Terraform) for risky settings before launch.
- API security gets special attention—testing for weak auth, fuzzing, and more.
- Supply chain checks look at third-party libraries and dependencies for vulnerabilities.
- Secrets testing ensures credentials and tokens are stored and handled safely.
18. Advanced RPA and Intelligent Automation Testing:
Automation is getting smarter—and so is testing.
- Cognitive RPA testing validates bots that use AI to read text or make decisions.
- IDP validation checks systems that extract data from documents for accuracy.
- Chatbot testing makes sure virtual assistants understand users and respond correctly.
- Process mining helps find automation opportunities and checks that bots are doing what they should.
- Human-bot collaboration tests make sure workflows between people and bots go smoothly.
19. UI/UX Testing for Next-Gen Interfaces:
Interfaces are changing—and testing has to keep up.
- Voice interface testing checks speech recognition and response quality.
- Gesture and eye-tracking tests ensure accuracy in touchless interactions.
- Biometric testing validates systems like fingerprint or face unlock for security and usability.
- Expanded accessibility tests go beyond web standards to cover all types of interfaces.
- Omnichannel testing checks that user experience stays consistent across web, mobile, voice, and more.
Why Companies Will Prefer Advanced Automation Testing Over Manual Testing
Automation testing, particularly intelligent and integrated automation, continues to gain preference due to multiple compelling factors.
- Intelligent Test Coverage: AI-driven test case generation and optimization provide exhaustive coverage with adaptive learning capabilities, surpassing manual limitations.
- Cost Optimization: Significant reduction in long-term quality assurance costs through automated processes, faster execution, and reduced manual effort.
- Early Defect Detection: Proactive identification and prevention of defects earlier in the development cycle (Shift-Left), reducing the cost of fixing bugs.
- Scalability & Speed: Ability to handle increasing application complexity, execute large test suites rapidly, and meet demanding release schedules.
- Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): Seamless integration with CI/CD pipelines enables continuous testing and faster feedback loops, accelerating delivery cycles.
- Consistency & Reliability: Automated tests execute precisely the same way every time, eliminating human error and ensuring consistent results.
Industry Growth Drivers Reinforcing Automation:
- The mobile and web application market's rapid growth necessitates automated testing solutions for faster time-to-market.
- E-commerce platforms demand continuous, automated testing capabilities to handle peak traffic, ensure optimal user experience, and support frequent updates.
- The automotive industry, especially with electric and autonomous vehicles, requires extensive automated testing for safety-critical systems.
- Cloud migration initiatives necessitate automated testing for configuration validation, performance, security, and multi-cloud compatibility.
- The rise of complex systems (IoT, AI, Microservices) makes comprehensive manual testing impractical.
Outsourcing vs. In-House QA: Strategic Considerations for 2025
QA is ever-evolving, and businesses understand this. That's why the trends show that most businesses will prefer outsourcing QA services rather than building an in-house team. Here are some reasons.
- Expertise: Outsourcing a QA team ensures that you leverage the experts in the field. The team of professionals consists of multiple people with specialized skills, which helps you obtain the best quality assurance services for your business.
- Cost-effectiveness: Outsourcing QA services can be more cost-effective for businesses than hiring an in-house team. An outsourced team helps you save money on employee salaries, recruitment expenses, and the costs associated with setting up a physical office space.
- Initial investment: When you outsource a QA team, there is no need to invest in expensive infrastructures like automation tools, devices, and licenses. This lowers the costs associated with QA testing significantly.
- Flexibility: Outsourcing QA services also gives you a lot of flexibility in terms of the size and scope of projects. While hiring managed QA services cost you more, you can opt for professional services.
- Faster Access to Technology: Immediate access to cutting-edge testing technologies, tools, and established methodologies without internal development or procurement delays.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Allows internal teams to focus on core product development and business strategy.
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies:
Key Challenges in 2025:
- Rapid Technological Evolution: Keeping pace with the constant emergence of new technologies, tools, and methodologies requires continuous adaptation.
- Skill Gaps: Significant shortage of QA professionals skilled in emerging areas like AI/ML testing, quantum computing validation, advanced cybersecurity, and TestOps.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating diverse testing tools, platforms, and automation frameworks into a cohesive and efficient QA ecosystem.
- Data Privacy & Security: Ensuring compliance with stringent data privacy regulations (like GDPR, CCPA) when handling test data, especially in outsourced or cloud-based scenarios.
- Cost of Advanced Tools: High initial investment and ongoing licensing costs for sophisticated AI-driven testing tools and platforms.
- Maintaining Test Data: Generating, managing, and maintaining relevant, realistic, and secure test data remains a significant challenge, especially for AI-driven testing.
Recommended Mitigation Strategies:
- Continuous Learning & Upskilling: Invest in robust training programs, certifications, and knowledge-sharing initiatives to upskill existing QA teams and attract new talent.
- Adopt Flexible & Modular Architectures: Design testing frameworks and automation solutions with modularity and adaptability in mind to accommodate new tools and technologies more easily.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborate with specialized QA vendors, tool providers, and technology consultants to leverage external expertise and access cutting-edge solutions.
- Phased Implementation & Pilot Projects: Introduce new technologies and methodologies gradually, starting with pilot projects to assess value and refine processes before full-scale adoption.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Foster strong collaboration between development, QA, operations, and security teams (DevSecOps/TestOps culture) to break down silos and integrate quality throughout the lifecycle.
- Focus on Test Data Management (TDM): Implement robust TDM strategies and tools for generating synthetic data, masking sensitive information, and managing test data effectively.
- Prioritize ROI & Value: Carefully evaluate the potential return on investment for new tools and technologies, focusing on those that deliver tangible business value and address key pain points.
Industries That Should Focus on Advanced Cybersecurity Testing:
With cyberattack damages projected to reach a staggering $10.5 trillion by 2025, robust cybersecurity testing is non-negotiable, particularly for:
- Financial Services (BFSI): Protecting sensitive financial data, ensuring secure transactions, and complying with strict regulations requires advanced threat detection, penetration testing, and compliance validation. Notably, over 75% of financial organizations experienced cyberattacks in 2024.
- Healthcare: Securing patient records (EHR/EMR), protecting connected medical devices (IoMT), and ensuring HIPAA compliance demand comprehensive security testing.Especially as over 50 million patient records were compromised globally in recent years.
- Government and Public Sector: Protecting critical infrastructure, sensitive citizen data, and national security applications necessitates specialized, rigorous security testing.
- Critical Infrastructure: Power grids, water supplies, transportation systems, and communication networks require robust testing against attacks that could have widespread societal impact.
- E-commerce & Retail: Protecting customer payment information, preventing account takeovers, and securing online platforms against fraud and data breaches are paramount.
- Technology Providers: Ensuring the security of software, cloud services, and platforms used by other industries is critical to prevent supply chain attacks.
Future Outlook: Testing Centers of Excellence (TCoE) Evolution:
Testing Centers of Excellence (TCoE) are evolving from centralized testing units to strategic enablers of quality across the organization, with a projected growth of 35% in 2025:
- Shift to Quality Enablement: Moving beyond just executing tests to defining standards, providing frameworks, coaching teams on best practices, and enabling distributed teams to own quality.
- Incorporating Advanced Capabilities: Integrating expertise and frameworks for AI-driven testing, TestOps, performance engineering, security testing, and sustainability metrics.
- Federated Models: Adopting more federated or hybrid models where a central TCoE provides governance and specialized expertise, while individual teams embed QA practices.
- Focus on Business Value: Aligning TCoE goals and metrics directly with business outcomes, such as faster time-to-market, improved customer satisfaction, and reduced operational risk.
- Tooling & Platform Strategy: Defining and managing the organization's strategy for testing tools, platforms, and infrastructure, ensuring consistency and efficiency.
Conclusion:
The Quality Assurance landscape in 2025 demands a strategic shift towards intelligent, integrated, sustainable, and ethically responsible practices. QA leaders must champion the evolution from traditional testing to holistic quality engineering, embedding quality throughout the SDLC and leveraging technology not just for efficiency, but as a strategic enabler.
Success hinges on embracing innovation, fostering a culture of continuous learning and adaptation, investing wisely in emerging technologies and skills, and aligning QA efforts directly with business objectives. By navigating these trends effectively, organizations can transform QA from a cost center into a critical driver of competitive advantage, customer trust, and sustainable growth.
About ThinkSys:
This comprehensive report reflects our commitment to delivering cutting-edge QA solutions and insights based on extensive industry research, expert consultations, and practical implementation experience across diverse technology domains.
Disclaimer:
Technology evolves rapidly. While these trends represent current understanding based on extensive research and industry analysis, organizations should maintain flexibility and commit to continuous learning and adaptation.
Share This Article:



