Security Testing Essentials for Enterprise Applications
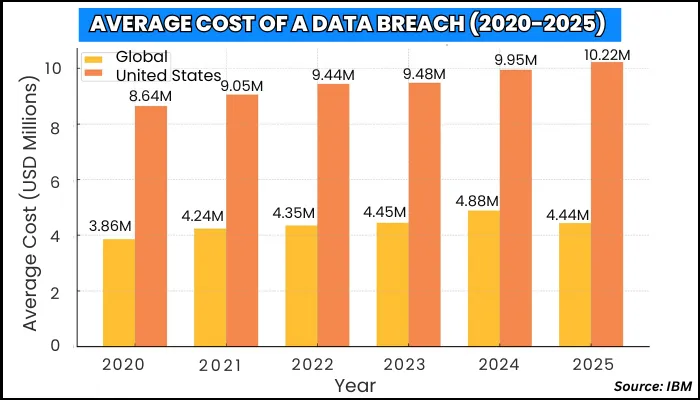
$10.22 million. That’s not the quarterly profit of an organization, but the average cost of a single breach in the US in 2025. That’s not just a line item in the security budget. That’s entire product launches, marketing campaigns, or R&D initiatives wiped out. And that’s just the direct cost. The real hit is to trust, brand reputation, and momentum.
Cyber threats are continually evolving, surpassing every traditional defense approach. Sticking with outdated security testing? That’s a gamble no forward-thinking leader can afford.
Enterprise applications are the leading targets of attackers simply because they hold higher volumes and more valuable data. When a target is on your back, the only way to remain safe is to strengthen your defenses. Companies using AI-powered security and automation resolved incidents almost 100 days faster while saving an average of $2.2 million per breach.
That’s just one method of safeguarding your enterprise application. This article focuses on security testing essentials for enterprise software that no organization can afford to leave behind.
Why Should Security Matter to You?
When it comes to managing organizations, enterprise software plays a crucial role. These kinds of systems can take care of big organizational duties, like managing employees and resources.
In the US, however, breach costs are more than twice as high as the global average of $4.4 million. But that's not everything. These are the reasons why you need more security for business apps.
- Legal Issues and Regulatory Fines: In 2025, data is protected more than ever, thanks to both businesses and government agencies. The SEC’s expanded cybersecurity disclosure rules mean breaches are now a board-level compliance concern.
In fact, 25% of organizations that suffered breaches faced regulatory fines exceeding $100,000.
Now the conversation isn’t limited to what-if. It's about knowing that in this day and age, it's not possible to evade legal responsibility when things go wrong, especially when the response is poor or careless. - Safeguard Business Continuity: When there is a security breach, the attack doesn't just affect the IT team; it stops the whole organization. Depending on the sector, downtime caused by cyber-attacks might cost thousands of dollars every minute.
Performance issues can also cause costly downtime. That’s why combining strong security testing with enterprise performance testing is key to keeping your app secure.
But the expense isn't only in money. While your competitors keep delivering, coming up with new ideas, and winning over customers, your team might be too busy recovering from the attack.
Every minute you spend cleaning up after an attack is the time you can't use to add new features, close transactions, or grow your market share.
That's why testing for enterprise-grade security is just as much about keeping data safe as it is about keeping money safe. It maintains your growth engine functioning smoothly, without any unexpected breakdowns. - Tackling the AI Threat Landscape: AI is a double-edged sword in security. AI-powered defenses are helping businesses find and stop threats faster, but attackers are also leveraging the same technology to make their attacks bigger.
More and more data breaches are happening that use AI. In fact, 1 in 6 attacks uses AI. This means that every time a new AI tool is added to the stack, whether it is formally approved or not, your attack surface gets bigger.
Today's security testing needs to consider these new vectors and make sure that policies, detection, and enforcement keep up with how employees and partners work. - Protect Your R&D and Market Expansion Budgets: Loose security puts the budgets you approve for product development, market expansion, and acquisitions at risk. Many may not realize this, but every dollar invested in proactive security testing of enterprise software has the potential to save multiples in avoided losses.
And unlike other investments, this one also protects intangible assets, including your brand, your credibility, and your customer relationships. - Maintain Market Valuation and Investor Trust: It’s an old saying that ‘markets never forget.’ Research shows companies experience 15–18% negative abnormal stock returns in the year following a breach, with equity risk climbing by 11%.
When a publicly traded company gets hammered like that, it shows up in analyst calls, letters to shareholders, and financial reports.
Even for private companies, valuation during funding rounds or acquisitions can take a nosedive after a security incident.
Also, when clients, partners, and the market regard you as weak, they are less likely to make a deal and keep doing business with you.
Components of Enterprise Security
What makes business software safe? The first step is to have a security-first mindset at all times, not just at the end. But that's not all there is. Here are the main parts that make up an effective enterprise security posture:
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Not only workers, but also contractors, partners, and perhaps even people from outside the company will use enterprise software in different parts of the world, on different devices, and at different times. Attackers enjoy roles that are too open, accounts that are no longer active, and service accounts that don't have owners.
IAM ensures that only the right individuals have the right level of access at the right time. Without robust IAM, the risk of privilege misuse increases.
Security Testing
You can’t defend what you haven’t tested, especially in complex enterprise environments. Consider security testing to be a health check for your software ecosystem. It should be ongoing, thorough, and customized to your business operations. It should include testing old integrations, third-party APIs, and complex authentication routines to make sure that what works on paper also works in the real world.
A well-created testing strategy layers automation with expert-led evaluation. Automated tools find common configuration errors, while manual testing finds more subtle design faults. This dual approach makes sure that your defenses aren't just ideas; they've been tested in real-life situations.
Data Encryption
Enterprise software may hold everything from consumer PII to health records to trade secrets worth millions of dollars. These assets regularly travel from on-site servers to different cloud providers and even to edge devices, which makes them vulnerable in many places.
Encryption of data is really important, but it isn't the only thing that works. It can lose its benefits if the key management is weak, the algorithms are old, or the encryption libraries are not set up correctly.
Encryption is only useful for business apps if it is consistently applied to everything, including backups, cloud storage, edge devices, and more. And remember: encryption that’s poorly implemented creates dangerous blind spots which you need to avoid.
Secure Design
It is important to build security into enterprise software from the start. The secure design philosophy makes sure that security is included in every step, from architecture and development to deployment. If you don't have that early-on approach, you'll wind up with fixes that are reactive and take a long time to work, not proactive defense.
Security Awareness Training
Without a doubt, your employees are your most valuable assets, but they may also be your biggest risk. A whopping 85–95% of breaches involve human error. That makes investing in awareness training one of the highest-impact actions.
Training is about making a team that can spot threats, tell someone about them, and keep an eye on things while excelling at their work. Investing in culture that doesn't let glare in, fake phishing drills, and continual training is worth it.
Patch Management
Here’s a truth many enterprise software testing teams learn the hard way: 60% of data breaches are caused by unpatched vulnerabilities. An attacker has a lot of time to take advantage of a security hole if you don't install fixes right away.
Automation is the best approach to keep your business software safe. They’re not just faster but safer as well. Automation helps reduce malware infections and significantly cuts remediation times.
Securing Enterprise Applications: The Process
Security testing of enterprise software grows with your application and the threats it faces. When it comes to the most essential security aspect, implementing the security testing process tops the chart. It’s necessary to follow a structured yet adaptable process where each step builds on the last. With that in mind, here’s how you can approach security testing.
- Define Security Objectives and Risk Profile: Before the security team starts running tests, they need to figure out the most significant parts of the business software. You need to know where sensitive data is kept, how it moves through the system, what functions are vital, and more. Also, understand the importance of data to your organization and the potential consequences of it falling into the wrong hands.
- Proactive Design and Planning: The initial phases of the SDLC are paramount for embedding security from the ground up, preventing vulnerabilities from becoming deeply entrenched in the software architecture. These include threat modeling and security requirements & scoping.
- Threat Modeling: Threat modeling is viewed as the primary and most strategic task in the shift-left security methodology. It involves using a systematic process to find and prioritize possible security risks and weaknesses in the design stage before any coding is done. But to deal with known dangers, you need to know the project inside and out, including where it might fail and how the current security measures work.
You can predict how attackers can exploit weaknesses by carefully looking at the program design, its business environment, and the intended user processes. With that information, you can make educated choices regarding essential security measures.
Popular frameworks, such as STRIDE (Spoofing, Tampering, Repudiation, Information Disclosure, Denial of Service, Elevation of Privilege) and PASTA (Process for Attack Simulation and Threat Analysis), which are risk-centric and focus on business impact, guide this crucial phase. - Security Requirements and Scoping: Utilizing the findings from threat modeling, this phase focuses on precisely outlining the security requirements and objectives for the business application. It's a crucial step that lays the groundwork for effective security testing tailored to the application's unique traits and risk assessment.
Additionally, it helps to establish the scope and depth of testing activities, ensuring that endeavors stay focused and aligned with business goals.
- Threat Modeling: Threat modeling is viewed as the primary and most strategic task in the shift-left security methodology. It involves using a systematic process to find and prioritize possible security risks and weaknesses in the design stage before any coding is done. But to deal with known dangers, you need to know the project inside and out, including where it might fail and how the current security measures work.
- Catching Flaws at the Source: After planning and design are finished, attention turns to protecting the application's codebase, using automated technologies to give developers ongoing feedback. In order to obtain ongoing code-level insights, Static Application Security Testing (SAST) and Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST) are used.
- SAST: SAST is one of the most effective methods for locating the underlying cause of vulnerabilities in the code. It is a white-box testing methodology that automatically scans an application's source code, bytecode, or binaries without actually running the app.
A wide range of vulnerabilities, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), unsafe coding techniques, the use of outdated dependencies, and the inclusion of hard-coded passwords, are easily detected by SAST tools, such as SonarCube, Checkmarx, Snyk, Veracod, and Klocwork.
- IAST: IAST works by putting security sensors, which are also called instrumentation, right into the code of the application. These sensors monitor how the application works in real time during the testing or QA phases. Also, when you analyze source code, runtime behavior, and HTTP traffic at the same time, it gives you results that are more accurate and with a lot fewer false positives than when you only use SAST.
IAST helps developers fix problems fast and effectively by giving them contextual remediation suggestions and pinpointing the cause of vulnerabilities, often down to the lines of code.
For complete code-level security, SAST and IAST need to work together. SAST does basic analysis before the code runs. It finds problems, including syntax errors, hard-coded credentials, and unsafe coding practices.
However, SAST isn't highly efficient in finding vulnerabilities in dynamic environments or outside of the actual code, like problems with third-party APIs.
IAST, on the other hand, provides deeper, more precise runtime analysis with direct code context by analyzing code as it executes, identifying vulnerabilities that might only become apparent during active application execution.
By adding SAST and IAST directly into developer workflows and CI/CD pipelines, you provide the development teams with the power to be responsible for security.
- SAST: SAST is one of the most effective methods for locating the underlying cause of vulnerabilities in the code. It is a white-box testing methodology that automatically scans an application's source code, bytecode, or binaries without actually running the app.
- Testing Live Behavior through Dynamic Application Security Testing: Testing the application's behavior in a live setting that mimics real-world interactions is crucial. DAST is a black-box testing technique that assesses an operational, live application from an external perspective without needing access to the source code. It means acting like real hackers, providing different forms of harmful inputs, and searching for problems, error messages, or strange behavior in how the program responds.
You can use DAST to simulate attacks in pre-production pipelines or staging environments before adding new functionality.
Modern frameworks even let you do continuous DAST, which means that tools are built into CI/CD pipelines and conduct scans automatically every time code is deployed. But DAST works best when combined with manual penetration testing by knowledgeable security experts, who are more creative than automated tools. - Real World Attack Simulation using Penetration Testing: Validating defenses against sophisticated, human-driven attacks requires a direct approach, particularly for high-value enterprise applications. Most people agree that penetration testing on enterprise software is the best way to check its security.
This testing is done by authorized experts who act like real attackers by trying to exploit known vulnerabilities, giving a more accurate picture of how well the system works.
For business applications, this means checking that security measures are strong enough and finding holes that could let hackers get in or corrupt data. These are critical issues for systems that deal with private or financial information.
You need to know about the five steps of the testing process in order to make sure that the testing is as effective as possible:- Reconnaissance: The testing professional will gather information about the business software and its security level before launching the attack. The information includes domain names, server IPs, technology stacks, open APIs, employee credentials that were leaked online, or even cloud storage that was set up incorrectly.
Example: The tester might find an exposed subdomain running outdated software, which becomes a potential entry point. - Scanning: After mapping the attack surface, testers look for weaknesses using both automated and manual methods. This step is similar to DAST, but the goal is clearer: using top tools, including Nmap, Nessus, or Burp Suite, to find the entry points that look most promising for exploitation.
For example, a scan could show that an enterprise login page isn't appropriately rate-limited, which makes it easy for brute-force attacks to get in. - Exploitation: The first few steps were all about getting ready, but this is when the pen test really starts. In this step, the tester will use controlled attacks to see how far they can get into the system by taking advantage of identified weaknesses. After this step, you'll know if there is a security vulnerability and the potential damage it could cause, such as stealing private information, giving someone more access, or halting essential workflows.
For example, an attacker could use a SQL injection flaw to extract private user records from the database. - Post-Exploitation Assessment: Testers will now explore what they can do with acquired access. Can they pivot into other systems? Steal business-critical data? Create persistence for long-term access? In this stage, simulating the real impact on business operations if an attacker were inside takes place.
Example: A compromised user account may allow the tester to move laterally and gain access to financial transaction data or internal dashboards. - Reporting: The last phase in this test is to inform the relevant parties what happened. The testers will prepare a well-organized report that describes what they found and how to remedy it. The fixes will be ranked in order of severity and how much they could affect the system.
Instead of just saying that the password reset endpoint is weak, the report should explain how it could let attackers take over executive accounts and access private information.
- Reconnaissance: The testing professional will gather information about the business software and its security level before launching the attack. The information includes domain names, server IPs, technology stacks, open APIs, employee credentials that were leaked online, or even cloud storage that was set up incorrectly.
- Remediation, Reporting, and Continuous Improvement: A robust security process starts with identifying vulnerabilities. Effective security testing includes a systematic approach to problem-solving, transparent reporting, and a dedication to continuous improvement.
- Prioritizing and Addressing Identified Vulnerabilities: Enterprise software complexity demands a strategic approach to fix identified vulnerabilities. The most crucial step is to repair vulnerabilities based on their severity level, potential for exploitation, and business impact. The effectiveness of remediation efforts increases when resources focus on fixing the most critical risks first.
- Ongoing Training: Security practices are constantly changing, so businesses need continuous learning to achieve effective results from their security measures. To manage threats effectively, you need to give all team members and business staff ongoing training. The training programs should teach how to write secure code, how to stay up to date on compliance issues, and how to leverage new technologies and insights from recent security testing cycles to make workplace apps.
- Actionable Reporting for Stakeholders: Security testing findings become valuable to the company only when presented in a manner that matters to the business. Writing reports is necessary to turn complicated results into strategic insights that are in line with business goals. The reports should include a summary of the identified risks, together with explanations of how they affect the business and suggestions for how to fix them.
The C-suite uses risk-based information about vulnerabilities to make strategic resource allocation decisions that minimize risks while maximizing return on investment (ROI) because they understand the business significance of these risks. - Establishing Feedback Loops: Maintaining the security of business software is a continuous process. The insights obtained from security testing should guide future design choices, coding best practices, and testing methods. The iterative feedback loop, along with continual monitoring, makes sure that the security posture is always getting better and can quickly adapt to new and emerging threats.
SAST vs DAST vs IAST
| Feature | SAST | DAST | IAST |
|---|---|---|---|
| When Used | Pre-runtime (code phase) | Runtime (test/staging) | Runtime with code instrumentation |
| Access Needs | Source code | Running app | Code + runtime |
| Finds | Code bugs, logic flaws | Runtime issues (e.g. XSS, SQLi) | Deeper, contextual vulnerabilities |
| False Positives | Medium to high | High | Low |
| Setup | Easy to integrate in CI/CD | Needs test env | Complex (requires sensors) |
| Best For | Early dev/code reviews | Pre-prod validation | Deep QA with runtime analysis |
| Tools | SonarQube, Veracode | ZAP, Burp Suite | Contrast, Seeker |
Achieving Compliance and Building Trust
Robust security testing isn't just about finding and mitigating risks right away. It is essential for meeting several industry and regulatory requirements. Following these regulations will make your business software safer and help you avoid expensive fines, legal problems, and damage to your reputation, while also building trust with customers and stakeholders.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): It is necessary to meet several industry and regulatory criteria. Following these regulations will protect your business software and help you avoid costly penalties, legal issues, and damage to your reputation, ensuring compliance while safeguarding user privacy.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): PCI DSS applies to any software that stores credit or debit card information. To comply with PCI DSS, you need to protect your business software from SQL injections, weak authentication, and network vulnerabilities by using firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems.
- ISO/IEC 27001: ISO 27001 is all about setting up, running, and keeping up an Information Security Management System (ISMS). You need to have systems for continuous vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and compliance audits, as these support ISO’s controls for risk management, incident response, and data protection.
Best Practices for Securing Enterprise Software
With legions of users dealing with all kinds of data, keeping enterprise application security should always be a priority. To do that, you need to know the best ways to make security testing a regular activity. You can keep your business software safe in the long run by using the following security testing practices.
- Performing Penetration Testing Regularly: There's no doubt that enterprise apps are complicated, with a lot of concurrent users. Taking that into account, it's a good idea to undertake pen testing regularly to uncover holes that hackers could use to attack you in the real world.
One thing that makes enterprise-grade penetration testing different is that testers have to look at more than just the technological flaws. They also have to think about how these flaws could affect critical business activities. - Implementing Artificial Intelligence for Adaptive Security: AI is great at seeing trends and signals of problems that aren't obvious. Machine learning models can also mimic the behavior of large-scale attacks, which can assist in discovering vulnerabilities that traditional testing might overlook.
Enterprise software can stay ahead of new attack methods by using both of these technologies together instead of waiting until damage has been done. - Prioritizing Compliance-Driven Security Testing: Compliance is mandatory to function in specific geographies, but that isn’t the only reason why companies should follow the regulatory norms. Meeting compliances mean that you’re securing your enterprise software. You don’t have to treat compliance as a separate activity but as an integrated layer of security testing. Mapping test cases directly to compliance requirements ensures continuous readiness for audits while simultaneously strengthening overall security.
- Building Security Awareness Across Teams: Even the best security testing tools can't make up for mistakes made by people if they don't know what the best practices are. So, it's essential to give developers, testers, and stakeholders ongoing training on secure coding practices and how to prevent attacks.
ROI of Security Testing
In an organization, every decision undergoes rigorous levels, ensuring that it brings value to the company as a whole. The strongest case for security testing is that it can save you money. It's clear that stopping a data breach costs less than dealing with one.
As mentioned above, the average cost of a data breach is $4.45 million globally and $10.2 million in the USA. An investment of $10,000 in regular vulnerability assessments can prevent a $4.45 million breach, yielding an ROI of over 44,000%. And if you’re in the USA, the ROI can be over 100,000%. This showcases that preventing a single breach can effectively cover the cost of years of security assessments.
Beyond direct cost avoidance, proactive security can:
- Build customer trust, as 87% of consumers indicate they would stop doing business with a company if they distrust its handling of sensitive data.
- Attract investors, as they consider cybersecurity and privacy among the primary factors in their investment decisions.
With secure enterprise software, you can witness sustained customer loyalty, a significant competitive advantage, and ultimately, increased revenue.
Conclusion
Securing an enterprise application is a mandatory action that protects confidential data while generating trust in the app. Now, you understand the complete journey of security assurance and security essentials for enterprise software that will help you create a security ecosystem that ensures vulnerabilities are not only found but also prevented, monitored, and remediated systematically.
But the security landscape is highly dynamic with emerging threats such as AI-powered cyberattacks, supply chain compromises, and cloud-native vulnerabilities. As an organization, you need to think beyond present defenses.
Automation, AI-driven anomaly detection, and continuous testing pipelines that change in real time are the keys to the future of enterprise software security. These will make sure that your security approach is always up to date. Businesses that implement these practices early will witness minimal risks while gaining a competitive advantage.
With that said, getting to a high level of security maturity takes more than just technologies. It also takes specialized knowledge, a strict procedure, experience, and frameworks that have been tested in the market. Most in-house teams are good at development, but they struggle to keep pace with the speed of evolving threats. When you work with professionals for security testing services, you get structured methods, cutting-edge tools, best practices, and experienced testers who can find and stop risks before they become a problem.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Has experience with enterprise-scale systems.
- Understands compliance frameworks relevant to your industry.
- Uses a mix of manual and automated testing.
- Provides actionable remediation guidance, not just raw scan results
Share This Article:







