How to Perform Regression Testing for Stable and Reliable Application?
Keeping your software stable while delivering new features and updates is a delicate balancing act. Every code change comes with the risk of unintentionally breaking existing functionality. A feature that worked perfectly yesterday could malfunction today. Regression testing serves as a safeguard, helping you identify and address these issues early, ensuring your software remains stable and reliable as it evolves.
This blog explores why regression testing is important, when to perform it, and how to implement it effectively. By the end, you’ll understand how this critical testing process protects your app’s functionality while allowing innovation to thrive.

What is Regression Testing and Why is it Important?
Regression testing involves retesting previously verified functionality to ensure recent code changes haven’t caused unintended issues. It is a vital step in the software development lifecycle for ensuring application stability and maintaining user satisfaction.
Regression testing can be automated or performed manually. Due to its speed and consistency, automation is often preferred for larger, frequently updated projects. Studies show that around 75% of organizations actively perform regression testing, underscoring its importance in the QA process.
Why Companies Perform Regression Testing?
With that in mind, the following are the top reasons why the majority of companies perform regression testing.
- Preserve Core Functionality: Your app’s core features are what users rely on most. With regression testing, you can ensure that these features continue to work as intended, even as you introduce new updates or fixes.
- Ensure Consistent User Experience: Users expect your app to perform the same way each time they use it, regardless of updates. Regression testing helps you maintain that consistency by catching any unintended side effects of new code, allowing you to deliver a reliable experience that retains users.
- Identify Bugs Early: Every new feature or update can potentially introduce bugs that weren’t there before. By performing this testing, you can catch these issues early on and prevent problems from escalating and affecting other parts of your app.
- Save Time and Reduce Costs: While regression testing does require time and resources upfront it can save you significantly in the long run. By identifying issues early, you avoid costly fixes and potential rollbacks later. Doing so reduces the time and expense involved in maintaining your app.
- Improve Software Quality: Regular testing helps maintain a high-quality app as it evolves. With each test, you address issues introduced, continuously improving your software and keeping it aligned with user expectations.
When Do You Need Regression Testing?
Regression testing should be conducted under various scenarios where changes might impact the app’s functionality. Here are the key triggers for performing regression testing:
- After Bug fixes: When you fix a bug, the goal is to resolve an issue without creating new ones. However, sometimes a fix can inadvertently cause other problems. Running regression tests after bug fixes ensures that everything still works smoothly, giving you peace of mind that the fix hasn’t led to unexpected behavior elsewhere.
- When Adding Features: Introducing a new feature can enhance your app, but it may also affect existing functionality. By performing regression testing after adding a feature, you can confirm that the new addition doesn’t disrupt anything that users already rely on.
- Post-Code Refactoring: Refactoring is all about improving your code, and making it cleaner and efficient. However, even positive changes can introduce bugs. After refactoring, regression testing helps you verify that the code still behaves as expected, ensuring that the improvements don’t come at the cost of stability.
- For System Upgrades: Upgrading your OS, database or other critical infrastructure can impact how your app runs. Performing regression testing after such upgrades ensures that your app remains compatible and continues to function properly.
- Before Major Releases: Preparing for a significant release or update is an exciting time, but it also comes with risks. Before pushing an update, you can perform regression testing which allows you to catch underlying issues ensuring that your users receive a polished update.
- After Software Integrations: Integrating new components, libraries, or third-party services can cause compatibility issues. As regression testing involves checking that everything is working harmoniously, it ensures that integrations don’t hamper the functionality or user experience of your software.
Types of Regression Testing
Understanding the different types of regression testing is crucial for ensuring that your software remains stable as it scales. Depending on your project’s size, complexity, and goals, each regression testing type serves a different purpose. Let’s break down the main types and help you decide which one suits your needs.
- Unit Regression Testing: Unit regression testing focuses on re-testing individual units of code after changes. It’s done in isolation, meaning external dependencies like APIs or databases are often ignored. Mostly, this type is useful when you’ve made small changes to a specific module or function and you want to ensure that those changes don’t introduce new bugs.
- Partial Regression Testing: Partial regression testing is performed when only some parts of the code have been modified. It is often used in agile environments where you release smaller updates frequently.
- Complete Regression Testing: As the name suggests, complete regression testing involves re-testing the entire application from end to end. This is essential for major code changes that may affect multiple modules.
- Progressive Regression Testing: This type of regression testing is used when new test cases are created alongside the new features being added, making it ideal for ensuring that both new and existing functionalities work as anticipated after expanding the codebase.
- Selective Regression Testing: Selective regression testing focuses on testing specific areas of the codebase that are most likely affected by the recent changes. By picking the most relevant test cases, you can reduce the testing time while still ensuring that no critical parts are broken.
Which Regression Testing Type Should You Use?
Choosing the right type depends on the scope of your changes and how critical the software’s stability is:
- For small updates or bug fixes, you can often rely on unit regression or selective regression testing.
- If you’ve made moderate changes such as introducing a new feature, partial regression or progressive regression testing is the way to go.
- For major releases or significant system overhauls, nothing beats complete regression testing to ensure that everything is working smoothly.
Why Do Some Businesses Skip Regression Testing and Common Hindrances?
Even with regression testing’s clear value, some businesses skip it or encounter challenges while implementing it. Here’s why, along with ways to address these issues effectively:
- Limited Budget or Resource Constraints: For smaller businesses, regression testing may seem like an unnecessary expense when resources are tight. This often leads to a focus on new features at the expense of testing existing functionality, resulting in poor UX and user churn.
- Solution: Start small by prioritizing high-risk areas and automating repetitive tests to reduce manual effort. This ensures some level of regression testing without requiring significant resources.
- Lack of Test Automation: Manual testing alone can make regression testing time-consuming and costly. Some teams skip it altogether, while others attempt full manual regression testing, which can be overwhelming.
- Solution: Automate frequently executed test cases to save time and resources. Tools like Selenium, Appium, and TestComplete can handle repetitive tasks efficiently, allowing manual testing to focus on complex areas.
- Assumption that Minor Changes Don’t Require Testing: Teams may assume that only significant updates need regression testing, overlooking the impact of small tweaks. However, even minor changes can disrupt core functionality.
- Solution: Build a habit of performing targeted regression tests for frequently used features whenever any change occurs, regardless of its size.
- Inconsistent or Outdated Test Cases: As apps evolve, test cases can quickly become irrelevant, leading to missed bugs and ineffective testing.
- Solution: Regularly review and update test cases to reflect changes in business requirements. Tools like TestRail and Zephyr help manage and update test cases effectively. Applitools can highlight UI inconsistencies to streamline visual testing.
- Underestimating QA Expertise: Some businesses rely on developers or in-house teams with limited QA experience, resulting in missed issues that compromise stability.
- Solution: Outsource regression testing to QA specialists to ensure comprehensive coverage and early bug detection. This approach allows in-house teams to focus on innovation while enhancing software quality.
How to Perform Regression Testing?
Performing regression testing is a rigorous process that involves various steps from identifying the need to fixing issues. To ensure its utmost effectiveness, you can implement the following process into your workflow. Here's are steps to perform Regression Testing.
- Understand Code Changes: The reason why you are performing regression testing is to ensure that the changes do not influence the existing features of your app. However, before you take any other action, it is crucial to understand the specifics of the changes made. Whether it was bug fixes, the addition of new features, a security patch release, or a maintenance upgrade, you need to have a clear picture of the changes done to the app to determine areas vulnerable to issues. You can perform this step effectively by:
- Communicating with Developers: Developers can explain the rationale behind the updates, point out potential areas of concern, and highlight any known side effects. Try to attain answers to questions like:
- What was modified?
- Were any core functions or algorithms adjusted?
- Are there any new features or components that need specific attention?
- Reviewing Change Documentation: You have to make sure that you review all available documentation that outlines what changes were made including:
- Release notes from the development team.
- Change logs in version control systems like Git.
- Pull requests or merge requests.
- Communicating with Developers: Developers can explain the rationale behind the updates, point out potential areas of concern, and highlight any known side effects. Try to attain answers to questions like:
- Select and Prioritize Test Cases: Once you’ve gained a deeper understanding of the changes made to the system, the next step is to select and prioritize test cases for regression testing, ensuring that you are testing the most critical areas while avoiding unnecessary coverage that doesn’t add value.
- To help you make informed decisions, answer these key questions before prioritizing your test cases:
- Does the feature directly relate to the update code
- Are there any dependencies that might be affected?
- How critical is this feature to user experience or business operations?
- Has the functionality or feature been problematic in the past?
- Could changes in the environment or configuration affect this area?
- Another factor that you need to keep in mind is to prioritize test cases. Once you have answers to these questions, you can prioritize your test cases more effectively by following these steps:
- Begin with high-risk areas such as mission-critical features or modules with a high potential for failure as they should be tested first. For efficient management of high-risk features, TestRail can help categorize and prioritize test cases based on risk levels.
- You need to test directly impacted areas first and include test cases for indirectly affected as well. For instance, if a core API was modified, any feature using that API should also be tested.
- Prioritize test cases based on the risk they pose to the system. Features that have a history of being faulty or require strict compliance with business-critical functions should always rank higher in your testing efforts.
- To help you make informed decisions, answer these key questions before prioritizing your test cases:
- Build a Regression Testing Plan: After selecting and prioritizing the test cases, the next step in the regression testing process is building a well-structured regression testing plan. To build an effective testing plan, you need to:
- Create Test Data: You should start by generating test data that accurately reflects real-world usage including both typical and edge-case scenarios. The key here is to create a variety of data types to ensure your tests are robust.
- Identify and Manage Your Resources: You have to assign the right people to the right tasks. For instance, automation testers can focus on creating and running scripts, while manual testers can tackle exploratory testing. Good communication between the team members is necessary, especially when issues are identified and need quick resolution.
- Gather Your Tools: To make your regression testing process as smooth as possible, you should use a blend of tools that cover tracking, reporting, and automating the testing lifecycle:

- Selenium, Appium, and Cypress for automating test cases.
- Jenkins and Travis CI to integrate your tests into the CI/CD pipeline.
- Jira and Bugzilla are industry standards for tracking defects and managing tasks.
- TestRail and Zephyr are used to manage and track test cases and results.
- JaCoCo and Coverage.py can help you measure your test coverage.
- Time Required to Review: Upon completion of tests, you need to determine the estimated time required to review the outcome.
- Test Coverage: Rather than focusing on testing everything, you should focus on the right areas. You have to review your test cases and ensure that they cover the most vulnerable areas first.
- Fixing Issues and Retesting: The goal is to fix the issues which is why you need to allot time for fixing bugs. Furthermore, it is crucial to allocate some time for retesting to ensure that bugs are fixed.
- Quality Assurance: Throughout the entire process, you need to maintain a strong QA focus. By establishing quality checkpoints at various stages, you ensure both functionality and performance are where they should be.
- Determine How Often to Run Your Regression Tests: Deciding how frequently you should run your regression tests is essential to keeping your app stable without overburdening your team or resources. When determining the frequency of your test runs, it’s not just about picking a random schedule as there are key factors that should guide your decision.
- Rate of Code Changes: The more frequently your codebase changes, the more often you need to run regression tests.
- Application Criticality: For apps handling critical operations, testing should be done more frequently, ideally after every build or deployment. Less critical apps may only require daily or weekly tests.
- Test Suite Size and Complexity: When you have a larger number of test cases, running the entire suite after every code change could be time-consuming. You need to segment your test based on priority and run the most essential ones frequently.
- Risk of New Defects: If recent changes involve complex or core features, you need to increase the test frequency. However, for small updates, you may opt for less frequent tests based on the risk level. Ultimately, the frequency of your regression test runs should align with the development cycle, risk factors, and automation capabilities. Regularly review your testing strategy and adjust the frequency as your app and team grow.
- Decide the Relevant Test Cases for Manual and Automated Testing: Selecting the appropriate test cases is essential for effective regression testing. By balancing manual and automated testing, you can ensure comprehensive coverage while optimizing your resources.
- Manual Testing: Ideal for UI validation, exploratory scenarios, and cases where human intervention is required. This is true for new features or areas prone to change.
- Automated Testing: Best suited for repetitive, high-volume test cases that require consistency. Automation is excellent when validating stable features, allowing for quick execution across various environments.
- Execute the Test Cases: Now that you’ve determined the test cases you want to run and their frequency, it is time to perform the tests. Depending on your requirements, implement manual or automated testing or a blend of both. Performing both testing types is a bit different and their process goes as follows:
- Manual Testing: This testing type begins after you’ve prioritized test cases.
- Automated Testing: Automated testing is mostly suitable for redundant and frequently tested test cases.
- Manual Testing: This testing type begins after you’ve prioritized test cases.
- Evaluate Test Results: Upon successful execution of test cases, it is time to evaluate the results. While executing tests, you have logged any issues or defects faced. It is best to create a detailed report on these issues and involve factors including:
- Defect ID.
- Summary.
- Steps to reproduce.
- Expected result.
- Actual result.
- Severity and priority.
- Environment details.
- Attachments.
- Whether caused by new changes or other factors.
Upon adding the necessary information to the report, the development team will try to fix the issue. Afterward, the desired tests should be re-run to ensure that the issues are fixed. If not, the entire process is repeated till the issue is resolved.
- Track and Analyze Test Effectiveness: After fixing defects, it’s vital to monitor the overall effectiveness of your regression testing. By tracking the following metrics, you can assess how well your process is working and where improvements can be made.
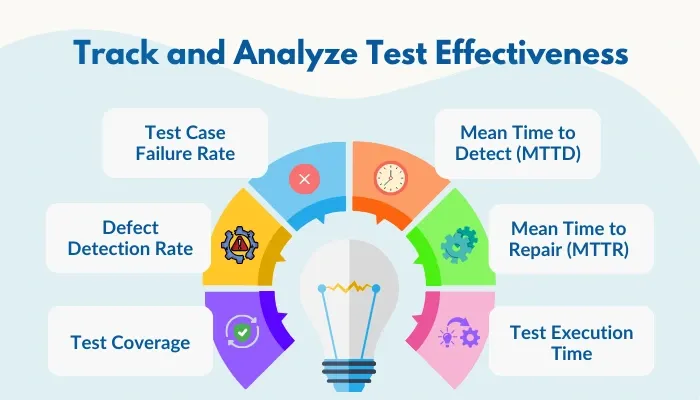
- Test Coverage: This metric is useful to measure the percentage of your app’s code or features that are tested. You have to aim for at least 80 percent coverage on critical functionalities as higher coverage reduces the risks of defects escaping into production.
- Defect Detection Rate: The defect detection rate indicates the number of defects identified during regression testing compared to the total number of defects reported in production. A detection rate of over 70 percent or higher suggests that your tests are effective at catching issues before they reach users.
- Test Case Failure Rate: The test case failure rate measures the number of failed test cases against the total executed cases. If this rate exceeds 10 percent, it showcases weaknesses in your testing suite or issues within the code that require further investigation.
- Mean Time to Detect (MTTD): Here, you will calculate the average time taken to identify defects after a code change. Setting a target MTTD of less than 24 hours enables your team to address issues seamlessly.
- Mean Time to Repair (MTTR): Here, you will measure the average time it takes to fix detected defects. An ideal MTTR of under 48 hours indicates that your team can respond efficiently to issues, ensuring quick resolutions without significant downtime.
- Test Execution Time: By tracking the total duration required to run your regression test suite, you can know when and where to optimize. If your test execution time exceeds two hours, it may be time to optimize your tests, either by automating additional cases or reviewing the suite for redundancies.
- Keep Your Test Suite Updated: As your app evolves, some test cases will become outdated, so it’s pivotal to regularly remove those and add new ones that cover recent changes or features. Take the time to check whether your test cases are still effective or if they need refining to improve performance. By continuously maintaining your test suite, you make sure your testing keeps up with the pace of development, catching any issues before they become major problems.
Top Regression Testing Trends You Should Know About in 2025
Staying updated with the latest regression testing trends is essential to ensure your processes align with modern development practices. Here are the key trends shaping the future of regression testing: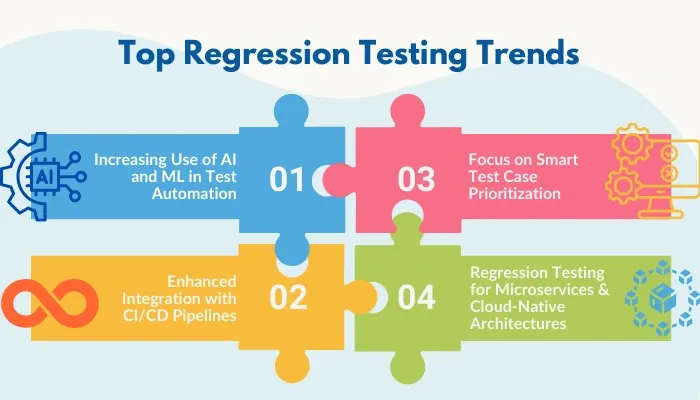
- AI and ML in Test Automation: AI and ML are revolutionizing regression testing by automating repetitive tasks, analyzing code changes, and predicting bugs. Tools like Mabl and Testim enhance accuracy, reduce time consumption, and allow teams to focus on high-risk areas.
- Integration with CI/CD Pipelines: Regression testing is becoming a core part of CI/CD workflows. Automated tests run with every build or deployment, ensuring updates don’t disrupt functionality, even in fast-paced DevOps environments.
- Smart Test Case Prioritization: With growing test suites, prioritization is critical. Tools analyze code changes and defect history to focus on high-risk areas, reducing unnecessary tests while improving efficiency.
- Regression Testing for Microservices: Microservices add complexity, requiring specialized regression testing to address interdependencies. Tools like Postman and JMeter ensure updates don’t ripple across services, keeping applications stable.
- Rise of Test Automation Frameworks: Frameworks like Cypress and Robot Framework are streamlining regression testing with enhanced cross-browser support and debugging capabilities, making automation more accessible and efficient.
- Visual Regression Testing: Tools like Applitools and Percy automatically detect UI inconsistencies caused by code changes, ensuring a consistent and polished user experience across platforms.
- Cloud-Based Testing: Platforms like BrowserStack and Sauce Labs enable scalable, on-demand regression testing, allowing teams to test across configurations without extensive infrastructure.
- Low-Code and No-Code Tools: Tools like Katalon Studio and Leapwork simplify regression testing with drag-and-drop interfaces, enabling non-technical users to build and execute test cases quickly.
By adopting these trends, you can enhance the efficiency and reliability of your regression testing processes, ensuring your applications meet modern development and quality standards.
Conclusion
Regression testing is a cornerstone of application stability, ensuring your software evolves without sacrificing quality. By understanding its importance, addressing common challenges, and implementing a robust strategy, you can deliver reliable and innovative applications that meet user expectations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Share This Article:




