How to Implement OAuth 2.0 for Secure User Authentication?
Ever wondered how apps let users log in with just a tap on ‘Sign in with Google’ or ‘Sign in with Facebook’ or seamlessly connect to third-party services without asking for your password? All that is possible with OAuth 2.0, a system that’s as secure as it is user-friendly.
This article will guide you through leveraging that same power in your app, from understanding how OAuth 2.0 works to setting up secure authorization flows. Let’s begin by briefly explaining OAuth 2.0.
Why You Should Consider OAuth 2.0?
OAuth 2.0 offers compelling benefits for businesses and their users. This section briefly explains how implementing it can benefit you and your users.
For example, Reddit, a global social forum network with over 50 million daily active users, witnessed a 50%- 60% increase in signups and a 10%- 22% increase in sign-ins with the 'Sign in With Google' button.
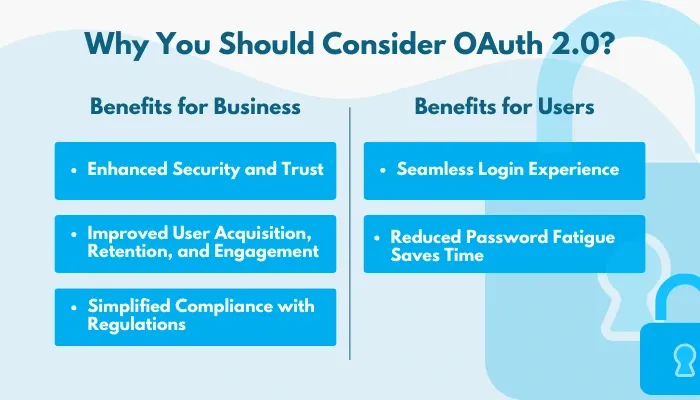
Benefits for Business
- Enhanced Security and Trust: The secure token-based authentication minimizes data breaches by reducing password storage.
- Improved User Acquisition, Retention, and Engagement: Simplified login increases conversion rates, encourages repeat visits, and fosters user loyalty.
- Simplified Compliance with Regulations: OAuth 2.0 provides a framework that supports data access transparency and minimizes personal information exposure.
Benefits for Users
- Seamless Login Experience: OAuth 2.0 enables authentication via trusted services, eliminating the need to create and remember multiple passwords.
- Reduced Password Fatigue Saves Time: By relying on single sign-on (SSO) mechanisms, OAuth 2.0 minimizes the burden on users to manage numerous credentials.
Technical Feasibility and Integration
Implementing OAuth 2.0 is a technical decision that requires careful evaluation of your existing systems, available tools, and long-term scalability needs.
- Evaluating Infrastructure Readiness
Before diving into implementation, take a good look at your current infrastructure—especially your authentication mechanisms, server capacity, and API setup. If you're already using APIs for user management, integrating OAuth 2.0 might mean tweaking your existing endpoints.
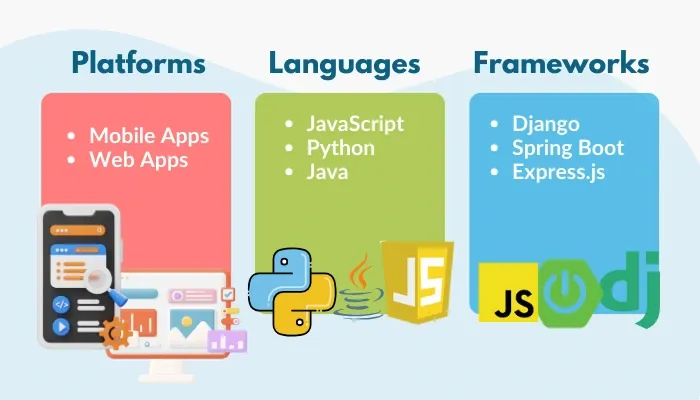
- Compatible Platforms, Languages, and Frameworks
OAuth 2.0 works across mobile and web apps with libraries for languages like Python, Java, and JavaScript. Additionally, frameworks such as Django, Spring Boot, and Express.js have inbuilt capabilities or plugins for implementing OAuth 2.0.
- Tools, Libraries, and SDKs
OAuthLib, Spring Security, and Passport.js are the top open-source libraries that help streamline the technical process. SDKs provided by identity providers such as Google, Facebook, and Microsoft ensure seamless integration for mobile apps.
- Ensuring Scalability
OAuth 2.0 is designed to handle large-scale systems, but it’s crucial to configure it correctly for scalability. For growing user bases, ensure your token storage and validation mechanisms can handle high traffic without performance bottlenecks.
Security and Compliance
By leveraging token-based authentication and aligning with modern data regulations, it offers businesses a secure and transparent way to handle user authentication.
How OAuth 2.0 Enhances Security?
OAuth 2.0 replaces passwords with secure tokens, reducing the risks of credential leaks. These tokens grant limited access for specific purposes and can be set to expire, minimizing misuse.
Common Risk and Mitigation
While OAuth 2.0 offers robust security features, improper implementation can introduce vulnerabilities. The following are the commonest risks and their mitigations.
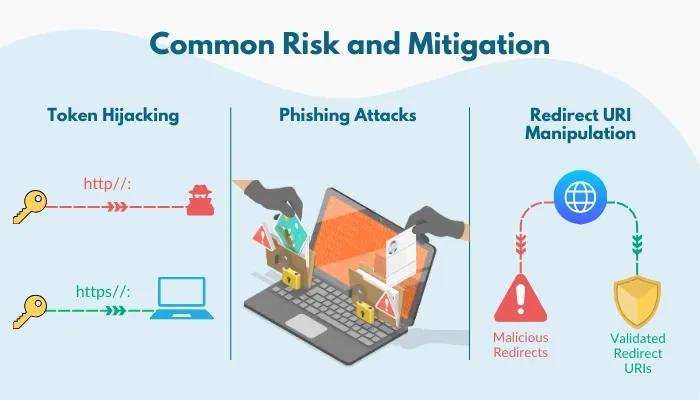
- Token Hijacking: Attackers can intercept tokens during transmission, risking data breaches and financial losses. You can use HTTPS to encrypt data during transit and implement token binding to associate tokens with specific devices.
- Phishing Attacks: Attackers create fake authorization pages to trick users into providing credentials. You can educate users about phishing risks and use trusted domain names for authorization prompts.
- Redirect URI Manipulation: Poorly configured URIs can redirect users to malicious sites, causing compliance issues and reputational damage. Mitigate this risk by validating redirect URIs and ensuring they match the ones registered with your app.
Compliance with Regulations
OAuth 2.0 helps businesses comply with data protection regulations, including GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, by supporting secure and transparent data handling practices.
- GDPR: OAuth 2.0 allows businesses to explicitly define the data they need access to, aligning with GDPR’s data minimization principles.
- CCPA: The token-based systems of OAuth 2.0 supports user rights under CCPA such as allowing users to revoke access at any time, giving users greater control over their data.
- HIPAA: In healthcare applications, OAuth 2.0 can ensure that sensitive data, such as health records, is accessed securely and only by authorized parties.
User Experience and Branding
By going beyond surface-level benefits, you can discover how OAuth 2.0 creates deeper value for businesses through innovative strategies and thoughtful implementation.
Optimizing Onboarding for Business Impact
Efficient onboarding is not just about ease of use but about reducing churn and maximizing user acquisition.
- Reduced Drop-Off Rates: OAuth 2.0 eradicates registration forms, letting users log in with existing accounts, leading to fewer abandoned registrations and more conversions.
- Increased Global Reach: Offering OAuth options such as Sign in with Facebook or Sign in with Apple ensures your app caters to users across different geographies.
- Faster Time to First Value (TTFV): By minimizing registration hurdles, users can interact with your core features faster, increasing the likelihood of retention and conversion into paying customers.
Customizing OAuth 2.0 for Competitive Advantage
Thoughtful customization allows businesses to create a seamless, professional experience that feels uniquely their own.
- Domain-Specific Scopes: Tailoring OAuth scopes to align with your business model can subtly reinforce your brand’s value.
- Dynamic User Onboarding: OAuth can enable various experiences based on the user’s identity provider.
- Localization of Authorization Pages: Businesses targeting global users can customize authorization flows in the user’s native language and context, enhancing trust and accessibility.
Scaling for Long-Term Growth
As your user base grows, its token-based system can handle increasing traffic without compromising performance. Moreover, third-party identity providers are designed to support millions of users, giving you enterprise-level scalability.
Cost and Resource Considerations
Understanding the strategic value and long-term implications of investing in OAuth 2.0 is one of the significant actions you should perform..
Development Costs
While the surface-level development costs are tied to coding and integration, deeper complexities can arise that business owners anticipate:
- Edge Case Handling: Overlooking scenarios like partial logins and session timeouts can frustrate users and lead to expensive post-launch fixes.
- Multi-Tenant Systems: Serving multiple clients? You'll need to configure tailored authorization flows, isolate data, and ensure each tenant meets security requirements without adding unnecessary complexity.
- Future-Proofing: Developing with future OAuth extensions in mind (Proof Key for Code Exchange [PKCE] or device flows) ensures scalability but requires upfront investment in design and testing.
Infrastructure Costs
Hosting an OAuth 2.0 solution involves more than renting server space and ensuring that the system is resilient, secure, and efficient.
- Zero-Downtime Upgrades: OAuth servers must stay operational during updates to avoid user access disruptions. Techniques like blue-green deployments or canary releases help but can increase hosting and operational costs.
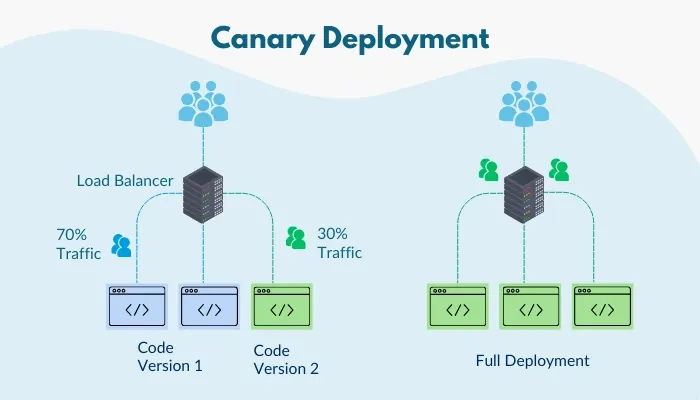
- Monitoring and Logging: Advanced tools like Splunk or Datadog are essential for tracking token issuance, detecting suspicious activity, and resolving API errors. However, these tools often come with subscription expenses.
- Token Storage and Revocation: Securely storing long-lived tokens and maintaining real-time revocation lists can be complex. In that case, you need to invest in dedicated database instances with encryption and rapid access mechanisms.
Third-Party Costs
Third-party OAuth providers are often seen as a turnkey solution, but businesses should evaluate these services carefully.
- Overage Charges: Rapid user growth or unexpected traffic spikes can lead to coverage charges that strain your budget. For instance, there is no charge for up to 49,999 monthly average users (MAU) using Google Identity Platform. However, the charge increases as soon as you hit 50K MAU.
- Customer Feature Requests: Many third-party providers offer custom solutions for unique business needs, often priced as premium add-ons.
- Vendor Lock-In: Choosing a renowned provider such as Auth0 or Okta means adapting to their APIs and workflows. Migrating away from a provider can be time-consuming and expensive, requiring significant redevelopment.
Human Resource Cost
OAuth 2.0 implementation requires collaboration across multiple teams, each with unique skill sets:
- Cross-Functional Expertise: Developers must work closely with legal and compliance teams to ensure that OAuth 2.0 implementation aligns with necessary regulations. Your customer support team may need training to address OAuth-specific user issues, such as troubleshooting token expirations or denied scopes.
- Specialized Talent: Hiring engineers with experience in OAuth, OpenID Connect (OIDC), and API security can be challenging and costly. For niche projects, businesses might even need to hire consultants.
Opportunity Costs
Beyond direct costs, there’s the question of opportunity costs:
- Time-to-Market: A complex OAuth implementation can delay your product launch. For startups or businesses in competitive markets, this lost time could mean missed opportunities to capture market share.
- Focus Shift: Diverting resources to build and maintain OAuth internally might detract from other strategic priorities, such as enhancing your core product.
Picking the Right Vendor
To make an informed choice, it’s crucial to evaluate vendors against well-defined criteria.
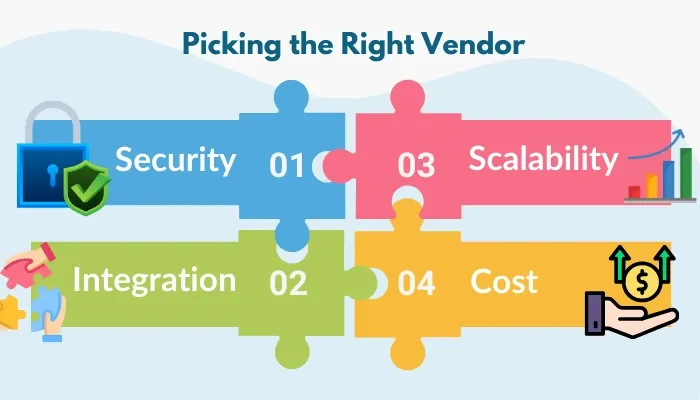
- Security: Make sure the OAuth 2.0 vendor complies with certifications like SOC 2 or GDPR and provides features such as PKCE and token encryption.
- Integration: The vendor should be compatible with multiple authentication protocols, including OpenID Connect and SAML, for a smooth transition.
- Scalability: Find evidence of low latency, effective rate-limiting, and consistent performance during peak loads to ensure a seamless user experience.
- Cost: You have to consider the total cost of ownership by considering factors such as API quotas, premium features, and support fees.
How to Implement OAuth 2.0?
Implementing OAuth 2.0 might initially seem overwhelming, but breaking the process into clear steps can simplify the journey.
- Understand Your Use Case: Identify whether it’s a web app, mobile app, or single-page app, and determine the level of security required. Moreover, define the exact permissions your app will need.
- Choose and OAuth 2.0 Provider: Google, Facebook, and GitHub are the top names that cater to different use cases. A well-chosen provider ensures smooth authentication and minimizes long-term maintenance.
- Register Your Application: After choosing a provider, register your app on their developer portal. You need to provide details, including your app name, redirect URIs, and requested permissions (scopes). Once registered, you’ll receive a Client ID and Client Secret, which must be securely stored as they are essential for token exchanges.
- Redirect Users for Authentication: To enable user authentication, set up a login button or link that redirects users to the provider’s login page. The redirect URL should include your Client ID, scopes, and a callback URI.
- Exchange Authorization Code for Tokens: When users are redirected back to your app, they bring an authorization code, which will be used to request access and refresh tokens from the provider’s API.
- Handle Token Expiry with Refresh Tokens: Since access tokens are short-lived, your app must use refresh tokens to maintain uninterrupted access. Request a new access token using the refresh token when an access token expires.
- Implement Token Revocation: Token revocation allows users to revoke app access anytime, enhancing security and control. Integrate the provider’s revocation endpoint into your app to invalidate tokens when users log out or withdraw permissions.
- Test Thoroughly Before Deployment: Simulate various scenarios, including successful logins, denied permissions, token expirations, and revocations. Make sure to validate that your app handles errors gracefully and refreshes tokens without disrupting the user experience.
- Monitor and Maintain the System: Once deployed, continuously monitor your OAuth 2.0 implementation to ensure its performance and security. Moreover, regularly update your system to stay compliant with evolving security standards and provider updates.
Measuring Success
Implementing OAuth 2.0 is a move that can redefine user experience and impact business growth. But how do you determine if it’s working as intended? By tracking the right metrics:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
The true value of OAuth 2.0 is reflected in measurable outcomes. Here’s how you can evaluate its impact.
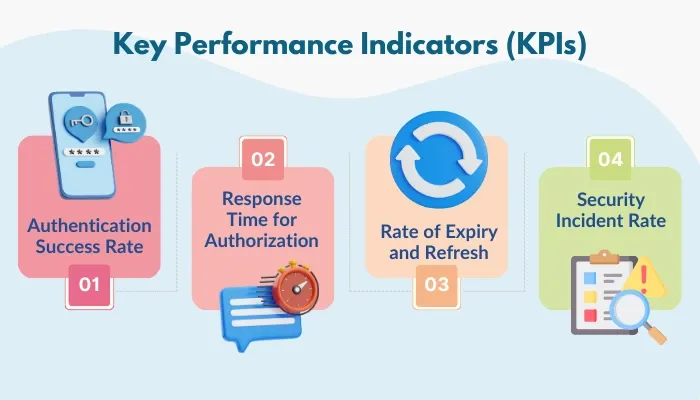
Authentication Success Rate:
- What to measure: Percentage of successful authentications versus failed attempts.
- Why it’s important: High success rates indicate that OAuth 2.0 is functioning smoothly for users, minimizing friction during login processes.
- Target KPI: Aim for a minimum of 99% authentication success rate post-implementation.
Response Time for Authorization:
- What to measure: Average time taken from initiating the authorization request to receiving the access token.
- Why it’s important: OAuth 2.0 should not negatively impact application performance. Faster authorization times contribute to a better user experience.
- Target KPI: A response time under 500 milliseconds is optimal for most use cases.
Rate of Expiry and Refresh:
- What to measure: Frequency with which access tokens are refreshed or expired, and the success rate of refresh operations.
- Why it’s important: Tokens should be appropriately refreshed without excessive requests, balancing security with user convenience.
- Target KPI: Less than 1% of token refresh operations should fail due to system or configuration errors.
Security Incident Rate:
- What to measure: Frequency of OAuth-related security breaches or vulnerabilities, such as unauthorized access due to misconfigured scopes or token theft.
- Why it’s important: Ensures that the integration adheres to security best practices and mitigates risk to user data and systems.
- Target KPI: Zero critical security incidents related to OAuth 2.0 within 6 months of implementation.
The Future of OAuth 2.0
One key step in getting the best outcome from OAuth 2.0 is to know about the current trends and future possibilities.
OAuth 2.1
OAuth 2.1 is making waves by streamlining the existing protocol. It eradicates outdated flows such as the implicit grant and mandates best practices, including Proof Key for Code Exchange and HTTPS for all communication. The simplification reduces one of the biggest challenges with OAuth 2.0: the implementation errors. Though OAuth 2.1 is not officially used, it is anticipated to be released in 2025.
Conclusion
OAuth 2.0 has become the gold standard for secure and seamless authentication in modern applications. Its flexibility, scalability, and robust security features make it an essential upgrade for businesses looking to enhance user experience and protect sensitive data.
However, as powerful as OAuth 2.0 is, implementing it is no small task. The process can quickly become complex, from selecting the right provider to configuring flows, ensuring compliance, and managing post-deployment monitoring. To ensure a smooth implementation, it’s worth considering professional assistance. Experienced teams can help you navigate the nuances, tailor the solution to your needs, and save valuable time and resources.
Choose ThinkSys for OAuth 2.0 implementation designed to streamline user access, enhance security, and adapt seamlessly to your app’s needs, boosting user satisfaction and building trust in your application.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Share This Article:








