QA Trends Report 2026
Published: December 22, 2025 | Last Updated: December 30, 2025
1. Executive Summary
Software is now a big part of everything we do, and companies are working harder than ever to make sure their apps and systems work well, stay safe, and move fast. This report explains the biggest changes happening in software testing and why they matter to leaders, teams, and anyone building digital products.
Why the Testing Market is Growing
- Businesses release new features more often
- More cyber threats require stronger validation
- Strict rules about privacy and safety must be followed
The AI Impact
- Many companies now use AI to find bugs faster
- AI creates tests automatically
- Testing time shortened from days to just a few hours
Regional Strengths
| Region | Focus Area |
| North America | Innovation and AI adoption |
| Europe | Safety and compliance |
| Asia-Pacific | Fastest growth due to large tech workforce |
Industries With Highest Testing Needs
| Industry | Why They Test More |
| Bank & Finance | Money and security risks |
| Telecom | Network outage prevention |
| Healthcare | Patient safety |
| Automotive & Manufacturing | Real-world safety impact |
QA Trends 2026 at a Glance: The global software testing market is projected to grow from $55.8B (2024) to $112.5B (2034) at 7.2% CAGR. Key trends include AI-first quality engineering (77.7% adoption), shift-left/right convergence, QAOps integration, and multi-framework automation (74.6% of teams using 2+ frameworks).
| 💡 Key Insight: 2026 is a big year for smarter, faster, and safer testing. Companies that invest in good testing will release better products, protect users, and stay ahead in a world where technology keeps changing. |
2. Introduction
To create this report, we studied many market reports, research papers, expert articles, and real data from software teams around the world. We also looked at global trends in technology, security, and regulations to understand why testing is becoming more important every year.
Our goal is to keep things simple, clear, and useful so both technical and non-technical readers can understand what is happening in the industry.
Today's software world moves fast.
Companies push updates many times a day, not just once every few months. Cyberattacks are growing. AI tools are becoming common. Many industries must follow strict laws to keep user data safe.
All these changes affect how teams test their software. Testing can no longer be slow, manual, or something done at the end. It has to be continuous, smart, and supported by the right tools.
This report gives readers a clear view of what is happening now, what is coming next, and what actions will help them stay ahead. It sets the stage for understanding the trends, numbers, and insights in the chapters that follow.
3. Market Overview
3.1 Market Size & Growth
Definition: Software Testing Market: The global industry encompassing all services, tools, and platforms used to validate software quality, including functional testing, automation, security testing, and performance testing.
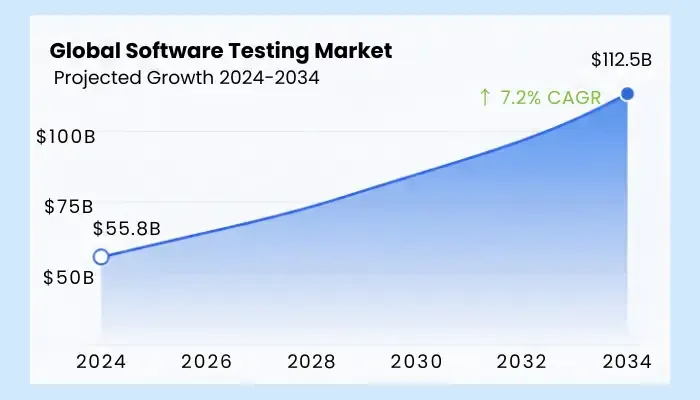
- Global software testing market: USD 55.8B (2024) → USD 112.5B (2034); 7.2% CAGR
- Outsourced testing: USD 39.93B (2026) → USD 101.48B (2035); 10.8% CAGR
- Automation testing tools/services: USD 28.1B (2023) → USD 55.2B (2028); 14.5% CAGR
- QA services (broad lens): USD 50.7B (2025) → USD 107.2B (2032); 11.3% CAGR
What This Means
The software testing market is more than doubling this decade. Automation-led segments are growing faster, signaling a shift from manual testing to AI-driven, CI/CD-native models.
2026 marks a key transition point. From a USD 60B base in 2025, spending will rise across the board, with automation, cloud testing, and managed service models leading. The outsourced segment alone is on pace to surpass USD 100B by 2035.
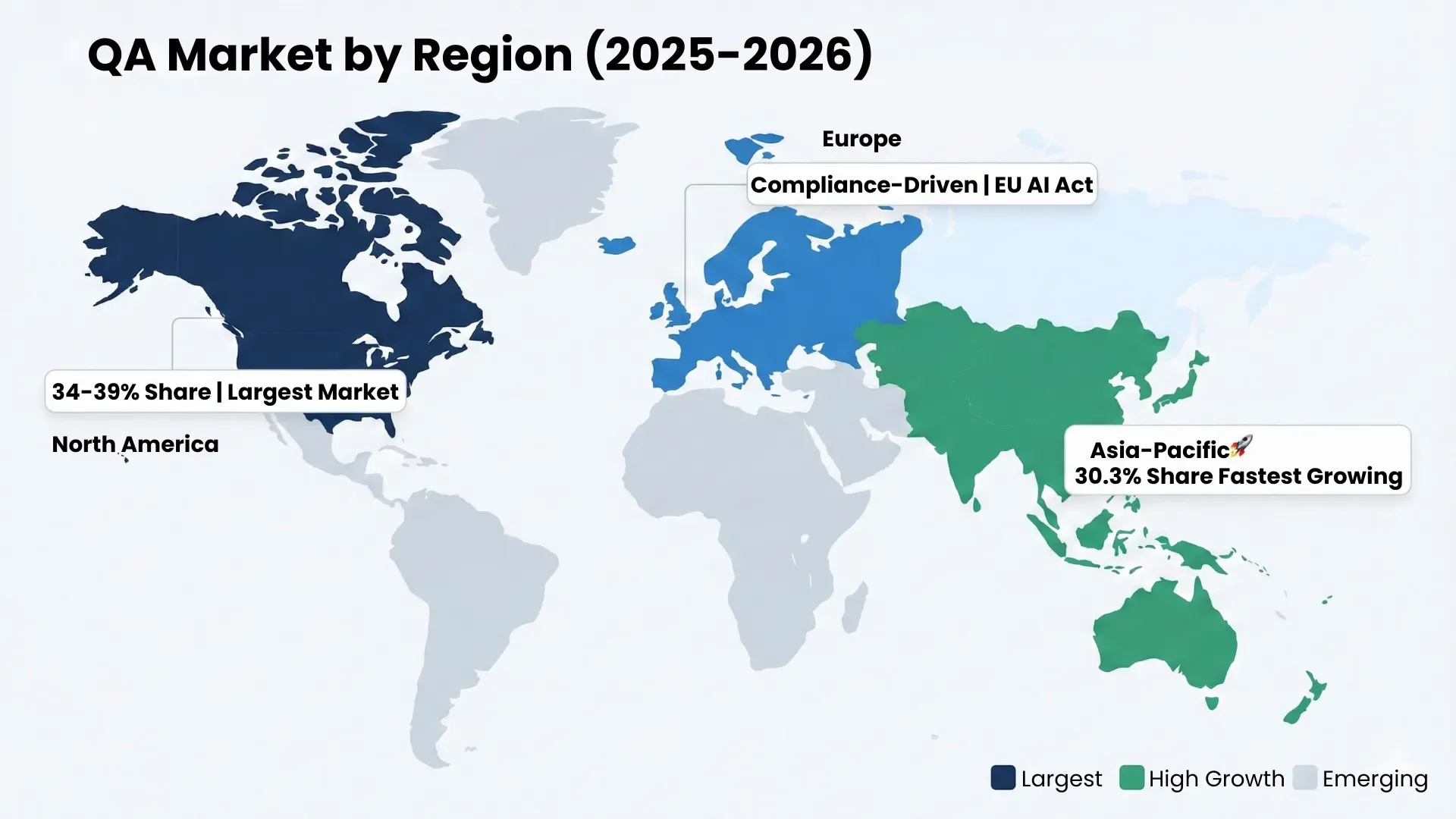
Regional Overview
North America remains the largest market, but Asia-Pacific is growing the fastest, driven by skilled talent pools and national digital programs.
Growth Drivers
- DevOps and CI/CD adoption: Faster release cycles and continuous testing make automation essential.
- AI-powered testing: Enterprises use AI for test generation, self-healing scripts, and predictive defect detection, boosting speed and coverage.
- Regulatory and security pressure: Sectors like BFSI, healthcare, and automotive demand rigorous functional and non-functional testing.
- Mobile-first, cloud-first delivery: Mobile testing leads many QA portfolios; cloud-based platforms and Testing-as-a-Service (TaaS) expand scale and flexibility.
Software testing is scaling alongside DevOps and AI.
The core market stands at USD 55.8B in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 112.5B by 2034 (7.2% CAGR).
Automation is growing even faster, from USD 28.1B in 2023 to USD 55.2B by 2028 (14.5% CAGR).
Outsourced testing is set to more than double, reaching USD 101.5B by 2035 (10.8% CAGR).
Rising demand is driven by regulated industries, mobile-first development, and cloud-native delivery models.
3.2 Market Segmentation
The QA and software testing market is expanding steadily, but spending clusters around specific services, technologies, and industries. Below is a breakdown based on 2025–2032 data.
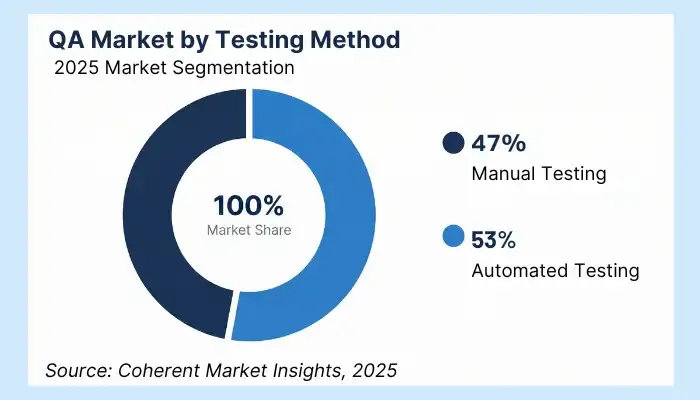
By Service Type
Manual testing remains the largest segment, holding ~47% of the global market in 2025.
Its value lies in catching usability and UI issues that automation still misses.
Automation is growing fast, fueled by cloud adoption, DevOps pipelines, and AI-based tools.
Testing-as-a-Service (TaaS) is also expanding, offering scalability and strong alignment with cloud-first delivery.
Service Type 2025 Share (Est.) Notes Manual Testing ~47% Best for UI/usability; widely adopted early Automated Testing Growing Driven by CI/CD and AI integration TaaS Expanding Cost-efficient and cloud-scalable 💡 Key Insight: Despite automation gains, complex UX testing still needs human review. Teams should plan for hybrid QA, blending people and platforms. By Testing Type
Functional testing dominates, ensuring core features work as intended.
In 2025, it held the largest market share.
Non-functional testing, covering performance, security, and compliance, is growing, especially in regulated industries.
Testing Type Notes Functional (unit, system, UAT) Largest share; vital for feature validation and UX Non-functional (perf, security) Growing due to compliance, security, and reliability 💡 Key Insight: Functional testing remains foundational. But as risk and compliance pressures rise, non-functional testing is no longer optional, especially in BFSI and healthcare. By Deployment Model
Cloud-based testing is outpacing on-prem deployments.
It supports scalability, integrates well with DevOps, and offers cost advantages.Deployment Trend Cloud-based Fastest growth; suits DevOps + distributed teams On-premises Declining; used for legacy or secure workloads 💡Key Insight: Cloud testing is faster and more cost-effective. Delaying cloud adoption risks slower releases and rising costs. By Interface
Mobile is the dominant and fastest-growing interface, reflecting mobile-first strategies.
Web remains stable. Desktop continues to decline. API and cloud interfaces are rising with microservices.Interface Trend Mobile Largest + fastest-growing Web Stable demand Desktop Declining API/Cloud Rising with microservices Key Insight: Testing must span a range of devices and environments. Skimping on mobile coverage risks poor UX and customer churn. By Buyer Size
Large enterprises drive most QA spending. They face complex systems, strict compliance, and higher stakes.Buyer Size Notes Large enterprise Largest segment: high-complexity needs SMB Growing slowly; cost-conscious buyers Key Insight: Enterprises demand end-to-end QA. SMBs prioritize flexible models or outsourcing to manage budgets. By Industry Vertical
BFSI is the top-spending vertical due to compliance, security, and risk.
Telecom, IT, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing follow. The public and automotive sectors also show growth, though more slowly.Industry Notes BFSI Largest, driven by compliance + risk Telecom & IT Growing with 5G and cloud adoption Healthcare + Life Sciences Regulation-heavy; data protection is critical Retail + eCommerce Needs reliability and scalability Manufacturing Growth tied to IoT adoption Public Sector Slower; compliance-led Automotive Growing with autonomous tech Key Insight: Most QA spend comes from industries where failure costs are high, whether in money, data, or safety.
3.3 Regional View
Demand for QA and software testing continues to rise globally, but drivers vary by region. North America leads in spend. Asia-Pacific grows fastest. India and Eastern Europe remain key outsourcing hubs. Across regions, BFSI and telecom drive the most demand.
- North America - Largest Market
North America is the top regional market for QA services, accounting for 34–39% of global spending. It has a 34.5% share, with Asia-Pacific closing the gap.
Buyers prioritize:- Security and compliance
- Automation for faster releases
- Cloud-based testing platforms
BFSI and healthcare maintain steady QA budgets due to regulatory pressure. Fast release cycles and digital transformation also fuel demand.
North American buyers expect mature, scalable QA solutions. It remains the most lucrative region for high-end services and tools.
- Asia-Pacific - Fastest Growing
Asia-Pacific holds 30.3% of the global share (2025) and is the fastest-growing region. Growth is powered by:
Deep engineering talent- Strong outsourcing ecosystems
- Rapid cloud adoption
- Mobile-first digital products
India remains the biggest contributor. China and Southeast Asia are scaling quickly, helped by local cloud platforms and booming fintech sectors.
Asia-Pacific offers the best opportunities for delivery scale. Enterprises are increasing QA spend as digital becomes core to every sector.
- India & Eastern Europe — Leading Outsourcing Hubs
These two regions remain the top global outsourcing centers. Growth is fueled by:- Skilled, cost-effective talent
- Mature QA ecosystems
- Hybrid delivery models (onshore + offshore)
Popular outsourced services include: - Functional testing
- Mobile testing
- Testing-as-a-Service (TaaS)
India also benefits from rising BFSI and telecom investment in mobile apps and transformation programs.
For scaling QA capacity, India and Eastern Europe offer strong cost-to-skill advantages and delivery flexibility.
- Europe — Compliance-Driven Growth
Europe sees steady QA spend, led by:- Banking and financial services
- Healthcare and life sciences
- Automotive and mobility software
New regulations like the EU AI Act (2025–26) are raising demand for validation and testing of AI systems—especially in finance and healthcare.
If your QA offering includes compliance or cybersecurity, Europe is a high-value market.
- BFSI and Telecom — Consistent Leaders Across Regions
Two verticals drive the bulk of QA spend in nearly every region:- Banking, Financial Services and Insurance (BFSI): Compliance, risk management, and transaction security keep budgets high
- Telecom: Digital services, 5G upgrades, and performance requirements sustain investment
Other notable sectors: - Retail / eCommerce
- Healthcare
- Public Sector
- Transportation & Logistics
QA providers targeting BFSI and telecom will find steady, cross-regional demand. These sectors invest in both volume and depth.
- 2026 Highlights At a Glance
| Region | Position | Strengths |
| North America | Largest | Tech maturity, security, and compliance |
| Asia-Pacific | Fastest growing | Talent, outsourcing, mobile-first markets |
| India & Eastern Europe | Leading hubs | Cost-efficiency, skilled QA delivery |
| Europe | Stable growth | Regulatory testing, especially in BFSI + Auto |
Key Takeaways
|
3.4 Six Forces Changing QA
QA is now an evolving process shaped by how software is built and delivered. These six forces are reshaping QA in 2026. Below, we break down each shift and what QA teams should do to keep pace.
- Agile, DevOps & CI/CD
Engineering teams ship faster. That compresses cycles and pushes testing into CI/CD pipelines.
As a result, automation testing is growing rapidly, from USD 28.1B in 2023 to USD 55.2B by 2028 at a 14.5% CAGR.
Analysts consistently name CI/CD as a top growth driver for automation tools and QA services.
Treat tests as code. Automate key user journeys and run suites on every merge. Track pipeline health as a core QA KPI. - Mobile-First Business Models
Enterprises are designing for mobile-first users, and testing spend is following suit.
In 2025, mobile holds the largest share among endpoint interfaces, with growth continuing through 2026.
QA budgets increasingly cover real-device testing, UX flow validation, and cross-platform reliability.
Focus on mobile performance, security, and end-to-end journeys. Build real-device coverage before expanding emulator use. - Digital Transformation
Modernization efforts continue to fund QA growth.
Reports cite digital transformation, Agile/DevOps, and CI/CD as top QA demand drivers. But to maintain momentum.
QA must show business value like faster releases, fewer defects, and better user experience.
Tie QA metrics to business KPIs, conversion, uptime, and NPS. Use data to defend the budget and focus resources on what moves the needle. - AI in QA
AI is reshaping how tests are created, maintained, and optimized. Analysts estimate that over 70% of enterprises will adopt AI for test authoring and maintenance.
Over 60% of QA pipelines are already automation-driven, and generative AI is accelerating this shift in 2026.
Start with AI-assisted test generation and self-healing locators.
Add safeguards, like test data governance and human review, to avoid automation debt. - Compliance & Security Pressure
Regulated sectors, especially BFSI and healthcare, face rising compliance scrutiny.
Reports call out regulation as a core QA market driver.
Banking studies highlight stricter governance, increased oversight, and zero tolerance for defects in production.
Integrate compliance and security tests early (shift-left) and post-deployment (shift-right). Build traceability from requirements to release artifacts. - Time-to-Market Pressure
Teams face constant pressure to deliver faster without increasing risk.
Vendors and analysts highlight QA’s role in reducing cycle time and time-to-market. But long feedback loops still slow delivery.
Research shows that slow test execution and poor test impact analysis are major blockers.
Shorten feedback loops.
Run incremental, risk-based test suites on every change.
Promote fixes within hours, not days.
3.5 Market Challenges
The QA and software-testing market is expanding quickly, but key barriers remain.
In 2026, the top three challenges are:
- Integrating testing with legacy environments
- Managing data security risks in outsourcing
- Addressing the shortage of skilled QA talent
These issues slow delivery, raise risk, and force teams to invest more in training, tools, and partnerships.
- Integrating With Legacy Environments
Many enterprises still depend on legacy systems that resist automation and don’t align with modern DevOps workflows.
These environments often require manual testing, custom integrations, or outdated tools, slowing releases and driving up QA costs.
A report showed manual testing held ~61% of the market, largely due to its ability to handle complex UI and edge cases that automation misses.
Functionally rich systems also require deep validation, extending test cycles, and limiting automation maturity.
These constraints stall modernization.
Teams must balance continuity with innovation, often needing to re-platform core systems before scaling automation or AI-based testing.
- Data-Security Risk in Outsourcing
Outsourced QA helps teams scale and reduce costs, but it also introduces data risks.
Sharing access to test databases, systems, and user data raises concerns,
especially in regulated industries like finance and healthcare.
Regulations like the EU AI Act and evolving financial compliance standards are expanding testing scope in the future.
Firms must prove system safety, privacy, and responsible AI behavior.
If outsourced partners lack strong controls, this introduces legal and operational risk.
Geopolitical tensions also affect delivery, raising costs and creating supply chain uncertainty, including tariffs on QA tools.
Buyers now prioritize partners with strong security certifications, transparent processes, and a proven ability to test regulated systems safely. Selection criteria go beyond price and scale; compliance strength and data handling are essential.
- Shortage of Skilled Talent
Despite gains in automation, demand for skilled testers continues to outpace supply.
The global shortage affects both in-house teams and service providers,
especially in areas like test automation, performance testing, and security QA.
Enterprises with large, complex IT stacks and strict compliance needs drive most QA spend.
This creates fierce competition for experienced talent,
especially those with deep domain knowledge and the ability to validate critical business workflows.
To cope, many teams increase training budgets or adopt AI- and low-code tools to offset skill gaps.
Still, tasks like test design, risk assessment, and compliance interpretation require human expertise.
Talent remains a core constraint in scaling QA in 2026.
3.6 Market Structure
This section outlines who’s leading the QA market in 2026,
how they compete, and where they operate.
It draws from the most recent market data and analyst commentary.
- Categories & Business Models
Provider Categories- Global Leaders (Full-Stack Services): Large integrators offering end-to-end QA and quality engineering across regions and industries.
- Specialist Challengers (Pure-Play QA): Focused firms with deep expertise in performance, security, or mobile testing.
- Tool-Led Platforms: Vendors driving AI, automation, and cloud-based test orchestration; shifting the services mix.
- Regional Specialists: Strong players in local or nearshore delivery corridors.
Business Models - Classic time-and-materials (T&M) and fixed-price models remain common.
- Managed QA / Testing-as-a-Service (TaaS) is growing fastest, offering elastic capacity and outcome-based SLAs.
- Cloud-based delivery is now the dominant deployment model for QA services.
Top 5 Leaders & Combined Share
The top five providers hold ~26% of the global market (2024 base):- Accenture (11.5%), market leader
- Cognizant
- IBM
- TCS
- NTT DATA
How they compete:
- Cognizant: AI + analytics for cloud-based continuous testing
- IBM: Predictive analytics and enterprise-scale automation
- TCS: QA at scale with integrated DevOps and cloud infrastructure
- NTT DATA: Fast, flexible delivery with cloud automation
These firms offer global reach, strong regulatory assurance, and platform integration—essential for BFSI, healthcare, and public sector buyers.
- Specialist Challengers (Pure-Play QA)
These firms focus on niche expertise and fast execution in Agile/DevOps environments.
Where they win:- High-touch labs for performance, mobile, and security
- Cost-effective regression testing
- Domain-led QA for BFSI, telecom, and regulated industries
- Regional Landscape
Market Overview- North America: Largest by revenue
- Asia-Pacific: Fastest growth
- India & Eastern Europe: Top outsourcing hubs
- China, Poland, Romania, Vietnam: Rapidly scaling delivery centers
- How Providers Compete in 2026
What to Look for:- Automation + AI Maturity: Over 60% of QA pipelines are automation-driven; 70%+ of enterprises use AI for test creation. But poor architecture creates automation debt, so governance is critical.
- Cloud-Native Delivery: End-to-end CI/CD integration is now table stakes; cloud-first models dominate.
- Compliance Strength: Regulated sectors demand traceability, data governance, and secure SDLC workflows.
- Flexible Service Models: TaaS and outcome-SLAs attract buyers seeking scalability and speed.
- What This Means for Buyers in 2026
- Regulated buyers (e.g., banks, healthcare): Choose partners with mature compliance controls and traceability across the SDLC.
- Speed- and elasticity-focused teams: Prioritize providers offering TaaS with deep CI/CD and cloud-native delivery.
- Cost-sensitive/mobile-first teams: Consider specialist challengers with offshore scale and device testing labs.
- AI adopters: Ask for governed AI usage, validated models, test data policies, and human oversight.
3.7 Pricing & Budget Trends
What buyers are spending on, and why it’s shifting
QA budgets continue shifting toward automation, AI-assisted tools, and cloud-based infrastructure.
Manual testing still receives funding, but mostly for high-risk, UI-heavy, or regulated use cases.
The focus is now on platforms and processes that reduce rework and accelerate delivery.
- Automation Lowers Cost per Test Hour
Over 60% of enterprise QA pipelines are automated.
GenAI adoption for test creation and maintenance now exceeds 70%, driving wider test coverage at lower marginal cost.
Both vendors and enterprises report cost savings from AI-driven automation, cloud testing, and low-code frameworks.
While upfront investment remains high, especially for SMEs, long-term operating costs drop.- Shift spend from manual regression to scalable automation and test data management
- Retain manual budget for complex UX, accessibility, and high-risk tests
- AI Raises Value per Tester
AI helps testers generate more cases, prioritize risks, and increase coverage, raising productivity and reducing design time.
Teams using GenAI for test authoring alongside telemetry-driven prioritization see faster cycles and fewer escaped defects. This allows flat headcount while expanding coverage.- Invest in AI-assisted test authoring, maintenance, and impact analysis
- Fund skills in prompting, data governance, and model validation to avoid automation debt
- Cloud Testing Spend Keeps Growing
Cloud is now the default delivery mode for QA, offering scalability, faster feedback, and seamless CI/CD integration.
Studies highlight the cloud’s speed and cost-efficiency. Containerization also boosts reuse and accelerates updates.- Increase spend on cloud environments, device farms, and usage-based test runs
- Budget for observability and orchestration to fully benefit from cloud scale
- Sourcing & TaaS: Scale with Caution
Testing-as-a-Service (TaaS) holds the largest service share, favored for its elasticity and fit with Agile/DevOps.
Outsourced QA grows at ~10.8% CAGR (2026–2035).
North America remains the biggest buyer, while APAC grows fastest, driven by cost efficiency and global coverage.
But outsourcing isn’t risk-free. Data security and communication gaps can add hidden costs through rework or compliance failure.- Account for controls, documentation, and risk mitigation in outsourcing budgets
- Prioritize vendors with governance maturity, not just price or speed
3.8 Buyer Behavior
Buyers are more selective, outcome-driven, and risk-aware. They expect QA partners to accelerate delivery, support compliance, reduce failures, and deliver measurable ROI.
Vendors with automation depth, cross-platform coverage, and transparent pricing now win more deals.
What Matters Most to Buyers
- Compliance & Security Expertise
Compliance is a top priority in regulated sectors. In BFSI, new rules like Consumer Duty regulations affect ~36% of firms, increasing demand for compliance-ready QA services.
Autonomous-vehicle testing is also expanding due to standards like NATM, fueling a new category of validated safety and compliance testing.
Buyers expect QA partners to:- Understand domain-specific standards (AML, HIPAA, PSD2, PCI-DSS)
- Provide audit-ready artifacts
- Ensure secure data handling
This demand is strongest in North America and Europe.
- Time-to-Market Acceleration
Speed is a critical buying factor, especially in BFSI and retail, where competition and customer expectations drive rapid delivery.
QA vendors that support Agile, CI/CD, and cloud-based continuous testing gain traction. The rise in mobile app testing reinforces this need, where fast cycles and reliable UX are non-negotiable. - Automation Maturity
By 2025–2026, 80% of software teams will adopt AI-driven testing. Buyers now screen vendors for automation skill, including:- Predictive analytics
- Self-healing scripts
- Stable automation frameworks
They often request:- Automation maturity scorecards
- Test coverage dashboards
- ROI impact metrics
- Cross-Platform Coverage
With mobile at the center of digital strategy, buyers demand seamless QA across web, mobile, API, desktop, and embedded systems.
High-growth verticals like BFSI, retail, and healthcare require secure, reliable testing across diverse device and system types, especially in APAC and North America.
QA partners must offer:- Full endpoint support
- Cloud + API + microservices testing
- Real-device labs
- Pricing Transparency
Budget pressures from compliance, tool costs, and global trade uncertainty push buyers toward transparent, modular pricing.
QA vendors must:- Present detailed effort models
- Offer modular pricing for services (e.g., automation, performance, compliance)
- Prove short ROI cycles
TaaS models, with SaaS-like billing, reinforce this expectation.
How Buyers Choose Partners
| Decision Factor | Buyer Expectation (2026) |
| Compliance Capability | Audit-ready, industry-specific frameworks |
| Security Maturity | Certifications and secure workflows |
| Speed | CI/CD, continuous testing |
| Automation | AI-native, self-healing test suites |
| Cross-Platform | Web, mobile, API, embedded coverage |
| Delivery Model | Onshore/nearshore/offshore mix |
| Pricing | Transparent, outcome-based |
| Domain Experience | Proven use cases by industry |
Industry Spotlight — BFSI
BFSI is the most mature QA-buying segment, driven by:
- Regulatory intensity
- Complex IT stacks
- Security and privacy demands
- High cost of system failure
~36% of BFSI firms face new regulatory pressure, increasing demand for testing in:
- API security
- Compliance validation
- Regression and functional QA
- High-load performance
- Mobile app security
BFSI buyers favor:
- Regional regulatory fluency
- Full-stack test automation
- Microservices testing capability
They also push TaaS, hybrid delivery models, and cloud-native QA platforms.
What This Means for Providers
Buyers now expect QA firms to deliver business value, not just defect counts. To stay competitive in the future, providers must:
Invest in compliance frameworks tailored to BFSI, healthcare, and telecom
- Build AI-native automation with traceability
- Offer labs with mobile, web, and API coverage
- Present transparent pricing and measurable outcomes
High-performing QA partners bring: - AI-based test optimization
- Continuous testing at scale
- Flexible delivery and talent models
- Industry-specific consulting
These firms win more multi-year, strategic engagements.
💡 Key Takeaways
|
Buyers in 2026 expect partners who help them ship faster, stay compliant, and reduce exposure. Vendors who prove automation maturity and compliance expertise will lead the market.
4. Macro Drivers
4.1 AI & GenAI Acceleration
Definition: AI & GenAI Acceleration refers to the rapid integration of artificial intelligence and generative AI technologies across the software development lifecycle, fundamentally changing how software is built, tested, and released.
AI is reshaping how software is built, tested, and released. Teams using GenAI across the product lifecycle ship faster, find issues earlier, and improve quality more consistently.
AI now does far more than write code. It can:
- Generate and maintain test cases
- Automate test execution
- Detect and prioritize defects
- Repair broken test suites
- Orchestrate entire QA workflows
This shift has raised expectations around speed, coverage, and reliability.
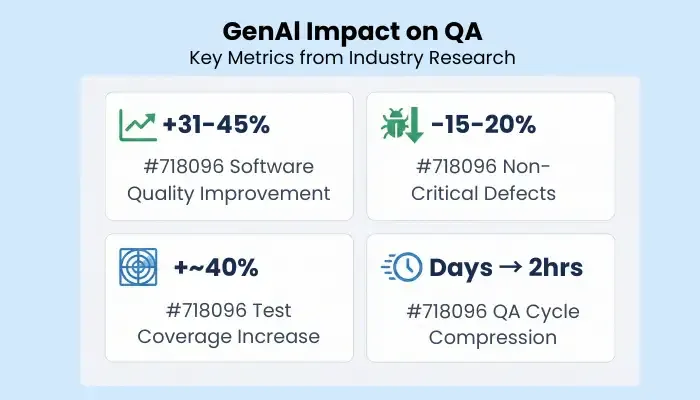
GenAI across the development lifecycle improves software quality by 31–45% and reduces non-critical defects by 15–20%, strong evidence that AI will remain core to QA strategies.
How AI Is Transforming QA
- AI-Native Software = More Testing Demand
As GenAI is embedded into planning, design, and development, teams produce more code faster.
Many developers now delegate 20–50% of coding tasks to AI copilots. That code still needs validation, increasing demand for faster, deeper testing cycles. - GenAI-Driven Test Creation
AI can now generate functional, mobile, UI, and API tests at scale.
Reports say ~40% increase in test coverage within one month using GenAI. Teams can:- Auto-generate tests from requirements
- Convert user stories to automation flows
- Update broken tests automatically
- Predict failure points before execution
This makes QA more strategic and less of a bottleneck.
- AI as the QA Orchestrator
AI is moving from assistant to owner of the QA flow.
Modern AI tools now:- Select tests based on risk
- Execute them autonomously
- Prioritize defects
- Recommend fixes
- Agent-Based Frameworks
Agent-based QA systems are gaining traction. These agents can:- Read requirements
- Create and run tests
- Diagnose issues
- Suggest and explain fixes
Experts label this the “next wave” of engineering automation—closing the loop between build → test → fix → deploy with minimal human input.
Impact on QA Roles
AI is changing what QA professionals do. Testers are moving from script writers to QA strategists.
New roles emerging:
- AI QA Strategist
- Prompt QA Architect
- Automation Workflow Designer
The value now lies in oversight, orchestration, and domain knowledge, not repetitive scripting.
Market Signals
| Signal | Evidence |
| Faster QA cycles | Zentester compresses days → ~2 hours |
| Higher software quality | +31–45% improvement with GenAI |
| Fewer non-critical defects | ↓ 15–20% defects with AI |
| Broader test coverage | +~40% within 1 month (AskUI) |
| Evolving QA skills | Strategy and prompt design are now core skills |
What Buyers Want in 2026
Buyers now seek QA partners with:
- AI-first automation frameworks
- Self-healing test infrastructure
- Multi-agent orchestration tools
- Large-scale test generation capability
- Explainable reporting and traceability
Buyers are paying for faster QA cycles, not cheaper testing hours
💡 Key Takeaways AI is the fastest-moving force in QA today. Organizations embedding GenAI into QA will:
|
Those who wait risk slower releases, higher defect costs, and deeper talent shortages.
4.2 Regulatory + Compliance Pressure
Regulation is tightening fast. It’s expanding beyond traditional data privacy into AI governance and cybersecurity. As a result, QA has become a compliance and risk-management function, not just a quality checkpoint.
1. AI Governance Becomes Mandatory
The EU AI Act is the most significant regulatory development. It places strict obligations on “high-risk” AI systems, including:
- Record-keeping and audit logs
- Conformity assessments
- Risk controls and human oversight
- Transparency and ongoing monitoring
Article 60 requires that providers enable full traceability by logging AI behavior and offering technical documentation to reconstruct decisions.
What this means for QA:
- Testing must prove compliance, not just correctness
- Traceability becomes a non-negotiable requirement
- Tools must support audit evidence and documentation
QA teams must now validate:
- Data quality and provenance
- Model performance and drift
- Logging, auditability, and explainability
- User transparency mechanisms
This expands QA scope far beyond functional validation.
2. Data Privacy Still Drives Testing
Data protection remains a global driver of QA investment. Teams must validate systems against stricter rules on consent, privacy, and AI-generated content.
Analysts cite rising regulatory focus on:
- Deepfakes and voice/visual impersonation
- Cross-border data flows
- AI-generated content oversight
QA teams are expected to verify:
- Data minimization
- Encryption and consent flows
- Identity verification
- Cross-border data handling
This demands close collaboration between QA, security, and legal teams.
3. Cybersecurity
Cyber threats now mix AI- and human-led attack vectors. A 2026 cybersecurity report marks this as the beginning of the “security-first delivery” era.
QA is expected to include:
- Early-stage penetration testing
- Secure code reviews
- Zero-trust design validation
- Identity, access, and API security testing
These are no longer optional—they’re baseline expectations.
4. Sector Impact
| Sector | QA Requirements |
| BFSI | Provenance, logging, and third-party oversight for AI classification |
| Healthcare | Patient-data safety and medical-AI validation |
| Government | Algorithmic transparency and data localization |
All three sectors now demand compliance-first QA.
5. Regional View
| Region | Pressure Level | Key Drivers |
| Europe | Very High | EU AI Act, GDPR |
| North America | High | Cyber and data-privacy enforcement |
| APAC | Medium–High | National data-protection laws |
| Middle East | Medium | Financial and cybersecurity rules |
Europe leads in regulatory maturity. North America is quickly increasing enforcement around AI, security, and data privacy.
6. How Regulation Affects QA Volume & Tooling
Increased Scope:
- More compliance-driven test cases
- Higher demand for traceability and audit logs
- Model explainability testing
- Continuous monitoring and change tracking
- Security and data-flow validations
Tooling Implications:
Teams now need platforms that provide:
- Traceable test execution
- Compliance dashboards
- AI model audit support
- Secure data-handling automation
- Risk-based scoring and documentation
7. Action Items for QA Leaders
- Adopt compliance-by-design: Embed traceability and controls early in the SDLC.
- Use audit-grade platforms: Select tools that support logging, evidence capture, and conformity checks.
- Expand security QA scope: Include APIs, identity management, and model-risk validation.
- Automate compliance documentation: Choose platforms that generate required artifacts automatically.
- Upskill teams: Train QA professionals in privacy, regulation, and audit-readiness.
- Partner with domain experts: Especially in BFSI, healthcare, and public sector projects.
💡 Key Takeaways
|
4.3 Cybersecurity & Pre-emptive Security-Testing Demand
Definition: Cybersecurity & Pre-emptive Security-Testing Demand refers to the shift from reactive "fix when found" approaches to proactive "anticipate, prevent, and contain" security testing, driven by evolving cyber threats and the need for continuous, integrated security validation
Cybersecurity is now one of the fastest-growing drivers of software testing. Security testing is continuous, integrated, and no longer optional. Organizations are shifting from "fix when found" to "anticipate, prevent, and contain."
Why It Matters
Cyber attackers are evolving faster than traditional testing methods. Today’s threat landscape includes:
- Multi-vector and identity-layer attacks
- AI-generated malware
- Software supply chain vulnerabilities
Report shows rising investment in security-first design, with validation embedded across infrastructure and application layers. Testing is now a core development function, not a final check.
Key Drivers & Angles
- Penetration & Vulnerability Testing Go Continuous
Modern architectures, cloud, mobile, and microservices have increased the number of entry points.
Testing is no longer annual or reactive. Instead, teams:- Automate scanning across cloud environments
- Run pen-tests aligned with release cycles
- Treat red-team simulations as standard practice
DevSecOps adoption brings security validation into every SDLC stage.
- Secure-by-Default
Security is now embedded from design through deployment.
Enterprise security playbooks emphasize:- Policy-driven enforcement
- Continuous controls
- Full application and data governance
QA now moves from testing functionality to validating trustworthiness.
What changes in practice:- Threat modeling at design
- Continuous scanning in CI/CD pipelines
- Automated compliance checks
- API & Identity Testing Take Center Stage
APIs are the backbone of modern systems and a prime target.
That’s why identity and access testing appear as a top enterprise priority, especially in zero-trust environments.
Core focus areas now include:- Authentication and session management
- Encryption and data integrity
- Least-privilege enforcement
- Cross-service access control
New Attack Surfaces
Zero-trust models eliminate implicit trust, raising the need for:
- Risk-based authentication
- Multi-step identity validation
- Privileged-access testing
Meanwhile, multi-agent AI systems create new security risks:
- Emergent behavior
- Compromised agent communication
- Coordinated misuse by malicious AI
Cost Logic
As breach costs rise, security testing becomes a cost-avoidance strategy.
Research shows organizations are modernizing pipelines to contain breach risk.
Cost comparison logic:
- Breach → High cost, operational impact
- Testing → Predictable spend, risk reduction
Industry Focus — BFSI & Healthcare
BFSI
- Classified as high risk
- Mandated identity audits
- Always-on security validation
Healthcare
- Sensitive patient data
- Remote care creates new exposure
- Medical devices increase threat surface
How QA Strategy Evolves (2025 → 2026)
| Old | New | Impact |
| Annual pen-tests | Continuous penetration testing | Proactive posture |
| Manual audits | Automated guardrails | Lower overhead |
| Perimeter defense | Zero-trust enforcement | Identity = the new edge |
| End-stage QA | Security built into SDLC | Prevention over patching |
| Reactive fixes | Threat modeling from day one | Find earlier, fix earlier |
💡 Key Takeaways
|
Must Read: Qa Trends 2025
4.4 Distributed + AI-Native Delivery Models
AI-native delivery has moved from experimentation to default practice. Organizations embedding AI throughout the product lifecycle, design, development, testing, and deployment, gain the biggest lift in quality, speed, and efficiency.
These delivery models combine distributed execution, autonomous test orchestration, and continuous QA embedded in pipelines. The result: faster releases, fewer defects, and lower cost of quality.
Why It Matters
AI-first delivery no longer stops at code generation. It shapes architecture, orchestration, and validation.
Enterprises integrating AI across the SDLC improve software development outcomes by ~30–45%, largely due to AI-powered planning, test automation, and early-stage defect prediction.
This transforms QA from reactive verification to AI-assisted prevention and self-healing correction.
Key Shifts Inside AI-Native Delivery Models
- Continuous QA Embedded in Pipelines
Testing now happens inside DevOps pipelines, not after.
Pipelines use:- AI-generated test suites
- Continuous regression execution
- Automated pass/fail gating
This reduces defect backlogs and accelerates delivery without waiting on manual QA queues.
- Autonomous + Self-Healing Regression
Regression testing, once the most labor-intensive QA function, is now automated and self-repairing.
Modern tools:- Auto-heal locators and test logic
- Replay broken tests
- Predict risk and prioritize failure points
AI tools compress multi-day QA cycles into ~2 hours, a major gain for distributed delivery models.
- Multi-Agent QA Ecosystems
AI agents now operate collaboratively, not in isolation.
Agent roles include:- UI validation
- Risk scoring
- Performance monitoring
Agents work asynchronously, enabling: - Self-service QA
- Rapid triage
- Precision execution
This value multiplies when AI spans the full delivery chain, from specification to deployment, rather than just augmenting individual steps.
Vendors are shifting from staffing models to automation depth and platform intelligence as the primary buying criteria.
Why This Is a Macro Driver
| Driver | Why It’s Macro-Level |
| AI embedded across SDLC | Impacts all lifecycle phases, not just testing |
| Bottleneck elimination | Reduces manual QA delays |
| Autonomous regression | Cuts QA cost and turnaround time |
| Multi-agent orchestration | Enables 24/7 decision-making without human triggers |
| Vendor ecosystem maturity | Enterprise-ready platforms replacing legacy test tooling |
Enterprise Implications
| Area | Shift |
| Speed | Build → test → deploy compression |
| Talent | Testers shift from execution → orchestration roles |
| Tooling | AI-native platforms become foundational infrastructure |
| Metrics | From defect counts → time saved + automation ROI |
| Risk Model | Continuous, real-time risk scoring becomes standard |
Enterprises adopting this model gain faster delivery, higher quality, and lower QA overhead. Those who don’t risk falling behind due to slower cycles and manual remediation costs.
💡 Key Takeaways Distributed + AI-native delivery is now a core macro driver of QA strategy in 2026.
|
4.5 Platform Complexity
Modern software spans more layers than ever. Products stretch across web, mobile, APIs, IoT, cloud AI workloads, and edge devices.
This interconnected surface raises the chance that one weak link breaks the experience.
As systems grow, QA must grow with them, covering not just logic, but orchestration, UI behavior, model performance, and device interactions.
Platform complexity is now one of the biggest reasons QA spend keeps rising.
Why It Matters
Most digital products aren’t single apps anymore. They’re networks of systems talking to each other:
- Mobile + web apps
- Embedded devices
- Cloud and multi-cloud platforms
- External APIs
- AI models running at the edge
Each new layer adds failure risk. And when something fails, the user notices. Teams can no longer rely on unit tests and call it done. System-level testing and real-device validation are now mandatory.
More Stacks = More QA
Think wearables, EV charging, retail POS, and connected homes. These use cases demand QA across multiple:
- Devices
- Interfaces
- Input types
- Connectivity scenarios
Because most bugs now come from:
- Device fragmentation
- Network instability
- API contract drift
Teams are shifting from fragile selectors to visual-based UI testing, since UI changes often break locator-based scripts.
Testers must now cover:
-Dynamic UIs
-Multi-form-factor workflows
-Multi-modal inputs
All in one go.
UI Fragility
Selector-based automation struggles with fast-changing front-ends. Teams are replacing it with AI-powered visual recognition, which:
- Works across frameworks
- Survives redesigns
- Handles dynamic UI states
This is especially important in mobile and IoT environments, where interfaces vary widely by device.
Multi-Device Orchestration + Edge Complexity
Today, logic doesn’t just run in the cloud; it runs on the edge, across devices and contexts.
Testing now must answer:
- Does logic behave differently at the edge?
- Do mobile + IoT devices handle concurrency well?
- Do AI models react correctly to local signals?
Modern platforms are more distributed and AI-enhanced, demanding deeper QA coverage across digital endpoints.
As systems get more connected, small bugs cause big damage. Passing unit tests no longer guarantees production stability. Teams must simulate full chains instead of individual steps.
What Leading Teams Are Doing
Top QA orgs now:
- Use visual-recognition testing for UI stability
- Expand integration + end-to-end testing
- Invest in real-device test labs
- Add resiliency checks + fallback paths
- Build AI-augmented scenario testing
- Validate full workflows—not just features
💡 Key Takeaways
|
4.6 QA Workforce + Skill Reshaping
QA is no longer about running checklists. It’s about managing automation, guiding AI agents, and aligning quality with business risk.
The job has changed because:
- AI handles repetitive tasks
- Automation scales faster than headcount
- Compliance and domain risk matter more
QA teams are now smaller, smarter, and more specialized.
AI Creates New Roles
AI does more of the execution work. Humans now focus on designing intelligent test flows and managing risk.
New roles include:
- AI QA Strategist: Plans AI-driven testing pipelines
- AI Test Architect: Builds hybrid automation frameworks
- AI Quality Engineer: Aligns QA with risk and business outcomes
These roles: - Tune AI-generated tests
- Shape risk models
- Integrate domain and compliance logic
Firms now look for quality strategists, not manual testers.
Higher-Value Skills: Domain + Compliance
AI handles common bugs. But it can’t replace judgment in complex or regulated systems.
Top teams hire testers who understand:
- Financial or healthcare workflows
- Regulatory frameworks (e.g., EU AI Act, HIPAA, PCI-DSS)
How to test for safety, risk, and data governance
QA teams are becoming part auditor, part strategist.
They must now:
- Trace model lineage
- Validate logs + documentation
- Prove systems behave safely under pressure
Salary Premiums for Scarce Skills
There’s a growing talent shortage. Firms are paying more for people with the right mix of skills. QA roles with AI or compliance expertise now earn 20–40% more.
This includes:
- AI Test Architects
- Compliance-first QA Analysts
- QA + Risk hybrid roles
The premium reflects:
- High demand
- Low supply
- Rising complexity
- Strategic value
This gap is largest in BFSI, healthcare, automotive, and robotics, where failures are costly and regulations are strict.
Skill Shift: From Execution → Orchestration
AI now:
- Writes test cases
- Maintains scripts
- Adapts to UI changes
5.
Team Structures Are Smaller, Smarter
Automation reduces repetitive work. But new complexity calls for specialized roles.
Modern QA teams now include:
- Domain-aware QA leads
- AI automation experts
- Compliance + privacy testers
- Security validation analysts
They look less like armies of test executors and more like cross-functional pods.
💡 Key Takeaways
|
4.7 Business Pressure
Speed has become one of the biggest forces shaping QA. Companies must release software faster to stay ahead, but faster cycles raise the risk of failure. This drives a clear shift: continuous, AI-powered testing is no longer optional.
Why Time-to-Market Matters More in the Future
The pace of software delivery keeps accelerating because:
- AI-assisted coding increases code volume
- Digital transformation continues across sectors
- Competition demands fast feature launches
As more features ship, testing must scale too, but traditional methods can’t keep up. That’s why continuous, intelligent QA is becoming the default.
AI Compresses Testing Cycles
AI eliminates QA bottlenecks. An AI model can now complete entire test cycles in ~2 hours, replacing what once took days.
This makes real-time QA possible in:
- Daily builds
- Feature branches
- Client-ready previews
Organizations using AI across the SDLC see 31–45% better quality and faster delivery.
With AI, testing no longer slows down the release.
Continuous + Intelligent Testing Becomes the Default
Old QA models ran late, in batches. Now, testing happens constantly, inside CI/CD workflows.
Modern teams:
- Use AI to detect issues during builds
- Debug with model-generated insights
- Gate production with real-time quality scores
This tightens the Dev ↔ QA feedback loop and reduces the chance of late-cycle failure.
Faster Releases = More Code = More Testing
Speed creates a paradox. Faster shipping creates more code, which demands more testing.
This creates pressure across three fronts:
- Regression load increases
- Integration points multiply
- Manual bandwidth gets stretched
AI helps by:
- Auto-generating tests
- Healing broken scripts
- Identifying risky code
- Recommending smart coverage
This is how teams maintain quality even as release frequency rises.
Organizational Behavior Is Shifting
The speed push is changing how teams work.
| 2020-2023 | 2024–2026 |
| Manual-first testing | Automation + AI-first QA |
| Testing late in cycle | Shift-left, continuous QA |
| QA in silos | QA embedded in pipelines |
| Measured by bug counts | Measured by speed + quality |
Now:
- Developers adopt QA ownership
- QA engineers act as strategists
- Talent demand grows for automation + AI fluency
Business Impact
Executives want:
- Faster time-to-market
- Fewer escaped defects
- Predictable quality outcomes
AI-based QA helps on all fronts:
- Shorter release cycles
- Less rework
- More stable builds
This is why digital-heavy industries, especially banking, retail, and mobile-first sectors, are driving higher QA budgets.
💡 Key Takeaways
|
5. Major Trends
5.1 AI-First Quality Engineering & Intelligent Test Automation
1. AI is Now the Core of Modern QA
AI has moved from an enabler of automation to the center of how quality engineering works.
Leading QA teams no longer just accelerate old tasks. They use AI to generate, prioritize, heal, and augment tests at scale. The result: faster delivery, better test coverage, and reduced manual effort.
2. AI Adoption is Now Universal
AI in QA is no longer emerging; it’s embedded.
According to reports:
- 77.7% of organizations now use or plan to use AI in QA
- Top AI use cases include:
- Test data creation: 50.6%
- Test case formulation: 46%
- Log analysis: 35.7%
The message is clear: AI is mainstream in test design, data generation, and analysis, the historically time-consuming layers of QA.
3. From Assistant to Autonomous Agent
AI no longer just assists. It executes entire test cycles, including:
- Generating test cases from user stories
- Prioritizing by code risk
- Healing broken scripts
- Identifying test gaps
- Creating synthetic data
- Updating test environments
This reflects the rise of agentic AI systems: tools that act with memory, intent, and feedback loops.
4. Key 2026 Capabilities
| Capability | What It Does |
| GenAI Test Authoring | Converts user stories, UI flows, or logs into test scripts |
| Risk-Based Prioritization | Uses churn, history, and traffic to focus test efforts |
| Self-Healing Automation | Fixes broken locators and workflows without human help |
| Test Impact Analysis | Flags affected paths and removes redundant tests |
| Synthetic Data Generation | Builds privacy-safe datasets for edge-case coverage |
5. Business Value in the Future
- Faster Cycles: AI models compress days of test effort into ~2 hours
- More Coverage: AI explores paths humans would miss
- Lower Maintenance: Self-healing removes brittle scripts
- Fewer Escaped Defects: Risk-based targeting finds issues earlier
- Smarter Resource Use: Dev + QA teams share quality responsibility, with AI support
6. Why It Matters Now
Software output is increasing faster than QA headcount. Teams now ship:
- More features
- More often
- On more platforms
Manual QA can’t scale to match that velocity. AI must scale the testing function. That’s why intelligent testing is a response to structural software growth.
7. Leadership Implications
| Area | Shift |
| Tooling | AI-first platforms become the norm |
| Skills | Demand rises for QE, automation, and AI fluency |
| Vendors | AI capability is now a selection criterion |
| Budgets | Spending shifts toward intelligent tooling |
| Governance | Synthetic, privacy-safe testing gains importance |
5.2 Shift-Left & Shift-Right Converge Into Continuous Quality
Testing Is Now Always On
Quality is no longer something teams check before release. It’s woven through every phase of the software lifecycle.
Testing starts early, continues in production, and uses telemetry to improve itself. High-maturity teams call this model Continuous Quality, and it’s becoming the new normal.
The Shift: Left + Right Merge
What used to be two strategies is now one loop:
| Strategy | Focus | 2026 Role |
| Shift-left | Test earlier in development | Prevent defects before code |
| Shift-right | Test in production | Improve test relevance with real data |
Together, they form a closed feedback loop:
- Early testing prevents issues
- Real-world signals improve upstream accuracy
- QA becomes both predictive and reactive
Proofs
71.5% of teams include QA in sprint planning
89.1% CI/CD adoption
These two signals show: Shift-left and shift-right are no longer best practices; they’re standard practice.
What’s Driving This
- AI helps test earlier: GenAI generates test cases from requirements, before development starts
- Production data makes upstream tests smarter: Teams use real errors and usage patterns to refine test suites
- Faster release cycles require continuous risk checks: Monthly or daily releases mean testing can’t pause
- Compliance pressure moves left: Regulated industries must prove safety and quality early, not just in audits
How Teams Work Differently Now
| Change | What It Looks Like |
| QA shapes stories | Testers define edge cases during planning |
| Security shifts left | Compliance and risk checks run with functional tests |
| Live monitoring drives test creation | Logs and errors generate new test cases |
| Risk-based execution | Teams run the most relevant tests first, based on what changed, who’s using it, and what could break |
Organizations that adopt continuous quality:
- Release faster
- Fix less post-release
- Avoid rework loops
- Focus on what users actually experience
In a world of frequent releases, continuous quality is how teams move quickly without surprises.
💡 Key Takeaways The industry has moved past asking when to test. Now, testing is always on.
Together, they form Continuous Quality, a loop that balances speed, stability, and learning This is how top teams deliver fast without losing control. |
5.3 QAOps Becomes the Standard Delivery Model
What’s Happening
QA is no longer a separate step at the end of delivery. Testing runs inside the pipeline. This model is called QAOps, and it’s how fast-moving teams keep quality and speed aligned.
Modern software is:
- Cloud-native
- Microservice-based
- Updated frequently
- Run across multiple platforms
These traits increase integration risk. To manage that risk, teams now embed test logic directly into CI/CD pipelines, where builds, tests, and risk checks all run as one flow.
The Evidence (2025–2026)
- 89.1% of companies use CI/CD pipelines
- 71.5% of teams involve QA in sprint planning
- ~50% of teams automate test data creation
- 75%+ of teams use 2+ test frameworks
These shifts confirm QA is now part of delivery architecture, not a separate function.
How QAOps Works (Core Elements)
| Components | What It Does |
| Pipeline Automation | Tests run automatically with builds, merges, and deployments |
| Shared Dashboards | QA, Dev, Product, and Ops all see the same quality + risk data |
| IaC for Test Environments | Code provisions consistent, fast-spinning test environments |
| Cross-Team QA | QA joins sprint planning and backlog grooming — not just handoffs |
QAOps Workflow
- Developer commits code
- Pipeline triggers:
- Unit tests
- API + UI tests
- AI-based test selection
- Self-healing updates broken tests
- Dashboards update risk + pass/fail
Why Teams Adopt It
| Driver | Why It Matters |
| Frequent releases | Testing must scale without slowing delivery |
| API/microservices | Integration risk is high |
| AI automation | Keeps test data + coverage fresh |
| Multi-framework stacks | Require orchestration + standardization |
| Compliance + security | Need embedded validation points |
Business Benefits
| Outcome | Value |
| Stable pipelines | Predictable releases |
| Shorter test cycles | AI + automation reduces delays |
| Lower defect escape | Tests run earlier + smarter |
| Happier teams | Less rework, less friction |
| Higher delivery speed | Without skipping quality |
Quick Comparison
QAOps is the default delivery model for fast, modern software teams.
Adopt QAOps For:
- Faster releases
- Lower cost of quality
- Fewer post-release incidents
Avoid QAOps For:
- Delayed delivery
- More production bugs
- Losing pace with competitors
💡 Key Takeaways
|
5.4 Multi-Framework + Multi-Cloud Test Stacks
Testing ecosystems are more complex than ever. Teams now blend multiple frameworks, clouds, and execution models to handle diverse platforms, stacks, and architectures.
This shift is driven by the need for scalability, coverage accuracy, and the ability to test across any environment, web, mobile, API, microservices, edge, and more.
Why This Matters
Testing is no longer tied to one tool or environment. Modern apps span many layers, UI, APIs, containers, edge devices, and AI-driven workflows.
No single framework handles this all well. So most teams now run mixed-framework stacks on hybrid infrastructure.
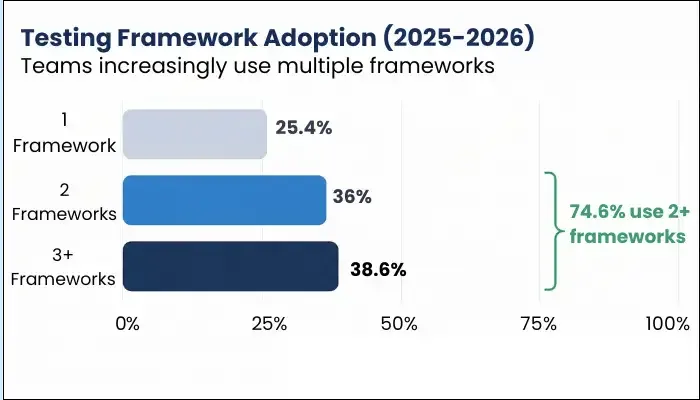
- 74.6% of organizations now use two or more automation frameworks
- 38.6% use three or more, reflecting specialization across layers
- 48% still run tests on local or in-house grids, showing that full cloud migration is still in progress
This data shows fragmentation in tooling, growing cloud adoption, and the rise of hybrid execution models.
2026 Focus Areas
- Cloud Infrastructure Adoption
Teams are shifting to cloud-based test execution for:- Wider device/browser coverage
- Faster parallel test runs
- Scalable, on-demand infrastructure
But many still operate local grids, so cloud migration remains a work in progress.
- Cost vs. Scalability Trade-offs
Local test execution offers control, but:- Requires upkeep
- Limits test throughput
- Slows delivery
Cloud boosts scale and coverage but introduces: - Usage-based cost variability
- Ramp-up friction
- Vendor lock-in risk
Tooling decisions in the future must balance flexibility with cost efficiency.
- Local + Hybrid Execution Models
Hybrid execution is now standard. Teams typically:- Run unit/API tests locally
- Use cloud for cross-browser/device coverage
- Perform performance testing on distributed infra
This gives faster feedback and better resource allocation.
- Stack Consolidation
With many tools in play, teams are working to:- Reduce redundancy
- Standardize workflows
- Unify reporting and dashboards
Typical stacks include: - UI: Selenium + Playwright + Cypress
- API: Postman + REST-assured
- Mobile: Appium + cloud real devices
- Execution: LambdaTest, BrowserStack
3. Strategic Impacts
| 2023 | 2026 |
| One or two main frameworks | Three or more frameworks |
| Local execution dominates | Hybrid + cloud mix |
| Manual environment setup | IaC + auto-provisioned infra |
| Basic reporting | Unified dashboards + AI |
4. What Leaders Need to Do
- Prioritize integration over just tool count
- Migrate to the cloud in stages
- Consolidate tools to reduce stack sprawl
- Upskill teams on orchestration + reporting tools
- Standardize test intelligence across platforms
5. Value Proposition
Multi-framework and hybrid execution unlock:
- Lower infrastructure cost
- Wider test coverage
- Faster parallel runs
- Better tool specialization
- Consolidated visibility for faster triage
Example: Playwright leads for browser automation. Appium handles mobile. API tools dominate shift-left validation.
💡 Key Takeaways Today, testing runs across multi-framework, multi-cloud, and multi-surface environments. Hybrid execution is the norm. Cloud usage is rising. The winners are teams who:
|
5.5 Data-Driven Testing & Test Intelligence
Data is at the center of software quality. Leading teams treat QA telemetry like product teams treat business intelligence: as a live signal used to prioritize, automate, and prevent failure.
This shift is driven by three mounting pressures:
- Faster delivery cycles demand smarter test selection
- Distributed systems introduce complex, hidden failure paths
- LLM-driven development expands the test surface faster than humans can cover
Together, these factors make test intelligence a strategic necessity.
Why It Matters
Software ships faster than teams can test it manually. Data helps answer three key questions:
- What to test first
- What to automate
- What presents the most risk
This improves both predictability and cost control. Instead of more testing, teams aim for smarter testing.
Core Capability Areas
- ML-Powered Detection of Flaky Tests
Flaky tests create noise and erode trust in pipelines. Modern platforms use model-based heuristics to detect:- Timing-based instability
- Volatile dependencies
- Platform drift
By flagging weak tests early, ML reduces failed runs, wasted triage, and late-cycle debugging.
- Code-Aware Test Prioritization
Instead of running full regressions, teams now focus on testing:- Code change graphs
- Dependency analysis
- Historical defect clusters
This narrows execution to where breakage is most likely, cutting test time and computing cost.
- Production Telemetry Feeds Pre-Prod Testing
Real usage data now guides test design. Teams mine:- Crash logs
- High-traffic user paths
- Device/browser distribution
- Infrastructure stress patterns
This makes testing more realistic, predictive, and aligned with customer behavior.
Synthetic data generation is being used to model these patterns safely in dev environments, supporting edge-case validation without privacy risk.
- Synthetic Data to Enable Safe & Scalable Testing
In regulated sectors, synthetic data now substitutes sensitive datasets. It enables:- Secure model validation
- Workflow simulation
- Broader scenario coverage
Especially in BFSI and healthcare, synthetic generation is a baseline input for privacy-compliant QA.
Adoption Gaps & Maturity Challenges
Even advanced teams still face:
- Inconsistent telemetry
- Fragmented reporting
- Weak cross-tool insight
This leads to:
- Missed flaky-test detection
- Repeat defects
- Low visibility into quality drift across releases
Without structured test intelligence, organizations rely too heavily on manual triage, slowing delivery and raising cost.
4. Business Value
| Business Goal | Outcome with Test Intelligence |
| Faster QA cycles | Targeted tests + fewer flaky runs |
| Fewer escaped defects | Risk-based prioritization + live signals |
| Lower QA cost | Shorter cycles, smarter automation |
| Better planning | Historical trends + root-cause insights |
| Higher satisfaction | Fewer surprises, more stable releases |
Teams using ML-based test intelligence report:
- Shorter mean time to diagnosis
- Better ROI on automation
- Fewer duplicate defect investigations
These gains support faster, more confident release velocity, a top business KPI in 2026.
💡 Key Takeaways Test intelligence is no longer a nice-to-have. It’s a core competency for modern software delivery. Instead of testing more, smart teams test better, using live data, synthetic modeling, and predictive tooling to reduce risk and increase speed. |
5.6 Hyper-Automation & Scriptless Testing
Hyper-automation and scriptless testing are no longer “next-gen”, they’re standard. With faster releases, complex apps, and limited QA headcount, teams need automation that doesn’t require deep coding skills.
That’s why organizations are leaning into tools that reduce scripting effort, use AI to generate tests, and make QA more accessible across roles.
Why It Matters in 2026
Hyper-automation reduces testing bottlenecks. Teams can now:
- Create tests without code
- Auto-update tests when UIs change
- Focus on test strategy, not test maintenance
AI increases coverage and lowers rework. It also enables early-cycle validation, powering faster builds and fewer defects.
Scriptless testing is now central to future QA strategies.
- 50.6% use AI for test-data creation
- 46% use AI for test-case formulation
This signals a clear trend: Testing is moving from manual scripting to AI co-creation.
2026 Focus Areas
- No-Code / Low-Code + AI Co-Creation
Today’s hyper-automation tools combine:- Visual test builders
- Record-and-playback flows
- AI-generated test scaffolds
- Plain-language test scripting (via NLP)
This enables wider participation, from QA engineers to analysts to product owners.
- Scriptless Authoring Rises
- Drag-and-drop test creation
- Motion/visual UI capture
- Browser-based recording
Scriptless workflows now dominate early-cycle automation, especially for UI validation.
- NLP + Visual-Driven Steps
AI tools now convert plain-English test cases into executable logic.- “When the user clicks Submit → expect confirmation”
- Conditional flows, API calls, mocks — all handled without code
This reduces learning curves and expands contribution beyond engineering.
- The Rise of Citizen Testers
Now, anyone on the team can build tests: Product managers, consultants, QA analysts, not just coders.
That means:- More test scenarios covered
- Better alignment with business intent
- Faster iteration and validation
2026 Value Proposition
| Benefit | Why It Matters |
| Wider QA participation | Anyone can test, not just coders |
| Higher test coverage | More contributors, more paths |
| Lower maintenance | AI heals scripts automatically |
| Faster onboarding | Less training time required |
| Lower cost | Fewer QA specialists needed for basic coverage |
2026 Outlook
Expect maturing in 3 areas:
- Autonomous test agents: Watch code commits, generate tests automatically
- Self-healing test ecosystems: Adapt as UIs change, without breaking
- Embedded citizen testing: Testing happens inside business workflows, not just engineering
Hyper-automation is the response to:
- Faster dev velocity
- API/microservices sprawl
- Shorter delivery cycles
- Lean QA teams
💡 Key Takeaways Scriptless testing and hyper-automation now form the foundation of modern QA. AI does the heavy lifting. People focus on coverage, risk, and quality outcomes. |
5.7 Testing for Microservices, APIs & Distributed Systems
Modern software is built on distributed systems. Most digital products will rely on microservices, APIs, and cloud-native infrastructure. These enable speed and modularity, but also introduce fragility. When one service fails, the entire chain can break.
As a result, microservices and API testing have become core QA disciplines, not edge cases.
Why This Matters
Microservices power critical systems across industries:
- Banking
- Ecommerce
- Logistics
- Healthcare
These services handle sensitive data and real-time events. Even small bugs can cause customer-facing failures or revenue loss.
Microservices testing is a major growth area, driven by the need to validate integrations and distributed behavior at scale.
Teams now invest in:
- Contract validation
- API test coverage
- Synthetic environments
- Chaos testing for resilience
Key Industry Signals
- Microservices testing is identified as a strategic need for large-scale delivery.
- 74.6% of teams use 2+ automation frameworks, mirroring microservices complexity.
- 48% still rely on in-house test infra, highlighting scale/reliability gaps.
- Testing focus is shifting toward cloud execution, API coverage, and contract safety.
Core Testing Focus Areas
- Contract Validation Becomes Standard
As services interact more frequently, small changes can break critical paths.
Contract testing helps teams:- Validate API compatibility
- Prevent schema breakage
- Release confidently
- API-First Testing
APIs are the core interface.
Testing now covers:- Functional behavior
- Version compatibility
- Data contracts
- Auth and security flows
APIs are often the first and most critical layer of quality assurance.
- Synthetic Environments + Test Data
Real environments are often:- Unavailable
- Costly
- Regulated
So teams simulate: - Downstream services
- Edge-case responses
- Load or concurrency
Synthetic test data improves coverage while meeting privacy standards.
- Chaos & Resilience Testing
Distributed systems fail in unpredictable ways. Chaos testing validates:- Fallback logic
- Failure isolation
- Recovery speed
Once reserved for large tech firms, chaos testing is now adopted by mid-market teams to prevent outages.
Business Impact
Stability at the service layer is critical because:
- Apps are modular
- APIs are real-time
- Outages hit fast and hard
Every release must validate:
- Microservice independence
- API contract stability
- Traffic/load resilience
- Failure boundaries
There is a growing need for full interaction testing across distributed platforms to ensure reliability.
Strategic Value
| Business Need | Testing Outcome |
| Faster release cycles | Faster release cycles |
| Faster release cycles | Fewer breakages |
| Transaction stability | Better customer experience |
| Downtime prevention | Lower outage cost |
| Scalability | More services, more coverage |
Buyer Priorities
When buying QA services or platforms, leaders now expect:
- Strong API testing
- Contract testing expertise
- Cloud + container testing
- Chaos/resilience validation
- Modern test frameworks (Postman, REST-assured, etc.)
5.8 Platform + Device Explosion → Cross-Environment QA
Software must run smoothly across a growing mix of platforms: Web, mobile, IoT, wearables, embedded systems, and early AR/VR. QA teams now test across browsers, devices, operating systems, network conditions, and edge environments.
Cross-environment quality is no longer optional; it’s expected.
The Challenge: More Platforms, More Testing Pressure
Modern apps must work across hybrid digital touchpoints. Report cites cross-device and OS coverage as a top automation priority, reflecting rising customer expectations for seamless, consistent performance.
This growing complexity means QA must now validate:
- Browser + mobile interactions
- Real devices across OS versions
- Edge-network behavior
- Accessibility and performance on constrained hardware
IoT & Embedded Systems Multiply Complexity
Connected devices keep expanding across:
- Smart homes
- Medical systems
- Industrial automation
- Automotive platforms
QA now includes:
- Hardware-in-loop testing
- Simulation of low-bandwidth and unstable networks
- Real-time response validation
- Safety-critical quality reporting
As embedded tech grows, testing goes beyond software, into sensors, protocols, and physical response behavior.
AR/VR & Wearables Introduce New QA Dimensions
Wearables are mainstream. AR/VR is emerging.
Testing now covers:
- Spatial interaction
- Environmental context variance
- Sensor synchronization
- GPU + thermal performance
These platforms introduce multi-sensory, real-world-aware testing challenges.
The Rise of Multi-Framework Environments
Teams no longer use a single testing framework. According to reports:
- 74.6% use 2+ automation frameworks
- 38.6% use 3+ frameworks
This reflects rising platform diversity. Teams align tools to environments:
- Web: Selenium, Playwright, Cypress
- Mobile: Appium, device labs
- API: Postman, REST-assured
- Execution: BrowserStack, LambdaTest, local grids
Tool choice is driven by coverage needs, not consolidation.
Execution Infrastructure Under Pressure
Despite cloud options, 48% of teams still rely on in-house test grids.
This stretches infrastructure teams to manage:
- Device labs
- OS/browser updates
- Grid maintenance
- Network condition simulators
As platform diversity grows, maintaining internal infrastructure becomes costly and unsustainable. Many teams are now migrating to cloud-based test execution for coverage, scalability, and speed.
QA Skills Are Evolving
Platform sprawl changes hiring needs. Leading QA teams invest in:
- Device-lab and environment management
- Network simulation + profiling
- AR/VR interaction design
- IoT protocol + firmware debugging
- Hardware/software integration testing
Testers now combine systems thinking with software fluency.
Why This Trend Matters
The product experience now spans:
- Mobile apps
- Wearables
- Browsers
- Embedded devices
- Cloud services
And users expect smooth, secure, and fast performance across them all.
QA must ensure:
- Seamless transitions between platforms
- Functional consistency across devices
- Stability under real-world network conditions
- Resilience under hardware constraints
Cross-environment quality defines product trust.
Business Value of Cross-Environment QA
| Business Priority | Business Priority |
| Omnichannel experience | Consistent performance across devices |
| Brand reputation | Fewer user-facing bugs |
| Release confidence | Better device + network coverage |
| Revenue protection | Lower environment-specific failures |
Organizations that test broadly and early prevent issues that would damage customer experience and increase cost later.
💡 Key Takeaways
|
5.9 Resilience, Cybersecurity & Privacy-Centric Testing
Security, resilience, and privacy will no longer be handled at the end of development.
They’re core QA priorities, integrated across the software lifecycle.
Driven by regulatory mandates, growing AI adoption, and larger attack surfaces, QA teams now focus on continuous, automated, and AI-aware security testing. The shift is clear: From scanning for problems to designing for prevention.
Why This Trend Emerged
Three forces reshaped QA:
Regulatory pressure surged. The EU AI Act mandates risk classification, documentation, testing, and ongoing monitoring for high-risk AI systems. QA teams must now verify transparency, traceability, and safety throughout the lifecycle.
Threat exposure increased. Cybersecurity reports confirm rising attack sophistication across applications, networks, and AI-enabled workflows.
AI adoption broadened the attack surface. Agentic AI systems introduce risks across data pipelines, inference endpoints, and model behavior, all now in QA’s scope.
Focus Areas
- AI Model Validation & Risk Controls
The EU AI Act requires rigorous validation for high-risk AI systems:- Dataset governance
- Model robustness + explainability
- Bias and fairness audits
- Version traceability
- Failure mode detection
QA now goes beyond pass/fail logic; it validates how AI decides and behaves.
- Privacy Guardrails & Data Governance
AI accelerates data use, increasing exposure risks.
QA priorities include:- Data masking + anonymization
- Synthetic dataset generation
- Purpose-bound access control
- Zero-trust data flows
Security and QA teams now collaborate to ensure compliance-first test environments, especially under data-protection laws and AI regulations.
- Continuous Security & Automated Resilience Testing
Security testing shifts left and right, integrated into pipelines, not isolated phases.
Modern QA stacks now include:- DevSecOps practices
- Automated penetration testing
- Continuous code + dependency scanning
- Runtime validation
- Zero-trust testing frameworks
These tools detect vulnerabilities earlier, without slowing delivery.
- Regulatory Reporting & QA as a Compliance Engine
The EU AI Act makes documentation and traceability mandatory.
QA now delivers:- Compliance checklists
- Policy-aligned test artifacts
- Incident disclosure workflows
- Supply chain + vendor QA validation
This makes QA essential for legal readiness, not just technical assurance.
Why This Matters
| Business Priority | QA Outcome |
| Meet regulatory requirements | EU AI Act compliance + market access |
| Reduce breach risk | Lower incident cost + exposure |
| Ensure trustworthy AI behavior | Safe, explainable, stable systems |
| Preserve customer trust | Higher adoption + brand protection |
What’s Different in 2026
Before 2025:
- Security testing was episodic
- Focused on tools
- Handled late in the cycle
- Owned by siloed teams
In 2026:
- Embedded + continuous
- Regulation-aligned
- Aware of AI risks + behavior
- Cross-functional (QA + Security + Legal)
Testing now spans data → models → APIs → runtime.
Value Delivered
| Benefit | How It’s Achieved |
| Lower compliance burden | Proactive testing + structured reporting |
| Reduced breach risk | Multi-layer defense built into pipelines |
| More reliable AI systems | Behavior validation, not just functional checks |
| Market + customer trust | Compliance maturity becomes a differentiator |
What Teams Should Do Now
To align with new standards:
- Classify systems under the EU AI Act risk categories
- Build AI-specific QA (robustness, bias, explainability)
- Integrate security into CI/CD pipelines
- Automate penetration, API, and dependency testing
- Produce audit-ready test evidence
- Track incidents + model behavior in production
- Align QA, security, and legal workflows
6. What Teams Should Do Next
The trends in this report only matter if teams know how to act on them. In the future, software moves fast, attacks happen often, and users expect things to “just work.” Because of this, companies need clear and simple steps that help them build better, safer, and more dependable apps. These recommendations come from expert opinions, common industry practices, and what many QA leaders say they are doing inside their own teams.
Test Earlier in the Development Process
Action Test earlier in the development process Why Makes it easier to catch problems before they grow into expensive issues Outcome Helps speed up release time Use More Automation and AI Tools
Action Start using more automation and AI tools Why These tools save time, run tests faster than humans, and help teams keep up with rapid releases Outcome Even small teams can benefit from adding automated checks to their daily work - Track Important Metrics
| Action | Track a few important metrics |
| Examples | How often bugs escape to production, how long it takes to run tests |
| Why | These numbers help leaders understand what is working and where improvements are needed |
| Outcome | Makes it easier to show the value of testing to the rest of the organization |
- Build Stronger Skills Within QA Teams
| Action | Build stronger skills within QA teams |
| Focus Areas |
|
Plan for Long-Term Improvements
Action Plan for long-term improvements, not just quick fixes Why A clear roadmap helps teams grow their testing maturity over time Outcome Release better products with fewer surprises
| Bottom Line: These actions give leaders a simple and practical way to stay ahead in a world where software never stops changing. |
7. How We Collected the Information
To create this report, we used a mix of research methods to make sure the information is accurate, fair, and useful for readers. We wanted the findings to come from real data, real experts, and real-world examples. This section explains how we gathered everything and how we checked that it was reliable.
Research Methods
| Method | Description |
| Industry Reports | Reading many trusted industry reports from well-known research groups, including studies on software testing, automation, AI, cloud systems, cybersecurity, and global technology trends |
| Expert Articles | Reviewed articles written by testing experts, technology leaders, and researchers who shared their experience working inside modern software teams |
| Practitioner Insights | Studied insights from interviews, conference talks, and playbooks created by QA leaders, giving a clearer view of how top-performing teams work and think about quality |
| Cross-Validation | Compared all the information across different sources to make sure the facts matched and the trends were consistent. Any conflicting information was cross-checked before being included |
Transparency Note: We will also provide links, references, and source details so readers can explore the material on their own if they want to learn more.
Sources
- https://www.statista.com/outlook/tmo/software/worldwide?srsltid=AfmBOop_6P9wVl7BZiZRs_PDo6PhBX8d5uLvJr5UbSdih_aKmndjOvRu
- https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/industry-reports/software-testing-and-qa-services-market
- https://www.thebusinessresearchcompany.com/report/software-testing-global-market-report
- https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/software-testing-market
- https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/automation-testing-market-113583451.html
- https://www.researchnester.com/reports/outsourced-software-testing-market/6989
- https://www.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/financial-services/future-of-software-engineering-in-banks.html
- https://www.verifiedmarketreports.com/product/software-outsourcing-market/
- https://www.practitest.com/assets/pdf/stot-2025.pdf
- https://www.gartner.com/en/articles/top-technology-trends-2026
- https://www.askui.com/blog-posts/test-automation-trends-2026
- https://medium.com/womenintechnology/ais-impact-on-software-testing-the-evolution-of-qa-engineers-sdets-and-automation-architects-71cd91e46401
- https://www.valido.ai/en/software-testing-in-2026-key-qa-trends-and-the-impact-of-ai/#:~:text=Embedding%20QA%20into%20DevOps%20culture,-Quality%20can't&text=By%202026%2C%2040%25%20of%20large,no%20longer%20just%20a%20checkpoint.
- https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/technology-media-and-telecommunications/our-insights/unlocking-the-value-of-ai-in-software-development
- https://venturebeat.com/ai/zencoder-just-launched-an-ai-that-can-replace-days-of-qa-work-in-two-hours
- https://www.testdevlab.com/blog/the-role-of-ai-in-qa
- https://artificialintelligenceact.eu/article/60/
- https://www.esecuritysolutions.com/2026-cybersecurity-solutions/
- https://techgdpr.com/blog/data-protection-digest-17072025-ai-generated-voice-and-visuals-potential-to-violate-peoples-rights-and-freedoms/
- https://www.browserstack.com/guide/automation-testing-trends
- https://www.lambdatest.com/blog/ai-testing-tools/
- https://www.lambdatest.com/future-of-quality-assurance-survey
- https://itidoltechnologies.com/blog/automated-testing-2026-scale-quality-without-slowing-speed/
- https://www.reddit.com/r/QualityAssurance/new/
- https://testrigor.com/blog/gartner-hype-cycle-for-ai-2025
- https://www.euaiactreadiness.com/?web_page_name=%2F
- https://onereach.ai/blog/agentic-ai-adoption-rates-roi-market-trends/
- https://www.openxcell.com/blog/ai-sandbox/
- https://testfort.com/blog/tmm-in-software-testing
- https://www.forbes.com/councils/forbestechcouncil/2025/08/15/why-agentic-ai-is-redefining-quality-assurance/
- https://www.reddit.com/r/webdev/comments/1dql2lc/people_employed_by_companies_what_is_the_ratio_of/
- https://quashbugs.com/blog/test-coverage-metrics-software-testing
- https://www.qt.io/quality-assurance/blog/is-70-80-90-or-100-code-coverage-good-enough
Frequently Asked Questions
Share This Article:





