How to Automate Testing for Cloud-Based Applications?
Cloud apps are made to grow fast, work anywhere, and update often. But with that flexibility comes a real challenge: keeping the app stable across different devices, networks, and user loads.
Manual testing can’t keep up. Apps change too quickly. That’s where automation helps. It catches problems faster, makes updates smoother, and improves the user experience.
This guide will show you how to automate testing for cloud apps, with key strategies and tips to do it well.
Why Manual Testing Isn’t Enough?
Manual testing still matters. It's good for spotting one-off problems and areas where human judgment is needed. But if you rely only on manual work, you’ll likely face issues like:
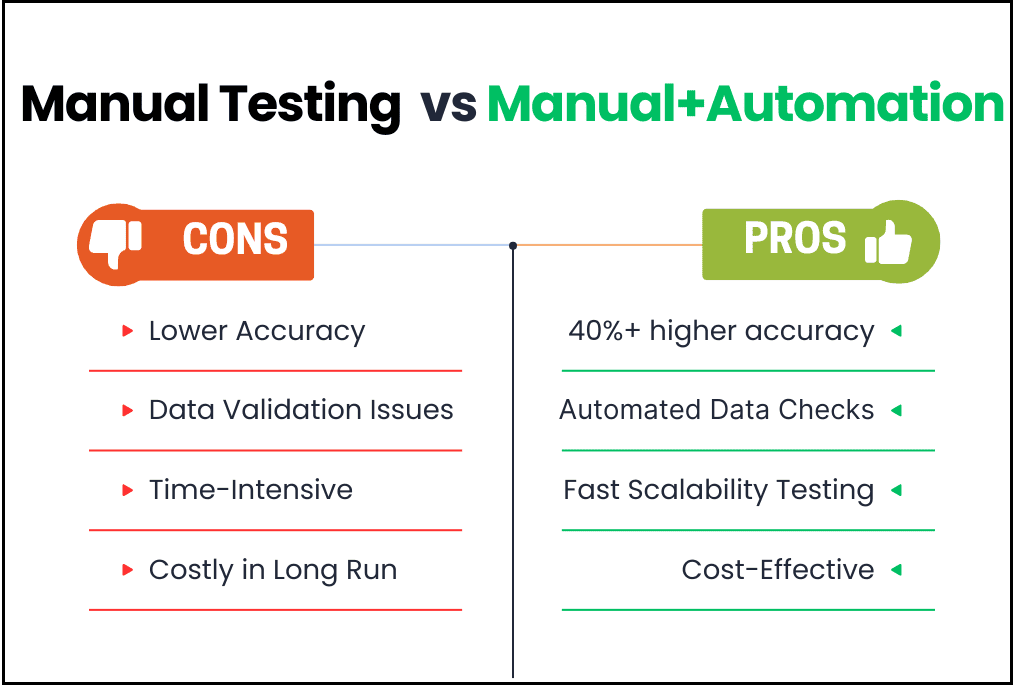
- Lower Test Accuracy
Repeating the same manual steps over and over leads to errors. Automated tests are consistent and catch bugs faster. In fact, over 40% of companies have reported higher test accuracy after implementing automation into their testing process. - Large Data Comparison is Near Impossible
Cloud applications handle large data volumes across different geographies and time zones. Validating such data manually is unrealistic. Automation testing allows your team to run high-volume companies within minutes, which would otherwise take days and risk consistency if done manually. - Manual Testing is Time-Consuming
Cloud applications are designed to handle varying scalability needs. Testing these fluctuating conditions manually can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, as testers have to evaluate and test accordingly. Automation testing can adjust per the requirements, saving a significant amount of time - Expensive in the Long Run
Manual testing takes a lot of labor. As your app grows, so do the testing demands—and your costs. - Hard to scale
When user traffic spikes, your app needs to handle it. Automation can simulate heavy traffic and tricky scenarios way faster than a manual team could.
How to Automate Testing for the Cloud-Based Application
Automating cloud-based applications is a customizable process as per your requirements. However, it surely follows a systematic approach to get the best outcome. With that in mind, here is the outline that you can follow to automate testing for your cloud-based app.
Step 1. Identify the Test Cases to Automate
Before you take any other step, you need to be clear about the test cases you need to automate, as not every test case can be automated. All you have to do is identify the answer to the following:
- Find tests that are redundant and need to run repeatedly: Review your deployment and testing history, including login flows, authentication, and API checks, to spot tests run after every release. In cloud apps, these are often regression tests that validate shared services or backend logic across distributed systems.
- Find tests need large datasets and several iterations: Cloud applications often deal with dynamic data, such as customer onboarding, product searches, or data imports from external sources. Look for scenarios involving dynamic data, like onboarding, searches, or imports.
- Find manual tests that are time-consuming: You need to consider testing activities such as validating UI across regions, checking real-time sync in SaaS apps, or simulating concurrent users, as such activities take hours or require repetitive action. These scenarios often show up as bottlenecks in sprint retrospectives or test execution logs.
- Find tests that need to be performed on various hardware and software: Cloud applications are expected to perform consistently across different browsers, OS versions, and devices. BrowserStack, Sauce Labs, or analytics from your own cloud platform can help you see which environments your users rely on most
In addition to these, you need to remember that not every test can be automated. The general rule of thumb is to automate tests that are stable, repeatable, and have a high business impact if they fail. These typically include:
- Regression tests
- Smoke and sanity tests
- Performance/load/stress tests
- Cross-browser and cross-platform compatibility tests
Avoid automating tests that are exploratory, highly volatile, or require frequent UI changes, as maintaining them may outweigh the benefits of automation.
Step 2: Make a Choice between an Automation Framework or an Automation Tool
To perform automation testing, you need either the right tools or the right framework. The choice depends entirely on your requirements, but how to make the right choice? By considering the following factors:
- Setup and Ease of Use: Using a test automation framework requires technical skills and coding knowledge, including familiarity with languages like Java, Python, or JavaScript, along with hands-on experience in frameworks such as Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, or TestNG. You either need to have an experienced team or spend on training the existing team to work with frameworks. On the other hand, tools are ready to be used out of the box and require minimal setup. Furthermore, non-technical teams can also use such tools for fast implementation.
- Customization: Test automation frameworks are known to be highly customizable, but tools lack this functionality. While using automation tools, you’re limited to working within the features offered by the vendor, whereas you can tailor frameworks to your application.
- Cost: Test automation frameworks are mostly open-source, meaning you don’t need to buy a license to use them. However, you may have to pour in investment in infrastructure and hiring skilled professionals, which can increase the cost by $10K. Even though automation tools also offer free versions, they are limited to small teams, and you may have to invest $3000-$5000 as your cloud-based application scales.
- Resource Efficiency: When it comes to resource efficiency, automation tools take the point as they are highly resource-efficient, making them a perfect choice for teams with limited resources. But that’s not the case with frameworks, as they require more time, effort, expertise, and maintenance, leading to higher utilization of resources.
In summary, you can consider using automation frameworks if your team has the necessary coding skills, the time required to manage and maintain the framework, and the utmost customization while working on test cases.
On the other hand, picking automation tools is the right choice for you if your team has very limited coding knowledge and is not looking for more customizations.
When it comes to picking the right tool or framework, you need to consider your app’s complexity, required integrations, budget, and long-term scalability needs. The top frameworks include WebDriverIO and Protractor. You can also create your custom framework with leading tools and languages.
Step 3: Perform Exploratory Testing to Identify Defects
Exploratory testing is unscripted. It’s where testers interact with the application to learn how it behaves. Why is it important? Because it helps you identify unstable features, usability issues, and edge cases that automation might miss or isn’t ready to handle yet, uncovering hidden bugs before you start automating.
You don’t rely on predefined test cases here. Rather, you need to focus on high-risk areas like recently updated code, complex workflows, or third-party integrations. By performing actions like trying unexpected inputs or out-of-sequence actions, you can test the system’s limits and observe how it responds.
Furthermore, ask yourself: What breaks? What’s unclear? What behavior seems off?
These insights will help you decide which tests are worth automating and which areas need more refinement first.
Step 4: Begin Writing Test Cases
Automation testing requires having defined test cases that the selected tool will run to complete the test. You need to write detailed and structured test cases, as these serve as the blueprint for your automation scripts and ensure consistency across your testing process.
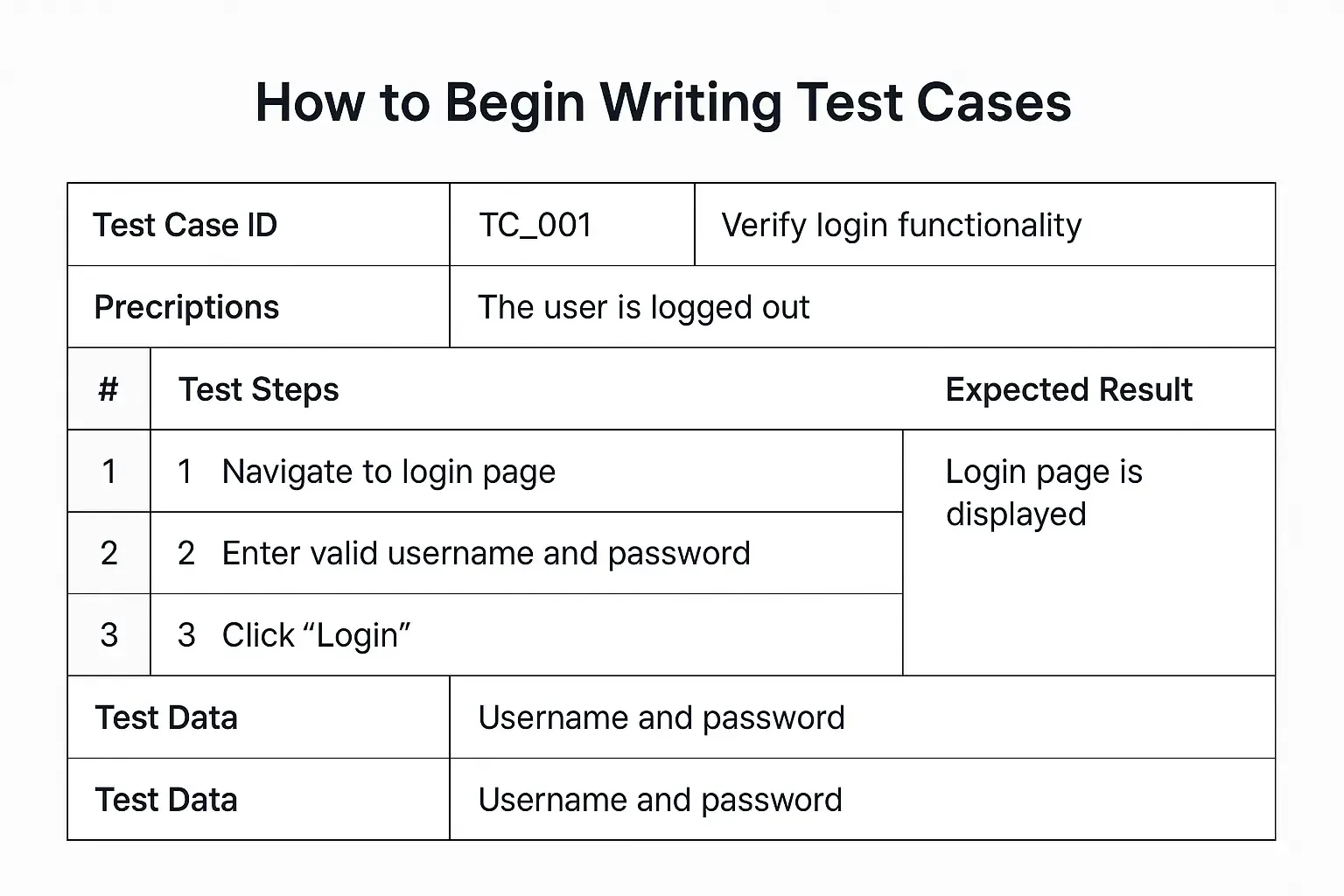
Each test case should have a defined objective, which may be ‘What feature or behavior are you validating?’
Then, break it down into simple, logical steps, followed by the expected result for each action. In addition, you can include preconditions (user must be logged in) and test data required for the test cases. Furthermore, cloud-based test cases must account for factors such as varying user environments, dynamic scaling, and integration points with other cloud services.
For the best outcome, try to keep your test cases:
- Clear and specific – avoid ambiguity so anyone can understand and execute them.
- Modular – focus on one feature or flow per test case.
- Reusable – structure them so they can be reused across different environments or scenarios.
Writing clean, well-thought-out test cases improves accuracy and makes automation easier to scale and maintain.
Interesting Read: How to write test cases in 2025?
However, you may face common pitfalls in writing test cases for cloud-based applications such as flaky tests from dynamic UI changes, failures caused by third-party API updates, regional data sync inconsistencies, and issues from auto-scaling infrastructure or fluctuating network conditions.
Modern AI-based tools can auto-generate test cases based on functional requirements, user journeys, and even natural language input. This reduces dependency on detailed scripting and helps speed up test coverage early in the SDLC.
For example, TestCraft uses AI to generate Selenium-based test cases with minimal manual intervention, while Functionize supports writing test cases using plain English. Other tools, such as TestRail, qTest, TestLink, and Zephyr, can also be leveraged to write and manage test cases.
Step 5: Create the Test Environment
To run your test cases, you need to define your test environment where the tests will run. As variabilities in the user environment, such as different devices, browsers, operating systems, network conditions, and even geographical regions, will directly influence performance and functionality, it’s essential to replicate these conditions in your test environment.
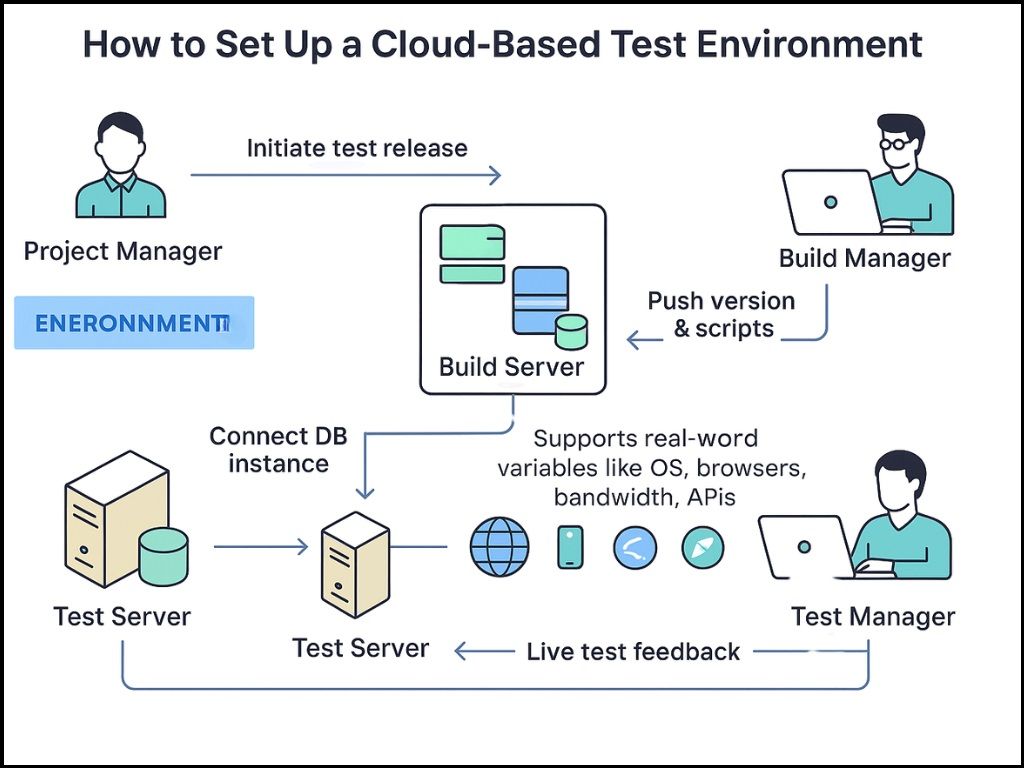
You need to have a stable and well-configured test environment.
Before running any tests, define your environment requirements based on the application's architecture, user base, and target platforms. For example, if you’re testing a microservices-based eCommerce app used globally, you’ll need to simulate distributed servers, diverse user locations, and compatibility across web and mobile platforms. This includes:
- Server and database configurations, including cloud provider, region, OS, and middleware.
- Browser and device combinations that reflect actual user usage.
- Operating systems and versions across desktop and mobile platforms.
- Network conditions such as high latency or limited bandwidth.
- Third-party services or APIs that your application depends on.
Depending on your team’s needs, infrastructure, and budget, you can pick the right environmental setup:
- Local Environment: Perfect for early-stage testing or small teams, as you can run tests on your local machines using local builds. However, limited scalability and configuration flexibility pose a challenge.
- Cloud-Based Environments: Testing cloud applications on cloud environments is highly recommended as it can mimic the actual working conditions of the application. BrowserStack, SauceLabs, AWS Device Farm, and LambdaTest are the top names you can use to access real browsers, devices, scalable infrastructure, and parallel test execution.
Step 6: Perform the Test and Monitor the Results
Now that you have your test cases and the environment is prepared, it is time to perform the test cases. With automation testing, you can efficiently run tests using your chosen automation tool or framework instead of manually executing each test. While running tests, you have to make sure that tests are executed across all requirements events, be it devices, OS versions, browsers, or network conditions. Ensuring that your tests cover all of these aspects guarantees that your cloud-based application delivers a consistent and reliable user experience, regardless of the diverse environments in which it is accessed.
Combine that with parallel testing, where you run multiple tests at the same time on different devices or browsers, to minimize execution time and increase your overall test coverage.
However, don’t end the process here, as you have to monitor the results to identify and fix bugs.
- Use dashboards or reporting tools provided by platforms like Allure, ExtentReports, TestRail, or your automation suite to review outcomes in real-time.
- Watch for patterns in failures: Are they isolated bugs or environment-related? Are the failures reproducible?
- Set up alerts for critical failures or build-breaking issues, especially in CI/CD pipelines.
- Track necessary metrics such as pass/fail rate, test coverage, execution time, and flaky tests.
Common Challenges You May Face During Automation Testing of Cloud Applications
Automating cloud application testing promises faster releases, reduced manual effort, enhanced test accuracy, and consistent software quality. However, even when done correctly, automating cloud application testing can be challenging. With that in mind, below are the key challenges you may face during automation testing.
1. Lack of Skills and Expertise
Undeniably, test automation reduces manual efforts. However, your QA team still needs specialized skills to write scripts, work with automation frameworks, understand test logic, and assess infrastructure damage. The biggest challenge today is the lack of such skills in QA teams, leading to failed automation efforts and underutilized tools.
The solution to this problem is to invest in dedicated training programs and take one step at a time (instead of going for custom frameworks, start with no-code or low-code platforms). If you think training is not feasible, consider hiring a test automation outsourcing company to perform testing for you.
2. Rapidly Changing Requirements
Cloud-based applications are updated frequently to meet evolving user needs and market demands. While that speed is a strength, it can create problems for automation testing. Even small interface or workflow changes may break tightly coupled test scripts, leading to frequent rework and delayed release cycles.
Automation becomes harder to maintain and scale in such a fast-moving environment. Solutions to this challenge include creating modular, loosely coupled test scripts and involving QA teams early in development to maintain stability and reduce test maintenance overhead.
3. Difficulty Integrating Different Tools and Frameworks
One of the biggest elements of automation testing is leveraging the right tools. Sometimes, teams use separate tools for API testing and UI testing. The challenge is not just using different tools but getting all of these to work together. Disconnected tools can lead to data silos, duplicate efforts, and missed defects, all of which undermine the value of automation.
You can choose tools that offer seamless integration with your existing development and deployment ecosystem, such as GitHub, Jenkins, and Jira, among others. Moreover, using a centralized dashboard to manage both manual and automated test results is highly efficient.
How Much Does Automating Cloud-Based Application Testing Cost?
Over 34% of companies have not adopted automation in their QA processes, highlighting some hesitation toward implementation. But why do some companies hesitate to implement automation testing? The commonest reason is the costs of tools, frameworks, infrastructure, and employee training. You can hire an in-house team and prepare to invest in the following components:
| Components | Estimated Annual Cost (USD) |
| Automation Engineer | $90,000 – $120,000 |
| QA Tester | $60,000 – $80,000 |
| Training & Upskilling | $5,000 – $10,000 |
| Test Automation Tools | $5,000 – $20,000 |
| Cloud Testing Infrastructure | $2,000 – $10,000 |
| Maintenance & Updates | $10,000 – $20,000 |
The overall average cost comes to $170,000 – $260,000. While the initial setup may require a larger investment and more time to ramp up, it lays the groundwork for long-term efficiency, customization, and deeper alignment with your internal workflows.
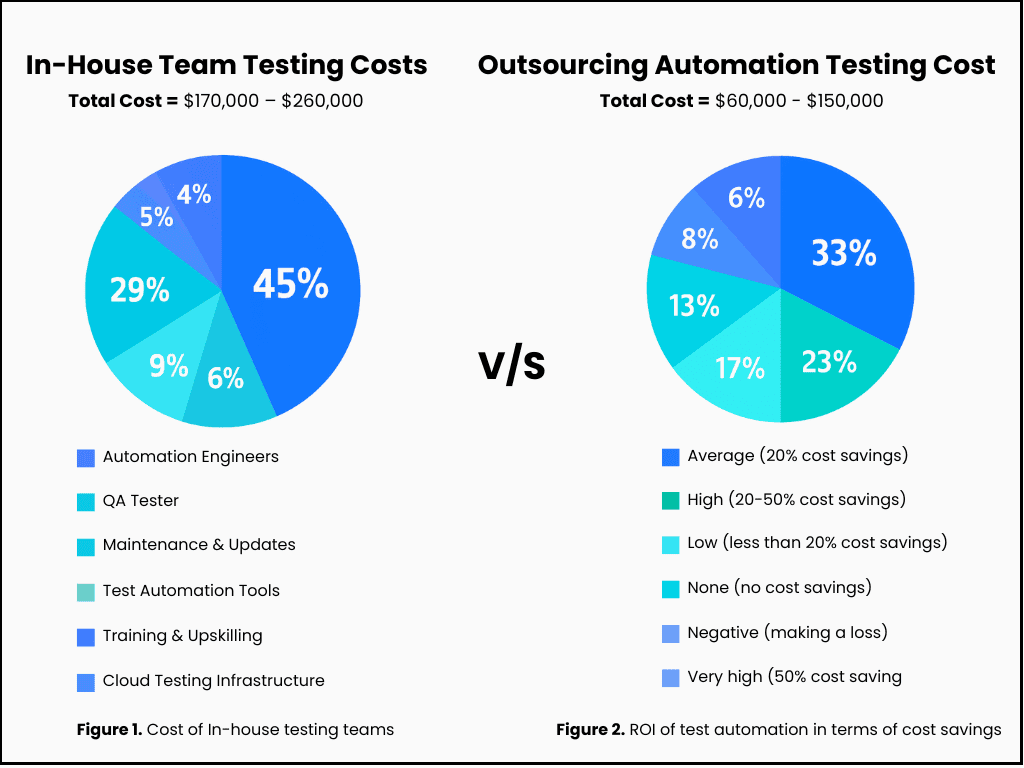
On the other hand, you can outsource the testing to a reliable automation testing service provider. The average cost would be between $60,000 and $150,000, depending on the size and complexity of the project.
Though it may seem a big expense, automation testing has given an ROI of over 20% to 64% of organizations, making it one of the best investments.
Conclusion
Testing cloud-based applications requires speed, scalability, reliability, and consistency, which manual testing solely may fail to provide. Automation testing speeds up the testing process, enhances accuracy, reduces long-term costs, and allows you to release your product faster.
But automation isn’t a one-time effort, as it requires the right tools, skilled teams, and continuous monitoring. And remember, automation isn’t there to replace manual testing but to accompany it in making testing easier and quicker.
If building and managing this internally feels overwhelming, many businesses choose to outsource testing to specialized partners who can bring in both expertise and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
Share This Article:



