How to Enhance Web Application Security: Best Practices to Protect Against Cyber Threats?
Web application security is no longer something you can afford to ignore. Securing your web applications is essential to prevent cyber attackers from exploiting vulnerabilities. This article covers some of the most significant cybersecurity threats facing web applications today and what you can do to protect them.

Even with the best defenses, applications can still get compromised. This guide will help you conduct a thorough web app security audit, highlight key security techniques, and offer best practices to keep your business secure.
Common Cyber Attacks to Protect Your Web Application From
Understanding the most common cyber attacks is the first step toward securing your web application. These are the key cyber threats you should defend against:
- SQL Injection: SQL injection happens when attackers insert malicious SQL code into your database queries. If successful, it allows them to access, alter, or delete your data. This can lead to significant data breaches, potentially leaking sensitive information.
Example: In 2008, a large SQL injection attack affected Heartland Payment Systems, exposing millions of credit card numbers. - Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): XSS attacks occur when hackers inject malicious scripts into your web pages. When users access those pages, the script can run in their browser, potentially stealing session data or personal information.
Example: In 2017, an XSS vulnerability in Steam's Community Market allowed attackers to steal user data by injecting malicious code into profile pages. - Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF): A CSRF attack tricks users into performing actions on your web app without their knowledge, such as changing account settings or making transactions. It exploits the trust your application has in the user's browser.
Example: In 2008, a CSRF vulnerability was discovered in the Netflix website, allowing hackers to change account details without the user's consent. - Remote File Inclusion (RFI): Remote file inclusion allows attackers to include files from external servers in your application, running malicious code on your server. This compromises your application and exposes your data.
Example: The infamous RFI attack on phpBB forums in 2005 allowed attackers to execute arbitrary code on vulnerable websites, compromising thousands of installations. - Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS): A DDoS attack floods your web application with traffic from multiple sources, overwhelming your servers and making your site unavailable to users. These attacks disrupt services and lead to downtime.
Example: In 2020, Amazon Web Services (AWS) mitigated a 2.3 Tbps DDoS attack, one of the largest ever recorded.
Example#2: In June 2022, a DDoS attack on a Google Cloud customer peaked at 46 million requests per second, with sources traced to over 130 countries. - Brute Force Attacks: In brute force attacks, hackers attempt to guess passwords or encryption keys by trying every possible combination. Weak passwords make it easier for attackers to access your system and sensitive data.
Example: The 2016 attack on Telegram accounts in Iran was reportedly a result of brute force attempts, compromising hundreds of accounts.
Why Web Applications Get Compromised Despite Security Measures?
Even with various web application security measures, vulnerabilities can persist. Here's why:

- Outdated or Incomplete Security Measures: If your security protocols aren't up to date, your application can easily become vulnerable. Cyber threats evolve rapidly, and outdated software or encryption provides attackers with opportunities to breach your system.
Example: The Equifax data breach in 2017 was due to an outdated version of Apache Struts, leaving their systems vulnerable to attackers. - Relying Too Much on One Type of Protection: It's risky to depend on a single security method, such as a firewall or encryption. These methods may block some attacks, but they can't stop others like SQL injections or cross-site scripting.
Example: A company might use a firewall to block DDoS attacks, but if they don't address vulnerabilities like XSS or SQL injections, their web app remains exposed. - Human Error: Human mistakes, such as employees using weak passwords or falling for phishing scams, can create vulnerabilities, even when strong security measures are in place. Regular employee training is essential.
Example: In 2019, a Capital One employee made a configuration mistake, exposing sensitive data to a cyber attacker. - Using Third-Party Tools and Dependencies: Many web applications rely on third-party tools and libraries, which may contain vulnerabilities. If these external components aren't regularly updated or monitored, attackers could exploit their flaws.
Example: The Log4Shell vulnerability in the widely-used Log4J library exposed millions of systems to attacks in 2021. - Not Testing Security Regularly: Without regular vulnerability testing or penetration testing, hidden security gaps may go unnoticed. It's important to frequently test your application to ensure all security measures are functioning properly.
Example: In 2020, the Twitter Bitcoin scam involved attackers gaining access to Twitter's systems, exploiting a gap that regular testing could have caught.
How to Conduct a Web Application Security Audit?
A web application security audit is a crucial process for identifying risks and strengthening your defenses. Here's a step-by-step guide to performing an audit:
- List All Your Web Assets: Make a comprehensive list of all assets connected to your application, including APIs, databases, and third-party tools. This will help you spot potential weak points.
Example: During an audit, a company may discover that an old API, no longer in use, is still connected to their app, serving as an entry point for hackers. - Evaluate Your Existing Security Setup: Now that you're aware of what's part of your system, it's time to look at your existing security setup. Ask yourself —
- What are you using right now?
- Do you have firewalls, encryption, or authentication measures in place?
- If yes, are they configured property and up to date?
- Are all your passwords secure and follow best practices?
- Are all connections encrypted with SSL/TLS?
- Identify Risks and Threats: Perform a risk assessment to identify the most vulnerable parts of your app, such as sensitive customer data or payment systems.
- Risk assessment: Look at the data your app handles. What would happen if someone accessed your customer data, payment info, or intellectual property? If unauthorized users gain access to this data, it leads to financial loss, reputational damage, or legal implications. By knowing what's at risk, you can prioritize which areas need the most protection.
- Threat modeling: Threat modeling involves thinking like an attacker to identify weak points—whether it's an unpatched vulnerability, weak password, or open API—and defending against potential threats.
- Third-party review: Check the security practices of any vendors or services you rely on. Do they update their software regularly? How strong is their security? A weak link in a third-party service could open up security loopholes in your application, so verifying that their security measures meet your standards is critical.
- Dependency scanning: If your app uses open-source libraries, you'll want to make sure they are updated. By using dependency scanning tools like Dependabot, you can monitor these dependencies and ensure they're updated.
- Pinpoint Vulnerabilities: Use automated tools to run vulnerability scans and perform manual code reviews to spot insecure coding practices that automated scans might miss.
- Vulnerability scanning: You will need automated tools such as Nessus or Acunetix to scan your app for known vulnerabilities, like SQL injection points or outdated software.
- Code review: If your app is custom-built, a manual code review can help spot flaws that automated tools might miss such as insecure coding practices or poor validation.
- Report and Act on Findings: Create a report detailing vulnerabilities and suggested remediation steps, along with a timeline for addressing each issue. This report will help guide your team in patching up security gaps.
- The final step in this audit is to compile all your findings into a comprehensive report which should include:
- A detailed list of issues identified.
- The risk level of each vulnerability (critical, high, medium, low).
- Suggested remediation steps for each issue.
- Any compliance gaps that need to be addressed.
- A timeline or roadmap for fixing the vulnerabilities.
Example: After finding vulnerabilities in third-party libraries, your report should recommend updating or replacing those libraries.
Best Practices to Protect Your Web Application from Cyber Threats
Here are best practices you can follow to protect your web application from cyberattacks:
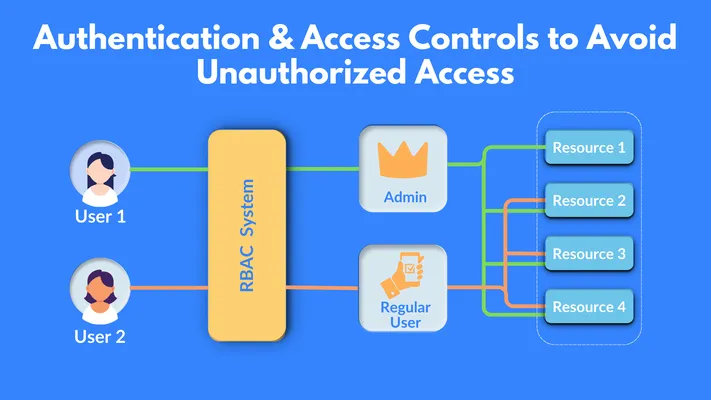
- Implement Strong Authentication and Access Controls: Authentication and access controls ensure that only authorized individuals can access specific features and data and protect sensitive information and functionalities from unauthorized access. This helps prevent data breaches and ensures that users can only access resources they are permitted to.
- Strong Authentication Mechanisms: Add additional layers of security by adding robust authentication measures. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) solutions such as Google Authenticator, Duo Security, or Authy can add this extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification beyond just passwords.
- Implement Secure Password Policies: Enforce policies that require complex passwords and regular updates. Tools like LastPass or 1PassWord can assist in managing and enforcing these strong password practices.
- Use Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC): Using RBAC helps manage user permissions based on their roles within the application. Assign roles and permissions effectively to ensure users have access only to necessary resources.
- Review and Update Access Controls Frequently: Make sure that you assess access controls periodically to ensure they reflect current roles and organizational changes.
- What it Costs: If you want to add MFA from the aforementioned names, the basic versions can be free, but for business-grade solutions, you may have to shed somewhere between $3 to $6 per month.
- Follow OWASP Guidelines: Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) is a nonprofit organization known for publishing the OWASP Top 10, which is a list of the most critical security risks to web apps, providing a comprehensive overview of common vulnerabilities, how attackers exploit them, and best practices to avoid them.
- Familiarize Yourself with the OWASP Top 10: The OWASP Top 10 is a great starting point for understanding the biggest security risks your web app might face. Each item on the list includes a detailed explanation of how the vulnerability works, how attackers exploit it, and what you can do to defend against it.
- Incorporate OWASP Best Practices into Your Development: Security needs to be integrated into your development lifecycle. This means following OWAP's best practices during every phase; from secure coding to deployment.
- Use OWASP Tools and Resources: OWASP provides a range of free tools to help you secure your web app. For instance, OWASP Dependency-Check can help you monitor your libraries and third-party software for known application security flaws.
- What it Costs: Incorporating these practices might mean more time and resources from your development team. Some tools like OWASP Dependency Check are free, but for more robust tools, you may have to spend $100 to $500 annually.
- Use HTTPS and TLS Encryption: Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure is an extension of HTTP, which is used for secure communication over a computer network. It's the standard protocol for safely transferring data between your users' browsers and your web application. Transport Layer Security (TLS) makes it secure by encrypting the data, ensuring that the exchange of sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, addresses, and communication details stays private.
- Get an SSL/TLS Certificate: First things first, you'll need an SSL/TLS certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority such as DigiCert or GlobalSign.
- Install the Certificate on Your Server: Once you have the certificate, install it on your web server. For servers like Apache or Nginx, the process is straightforward but may vary slightly by server type. Tools like Certbot can automate installation and renewal.
- Force HTTPS Connection: You don't want any traffic slipping through the cracks in plain HTTP, so make sure to configure your server to automatically redirect all HTTP traffic to HTTPS. You can do this in Apache by adding a rule in your '.htaccess' file or main configuration.
- Enable TLS 1.2 or Higher: Make sure you're using TLS 1.2 or higher as modern browsers need it. By doing so, you ensure that all your connections use the latest, most secure encryption.
- Test and Audit Your Security: After setting everything up, it's crucial to test your configuration. Use tools like SSL Labs' SSL Test or Hardenize to make sure your HTTPS setup is working as intended.
- What it Costs: Getting an SSL/TLS certification from a trusted provider can range from $50 to $500+ a year. Though there are free options like Let's Encrypt, they require frequent maintenance.
- Meet Compliance Regulations: Following compliance regulations isn't just about avoiding fines or legal issues, but also about building trust with your users. Most of these regulations push you to adopt best security practices, so by staying compliant, you're improving your web app's overall safety.
- Understand Your Obligations: The first thing you'll need to do is figure out which regulations apply to your business.
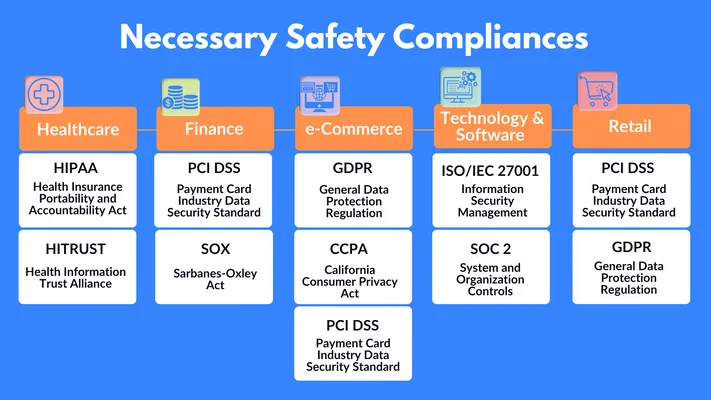
- Set Up Clear Data Protection Policies: Once you know which regulations apply to you, it's time to create clear policies around data protection. Your policies should explain how your app collects, stores, and processes user data.
- Implement Security Measures that Fit: Depending on the compliance standards, you need to implement the necessary security practices. For instance, if you handle healthcare data (under HIPAA), you need to encrypt patient information.
- Perform Audits Regularly: Staying compliant isn't a one-time thing. You need to audit your process regularly to ensure everything's in line with regulations. You can do this internally or hire a third-party organization to help. Tools like Vanta or Drata can automate parts of the process, so you can keep an eye on compliance without manual effort.
- What it Costs: The cost of attaining compliance depends on the regulations applied to your web app. For instance, HIPAA includes costs for encryption, audit, and employee training.
- Understand Your Obligations: The first thing you'll need to do is figure out which regulations apply to your business.
- Use Security Testing Tools: When you integrate security testing tools, you're using specialized software to automatically scan your web app for potential threats. Instead of manually combing through code to spot issues, these tools can help you quickly identify weak points like unprotected data, open ports, or potential entry points for hackers.
- Pick the Right Tools for Your App: There are several security testing tools out there, each designed for different needs.

- Integrate into Your Workflow: Many Security tools can be built right into your CI/CD pipeline, so they run automatically whenever you make updates or changes to your app.
- Run Regular Scans: After integrating the tools, make sure to run regular security scans. Regular scans help you stay on top of things, making it easier to fix issues before they become serious threats.
- Analyze the Results and Fix the Issues: Once the scans are done, the tools will generate reports showing potential weaknesses. It's crucial to take the time to review these reports carefully. Not every issue will be high-risk, so you'll want to prioritize which ones need attention first.
- What it Costs: Free tools like OWASP Zap exist, but for more advanced scanning, tools like Burp Suite or Acunetix can cost anywhere from $5K to $15K annually.
- Pick the Right Tools for Your App: There are several security testing tools out there, each designed for different needs.
- Perform Penetration Testing: Penetration or pen testing is about simulating a real-world attack on your web application to find security defects. Instead of relying solely on automated scans, pen testing involves ethical hackers trying to break into your systems, using the same methods an attacker would to test your defenses and see how secure your web app is.
- Bring in the Experts: Penetration testing isn't something you can do on your own unless you've got some serious security expertise. Hiring a professional team to do the testing for you is best. Additionally, tools like Metasploit or Core Impact can help automate some of the processes.
- Focus on High-Risk Areas: Make sure that the experts you get to focus on the areas that handle sensitive data such as your login systems, payment gateways, or anything involving user information.
- Simulating Real-World Attacks: During the pen test, the tester will simulate different attacks including SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and brute force attempts to guess passwords. The idea is to see how far they can get.
- What it Costs: Hiring a professional for pen testing depends on their experience, the size of the application, and its complexity. On average, you can expect a pen testing fee of $5K and more.
- Implement a Web Application Firewall (WAF): A WAF sits between your web app and the internet, filtering traffic to block threats and prevent attacks that may bypass automated tools or pen tests, reducing risks of breaches and downtime.
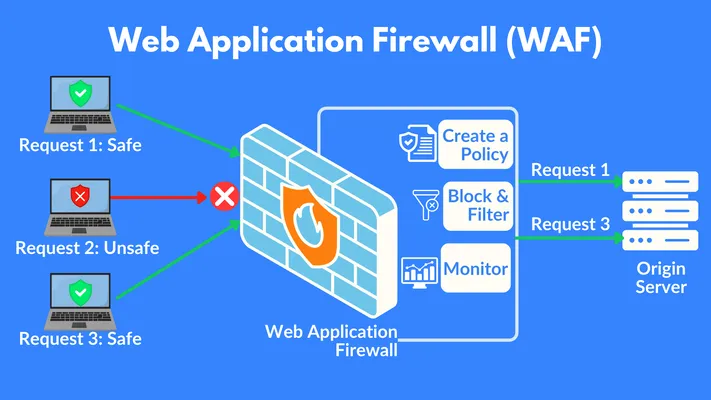
- Choose the Right WAF Solution: WAFs come in different types: cloud-based, hardware-based, and software-based. Cloud-based options like AWS WAF, Cloudflare WAF, and Akamai Kona Site Defender are popular for their easy setup and scalability, without the need for hardware management. For more control, businesses may choose hardware or software solutions they can configure themselves.
- Monitor and Analyze Traffic: A WAF doesn't just block malicious traffic, it also gives you insights into who's trying to attack your app and how. Many WAFs offer reporting and analytics features that help you understand what kinds of threats you're facing and how to mitigate them further. This information is useful for fine-tuning your security measures and staying ahead of new attacks.
- Update and Optimize Your WAF Regularly: Many WAF providers offer automatic updates to help protect against new vulnerabilities as they're discovered. However, you should also review and update your custom rules regularly to ensure they're still relevant to the latest threats your app may face.
- What it Costs: Cloud-based WAFs like AWS WAF or CloudFare WAF might cost you around $20 to $200 per month, depending on your needs. However, if you want better control with a hardware solution, the prices can start from $5K.
Determining Your Security Needs: Comprehensive Overhaul or Targeted Fixes?
Now that you know about the major issues, the auditing process, and the ways to protect them, it is time to know whether you need all, a few, or just one method to protect your web application.
- If your audit reveals significant weaknesses like:
- Weak authentication methods.
- Lack of database encryption or data encryption at rest.
- Exposure to common vulnerabilities.
- Absence of proper security policies.
Note: A comprehensive security overhaul is required including implementing multiple layers of protection, enhancing encryption, upgrading authentication, and patching all vulnerabilities.
- If your system is mostly secure but has a few security gaps such as:
- Outdated software libraries or dependencies.
- Insufficient access controls.
- Minor weaknesses found in specific areas like SSL/TSL implementation or session management.
Note: Focus on targeted security measures. Apply updates to software, strengthen access controls, and address specific vulnerabilities the audit reveals.
- If your app is small or low-risk:
- Minor security gaps such as missing software updates.
- Strong existing security practices in place.
Note: Make minor adjustments to optimize existing defenses. Make sure that your systems are updated with the latest patches and that you're using current best practices to maintain security.
Web Application Security Trends 2024
Cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving. Here are key web application security trends to watch in 2024:
- Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA): ZTA means trusting no one, whether inside or outside your network. Every user and device must be verified every time they try to access your systems, reducing insider and external threats.
- AI and ML in Security: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) help detect and respond to unusual activity faster than humans can. These technologies can flag suspicious behavior and stop attacks before they happen.
- DevSecOps: DevSecOps integrates security into every stage of the development process. By catching vulnerabilities early, you save time and ensure a secure product from the start.
- Cloud-Native Security: As more businesses move to the cloud, cloud-native security focuses on securing apps built and running in cloud environments. Tools like CWPP and CSPM help manage cloud security risks.
Conclusion
Enhancing web application security is crucial for protecting your business from evolving cyber threats. By following these best practices and performing regular security audits, you can safeguard your application and maintain trust with your users.
ThinkSys offers comprehensive services to help you perform a web application security audit and protect your app from potential threats.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What web application security services does ThinkSys provide?
How does ThinkSys identify vulnerabilities in my web application?
What types of threats can your company protect against?
How often should I test my web application's security?
Will implementing your security measures affect the web application's performance?
Share This Article:









