Top QA Mistakes to Avoid: Save Time, Cut Bugs, Ship Faster
Testing teams face many challenges. From scope changes at the last second to teams working in silos, we've analyzed the biggest roadblocks - and how to solve them.
This guide breaks down the main testing bottlenecks and shows QA leaders, testers, and developers exactly how to fix them. You'll learn specific techniques to run automation, get insights on improving team collaboration, and pick testing approaches that match your needs.
Many companies are already seeing results. Take Pfizer - they cut their regression testing from 5 days to 1 day. Industry veterans Kent Beck and Lisa Crispin have guided dozens of teams to better testing practices, and their inputs are covered in this guide.
So get ready to equip yourself with proven approaches to deliver better software today.
Let’s get started..
1. Frequent Last-Minute Changes
In 2024. BCG surveyed global businesses and technical side C-suite executives to find out the common reasons for delays. A prominent number of responses indicated frequent last-minute changes.
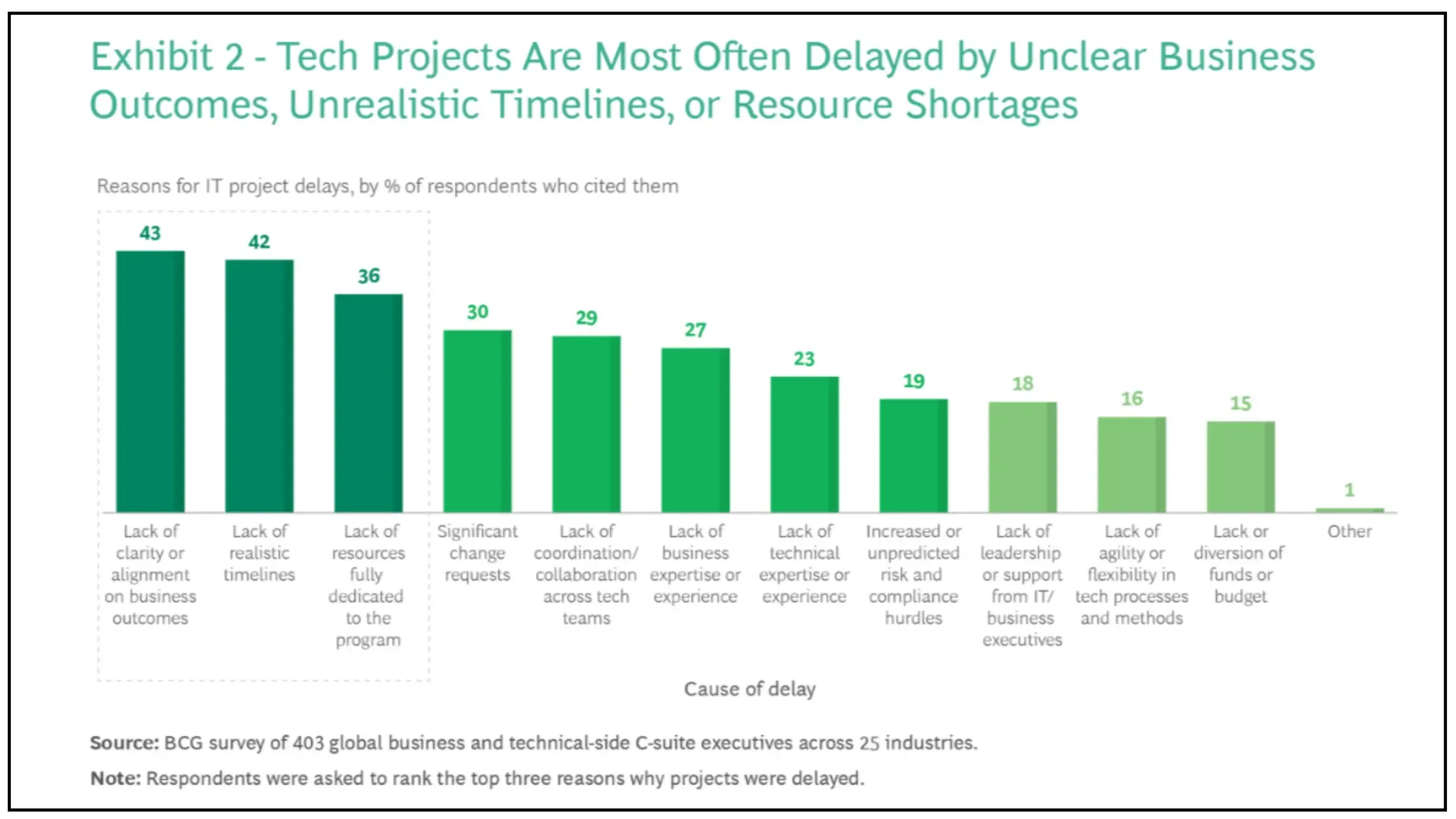
Last-minutes changes derail project success. When these changes occur, projects exceed budgets by 75%, fall behind schedule by 46%, and deliver 39% less value than planned.
Smart testers have found a better approach to deal with such changes. They create detailed user scenarios based on the app concept.
Here's how it works:
Last-minute changes typically come from three main sources:
- New market trends shifting requirements
- Unclear project objectives, creating misaligned expectationslimited
- Technological advances, making current solutions outdated
To handle these challenges, testers think ahead. As Kent Beck, one of the Agile Manifesto founders and cocreator of eXtreme Programming (XP) shows us that successful teams anticipate and adapt to change.

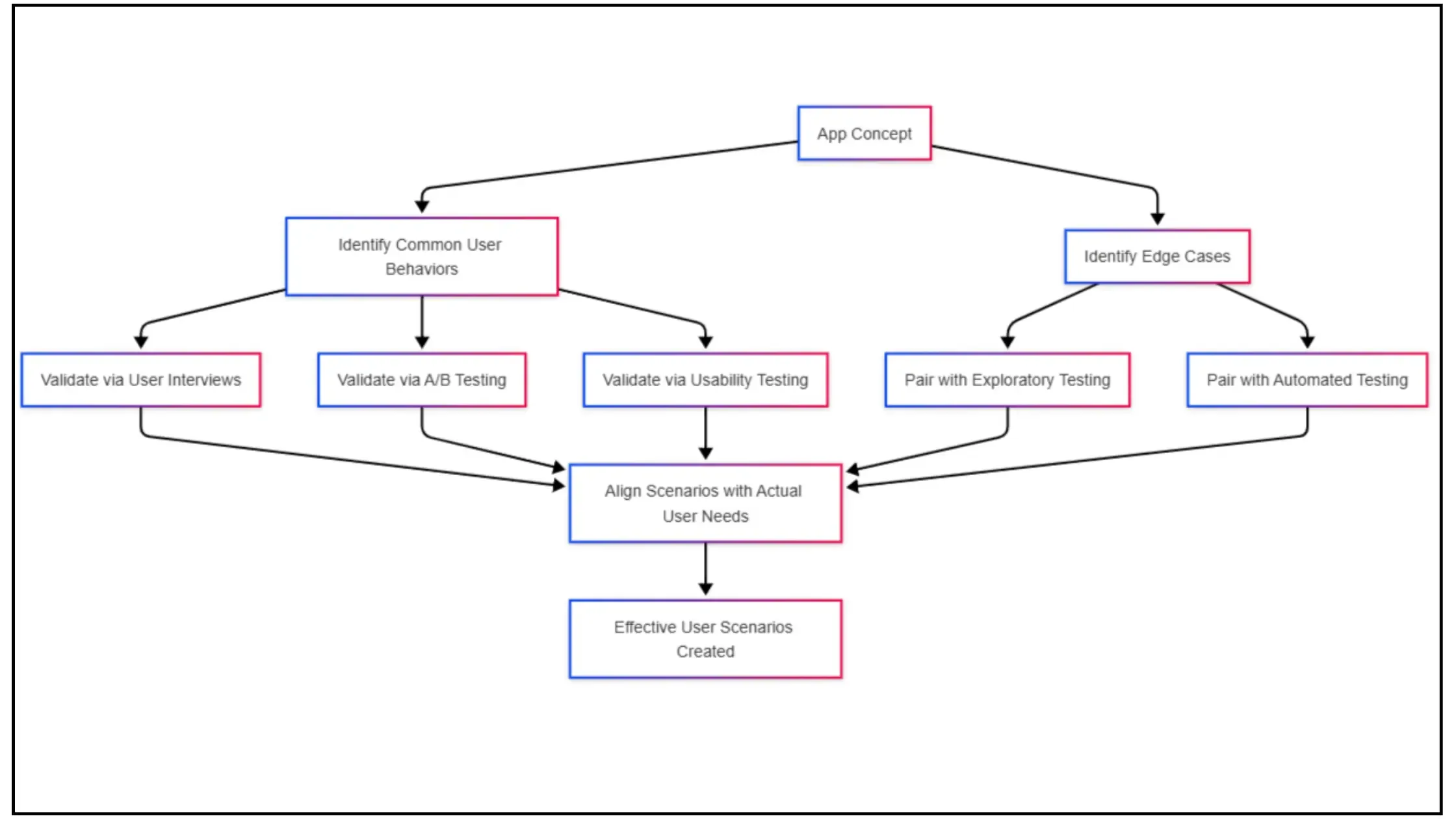
Here's how to create effective user scenarios:
Focus on common user behaviors and primary use cases. Then expand to include edge cases. Validate through user interviews, A/B testing, and usability testing to align scenarios with actual user needs.
For example, if an e-commerce app is under development, testers first create scenarios for essential user behaviors like browsing products, adding them to the cart, and completing a purchase. Once these primary use cases are solidified, they explore edge cases, such as users abandoning carts, retrying failed payments, or using different payment methods. They then validate these scenarios through:
User interviews: Engaging with real customers to understand how they interact with similar apps and their expectations.
- A/B testing: Running tests on different checkout flows to see which one leads to better conversion rates.
Usability testing: Observing users as they navigate the app to identify pain points and improve the overall experience.
Building scenarios on assumptions alone has downsides. You risk missing critical edge cases or creating solutions that don't match real user behaviors.
Successful teams pair scenario-based testing with:-
- Exploratory testing to find unexpected issues
- Automated testing to validate across multiple scene
When testers research and plan scenarios thoroughly, they spot potential issues early before they become problems.
2. Limited Automation
Recent studies show that 48% of companies still rely heavily on manual testing processes, significantly impacting their development efficiency and scalability.
Manual Testing plays a vital role, but overreliance creates substantial bottlenecks in the software development lifecycle.
Companies that have shifted to a balanced testing approach see up to 80% faster developer feedback response times, showing the real impact strategic test automation.
For instance, according to the World Quality Report 2024-25, 65% of organizations now use generative AI for test automation.

That shows that test automation and AI testing are necessary.
But what makes certain tests better suited for automation than others?
Repetitive, data-intensive, and regression tests work best with automation because they need consistent execution. Exploratory testing, usability testing, and ad-hoc tests work better with human intuition and adaptability.
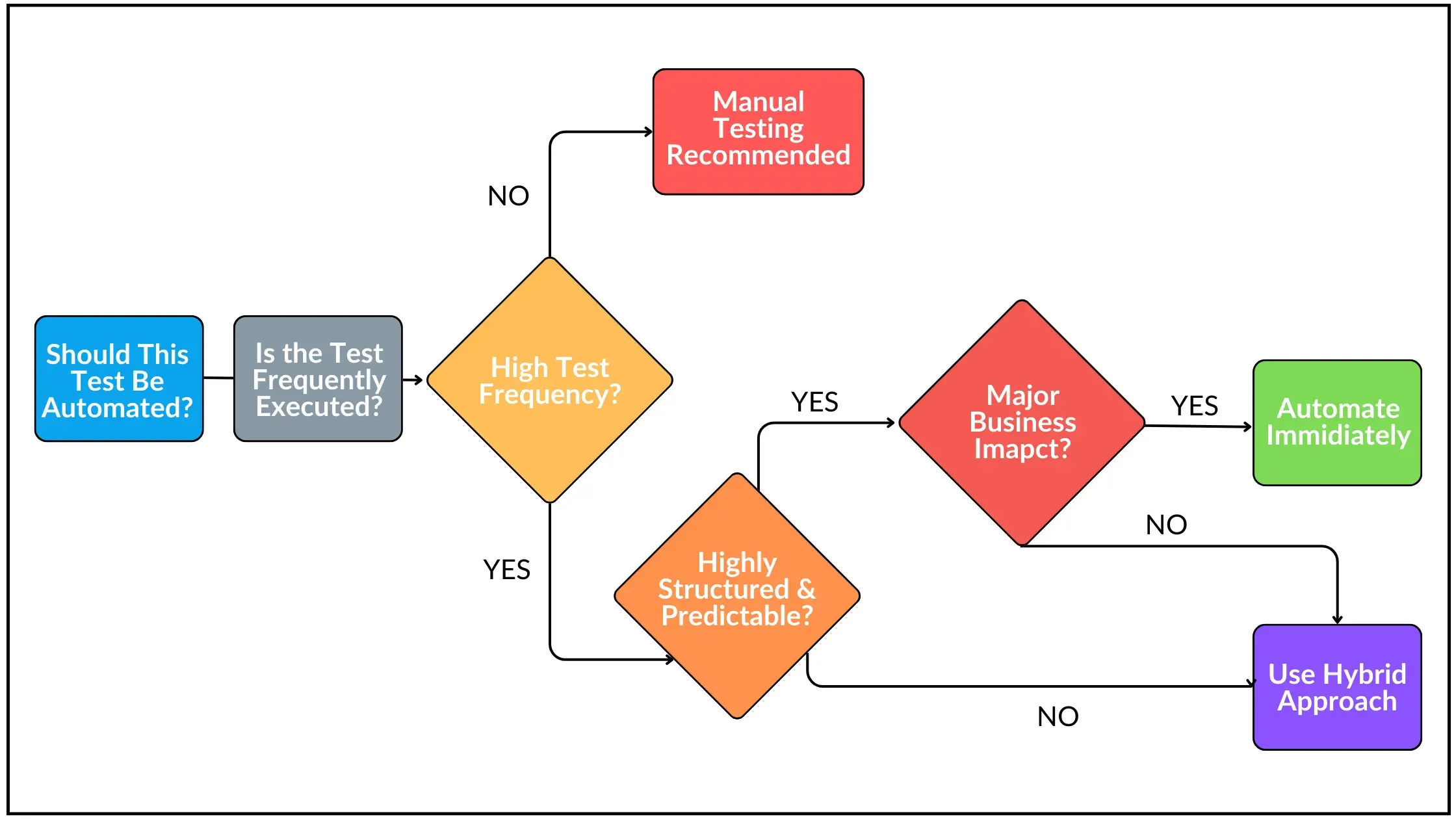
The key isn't eliminating manual testing completely. In fact, it’s about choosing the right testing approach for each scenario.
For companies still relying heavily on manual testing, this transition presents its challenges. Setting up automated testing requires significant investment in resources and expertise.
Interesting Read: Is Manual Testing Still Crucial in Today's QA Landscape?
But making that shift will surely provide you with a good ROI. Over 60% of companies see positive returns from their automated testing tools through time savings and better application quality. Additionally, misidentifying which tests to automate can lead to significant inefficiencies.
When you want to improve your software quality and are willing to invest money and resources - plus update some older processes - then this is your best option.
3. Lack of Skills & Staff
According to The 2025 State of Testing™ report, 33% of QA teams lack skilled professionals. As a result, they are not able to adopt AI in their workflows despite its benefits.

Not only that, QA teams are struggling with proficiency gaps in essential automation tools like Selenium, Appium, and Cypress. The industry benchmark suggests maintaining one automation QA engineer for every four to five developers, but many organizations fall short of this standard.
This imbalance creates a ripple effect throughout the development process, leading to extended testing cycles and compromised product quality.
Organizations with inadequate automation expertise face increased operational costs due to prolonged manual testing efforts, delayed releases, and potential revenue losses from slower time-to-market. As Jason Arbon, CEO of test.ai, covered this gap and new opportunities in an article on LinkedIn.
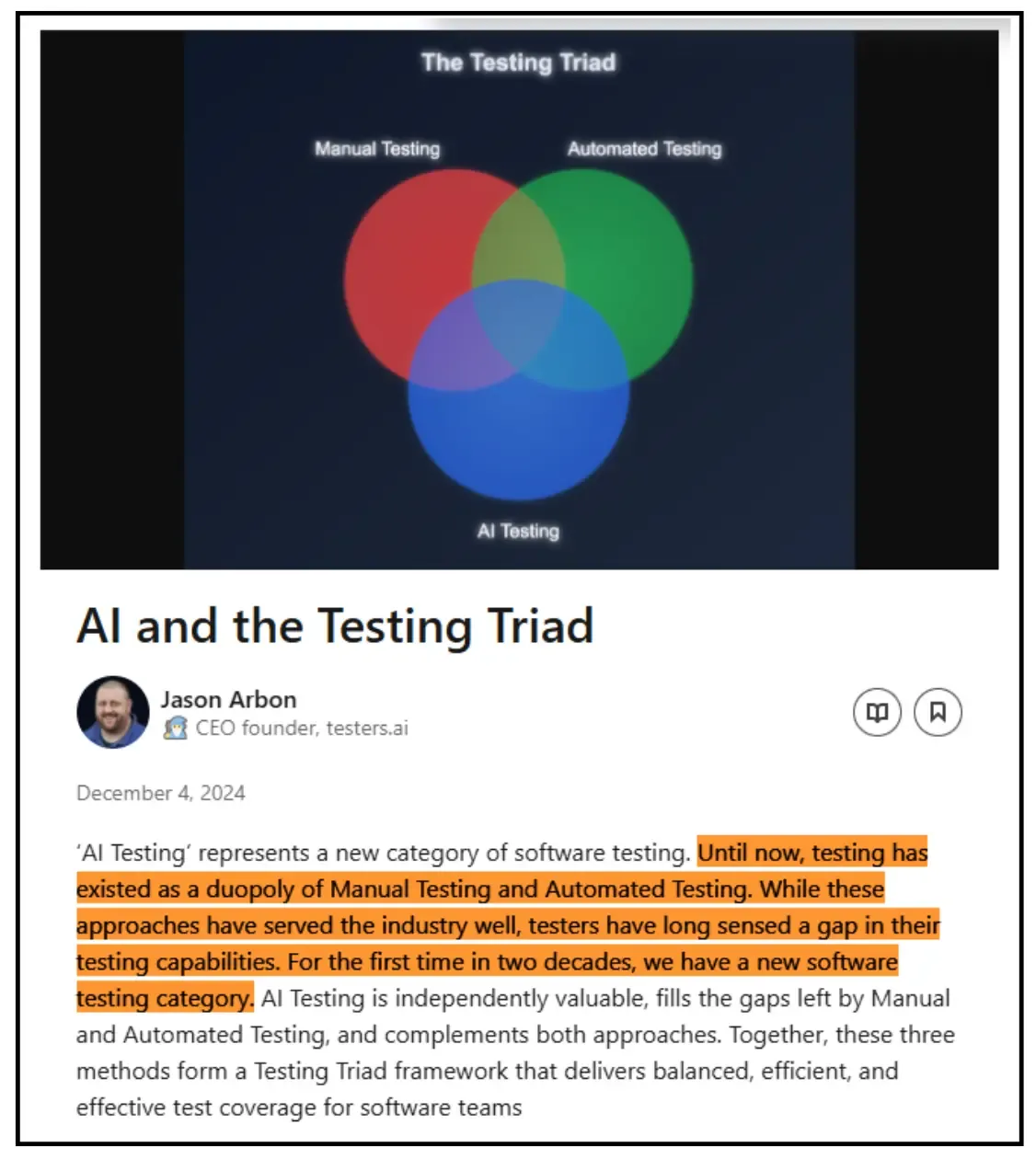
If your organization is struggling with these kinds of skill gaps, you need to invest in upgrading your teams first. An effective way to upgrade your team is to partner with a specialized QA team that is handling AI, automation, and manual testing simultaneously.
If you don't want to go for outsourcing and pair up your team with specialists, you can invest in regular, structured training programs for QA teams. While the learning curve varies, focused training initiatives, such as intensive courses covering Python and Selenium, or using LLMs like ChatGPT and Claude will prove effective.
To measure the success of your initiatives, organizations should track key metrics including:
- Reduction in manual testing time
- Increased test coverage
- Number of automated test cases executed per cycle
- Decrease in post-release defects
The cost of not addressing this skills gap can be severe. So it's better to have a proactive approach instead of learning after committing mistakes.
4. Poor Collaboration between Testers and Developers
Many studies point out the role of collaboration and its impact on overall performance. One of the most persistent challenges in software development is the collaboration gap between testers and developers.
Poor collaboration between testing and development teams creates significant delays and quality issues. Here's what actually happens behind the scenes.
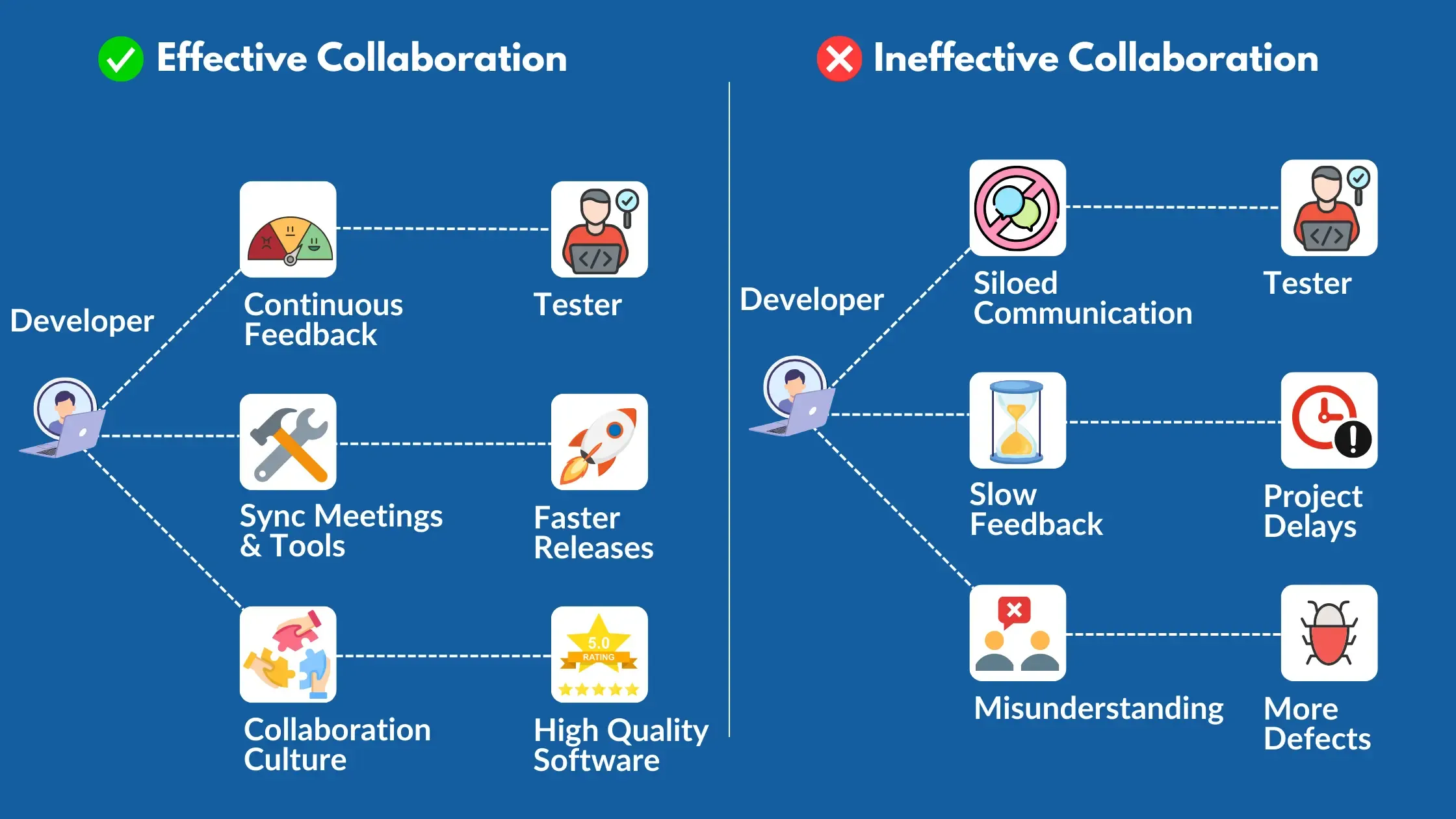
Communication barriers between testers and developers take many forms - from socio-cultural differences to geographical distances and time zone challenges. These barriers affect the entire development process, leading to more defects, project delays, and reduced software quality.
Also Read:- Types of Bugs
Industry research has identified several key metrics that show the direct impact of poor collaboration: Deployment Frequency, Change Lead Time, Change Failure Rate, and Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR).
David Farley, co-author of Continuous Delivery, notes that when developers, testers, and operations improve their collaboration, delivery teams can release changes within hours or minutes, regardless of project size or code complexity.
The question remains: How do team dynamics affect this collaboration?
Smaller teams typically communicate more effectively, while larger teams face more coordination challenges. Lisa Crispin, a renowned Agile Testing author, emphasizes that Agile success depends on testers and developers working together from day one.

Here's how successful teams improve collaboration:
- They use both synchronous tools (like video conferencing) and asynchronous communication methods to bridge geographical gaps
- Management creates a culture of open communication and provides effective collaboration tools
- Teams set up regular feedback loops and shared toolsets to maintain consistent communication flow
When teams implement these changes, they see improvements in code review speed and software delivery performance.
As a leader, it's your job to create an environment that supports cross-functional teamwork, provide appropriate tools, and establish clear communication channels. This approach reduces traditional silos and creates a more integrated development process.
5. Multi-platform and multi-device testing complexity
Device fragmentation creates major challenges for QA teams.
That’s why it is crucial to develop a strategic approach to cross-platform testing.
Testing across multiple platforms and devices requires more than running identical tests everywhere. You need a thoughtful, systematic approach for comprehensive coverage that maximizes your resources.
The challenge begins with platform selection. Start by identifying the platforms and devices your target users actually use. This process requires careful planning.
To effectively manage this, you need to start by identifying the platforms and devices your target users are most likely to use. This seemingly straightforward task actually involves several critical considerations.
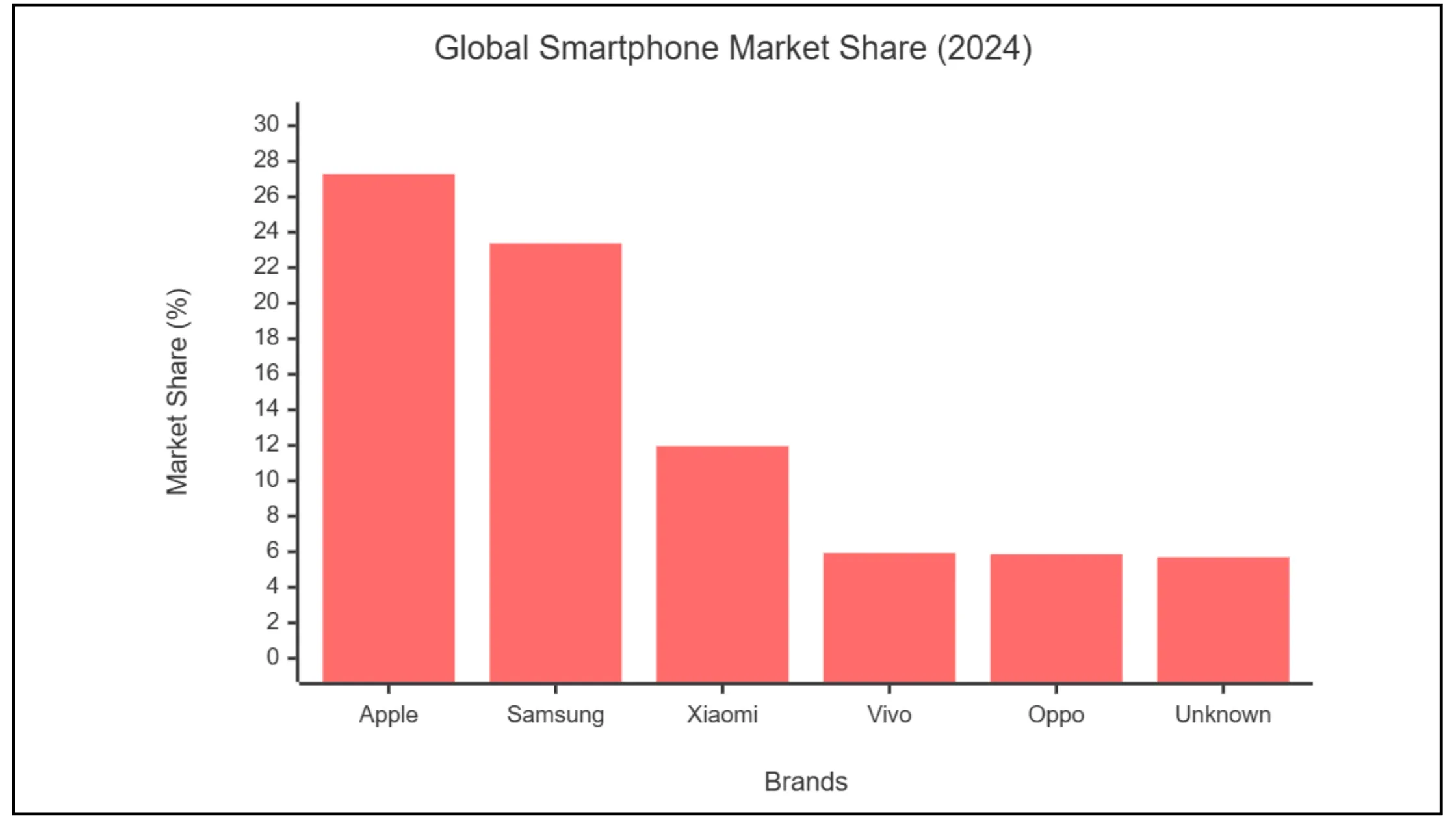
Here are the key aspects to focus on:
First, determine which configurations matter most to your target users by analyzing market shares and user demographics. In the smartphone market, Apple, Samsung, and Xiaomi lead with significant market shares, making them essential testing platforms.
But there’s one more thing to remember:
Beyond different manufacturers, you're handling various screen sizes, operating system versions, and hardware capabilities. Many QA teams find this balancing act challenging.
This is where many QA teams struggle and they end up trying to balance comprehensive coverage with practical limitations.
So what’s the practical approach to manage these challenges effectively?
For this, focus testing efforts on the most impactful devices ensures efficient use of resources and maximizes user satisfaction. To do this effectively, you can use automation tools in cross-platform testing that accelerates the process and enhances coverage across diverse environments.
As a rule of thumb, your testing strategy needs to consider both minimum and recommended testing configurations. The minimum should cover the least advanced devices and oldest OS versions still in significant use, while recommended configurations should include testing on the latest devices and OS versions.
Major companies have already established effective approaches to this challenge. For example, Facebook maintains dedicated device labs for comprehensive testing.

Several tools can strengthen your cross-platform testing:
- BrowserStack delivers cloud-based testing across browsers and devices
- Sauce Labs handles comprehensive automated testing
These solutions reduce the complexity of maintaining physical device labs.
Also, it's crucial to consider the financial implications of cross-platform testing. This includes tool licenses, device procurement, and ongoing maintenance expenses. However, cloud-based testing services can help mitigate some of these costs by providing access to a wide range of devices without significant hardware investments.
6. False Positives and Negatives in Automated Test Results
In this section, we'll cover why false results in automated testing can derail your QA efforts and how to effectively manage them.
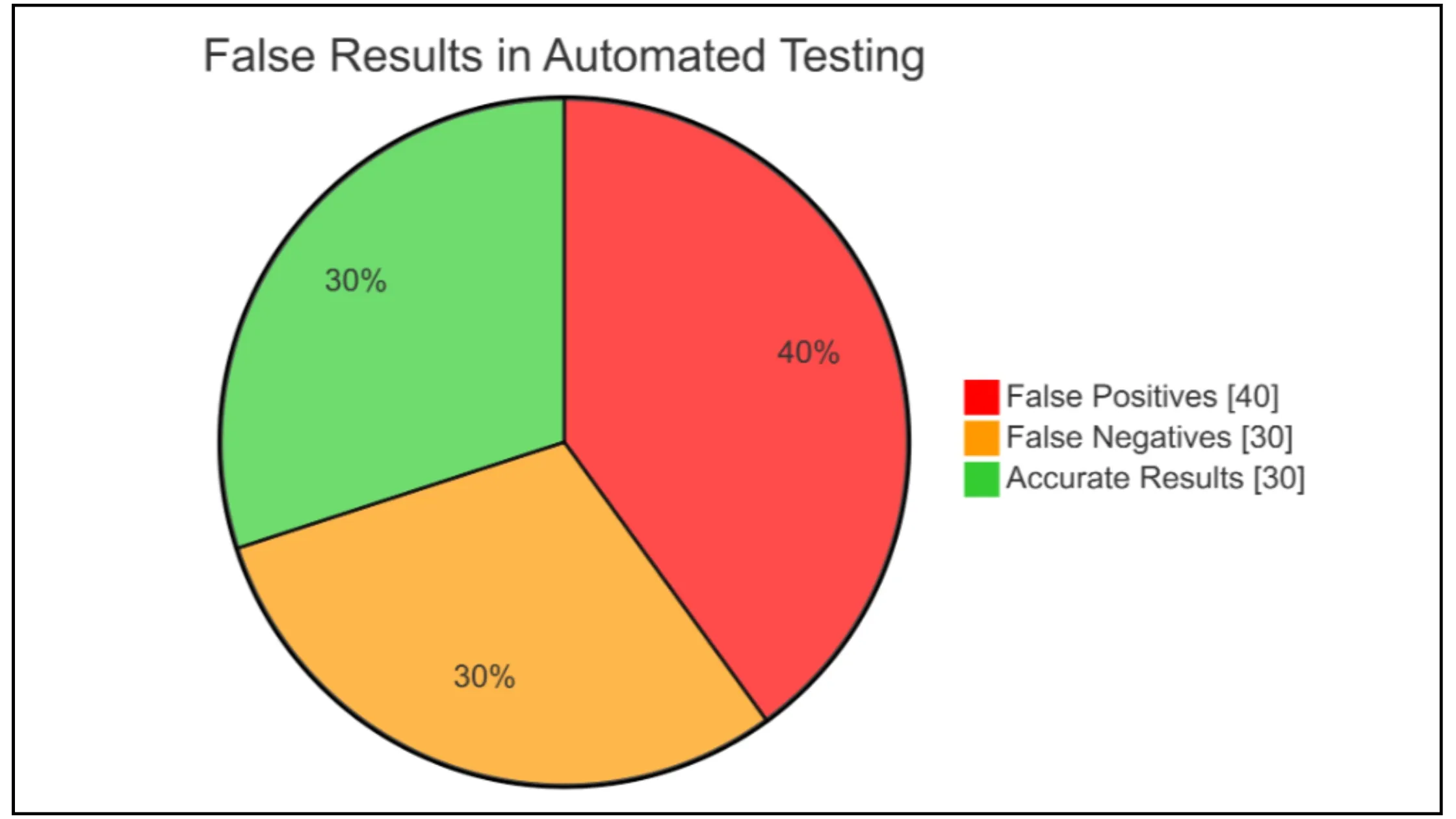
False positives and negatives are among the most challenging aspects of automated testing. They directly impact development efficiency and software reliability.
False positives occur when automated tests incorrectly flag a perfectly functioning feature as faulty. Picture this: your test reports an error in a critical payment feature that's working perfectly. This happens frequently, often due to outdated test scripts or misconfigured test data.
False negatives create serious problems too. These occur when tests miss actual defects, creating a dangerous sense of security.
The business impact of these false results hits hard. Teams waste precious time investigating non-existent issues while missing real deadlines. When false negatives let bugs slip into production, system failures and customer complaints follow.
Here's how to handle this challenge effectively:
Your test scripts need consistent maintenance, particularly after code changes or feature updates.
Watch for these key signs that indicate it's time to update your test scripts:
- Recurring false positives or negatives in your results
- Recent changes in application code or user interfaces
- New feature implementations
- Updates in your testing tools or frameworks
- Developers reporting inconsistent test results
These specific tools help reduce false results:
- Static Code Analysis Tools examine your test scripts without execution
- Test Coverage Analyzers ensure comprehensive testing coverage
- Continuous Integration Systems help identify inconsistent test outcomes
Managing false results requires making test script maintenance part of your regular development cycle. Regular updates keep your test suite reliable and accurate.
7. Budget Constraints on QA Resources and Tools
Studies show that fixing defects post-release can cost up to 100 times more than addressing them during development.
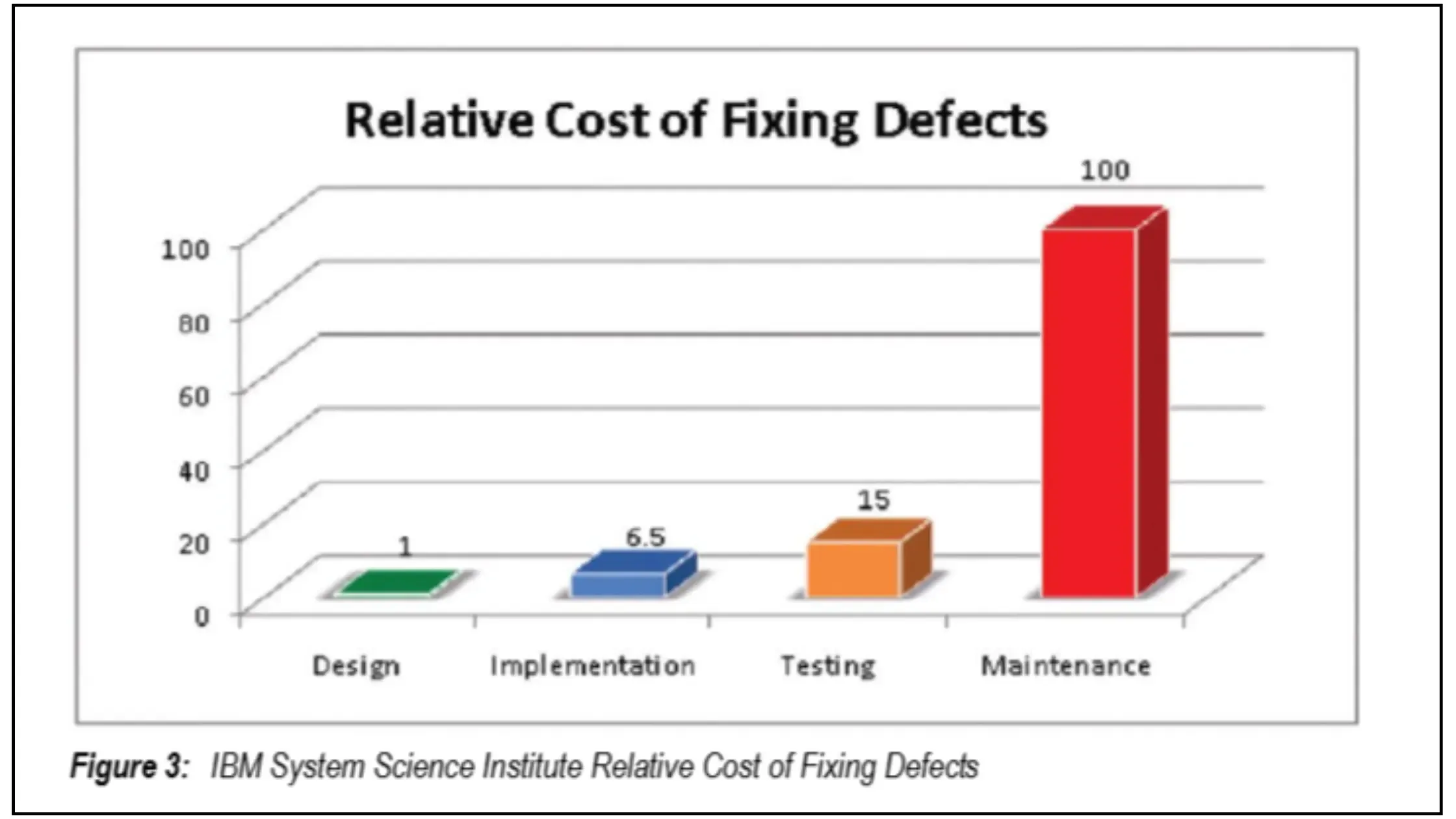
Quality Assurance budgets have shifted significantly over the years. Large enterprises typically allocate about 18% of their IT budgets to QA and esting. The industry saw a peak of 35% allocation in 2015, which settled to around 23% by 2019. These changes pushed companies to be more strategic with their QA resources.
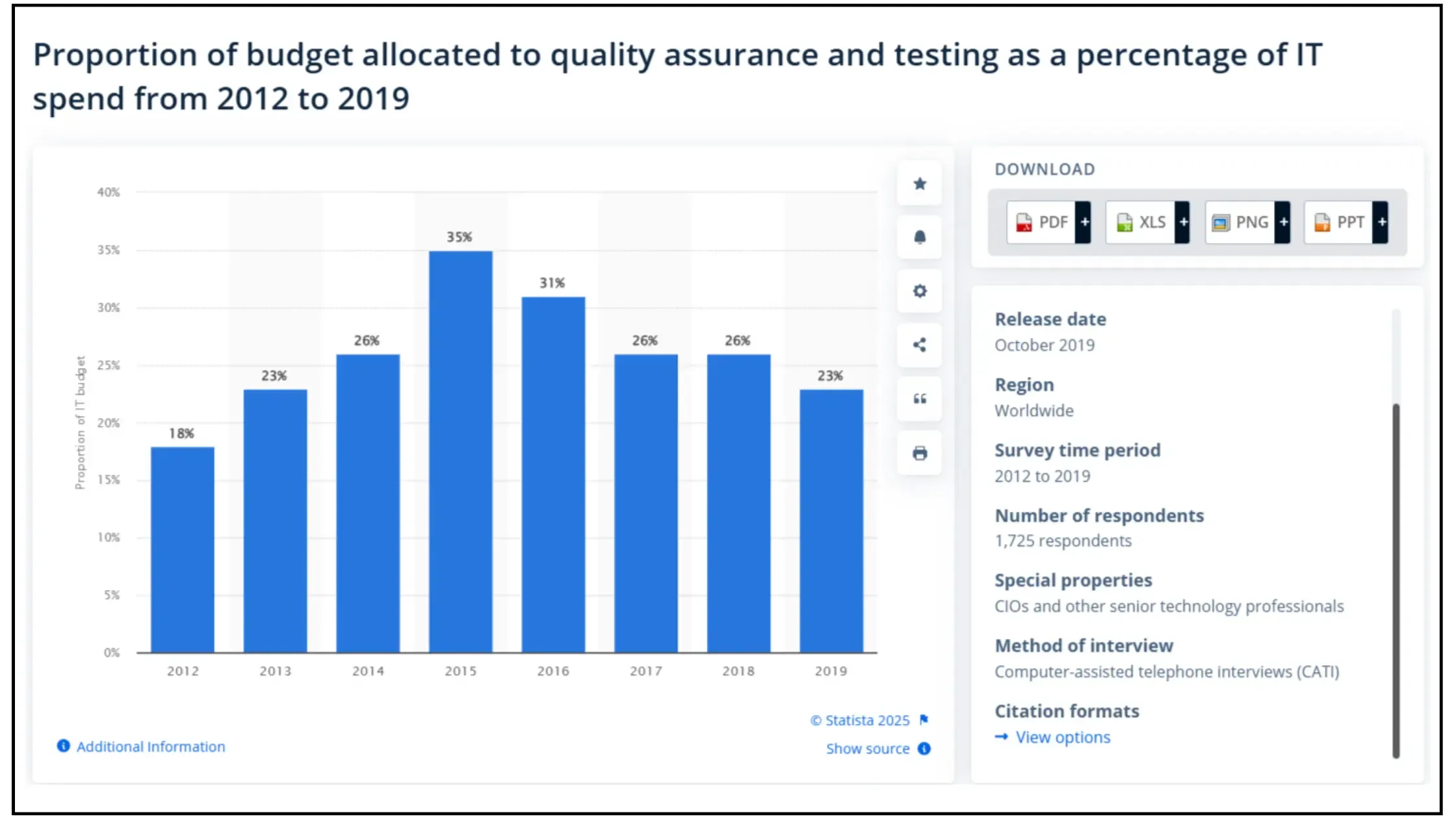
WhenA budgets fall short, companies face problems like reduced testing coverage and late defect detection. The ripple effects go beyond immediate technical issues. Poor QA funding leads to higher maintenance costs, unhappy customers, and serious reputation damage when flawed software reaches users.
A robust QA process needs these core tools, even with tight budgets:
- Test management tools for organizing testing activities
- Automated testing frameworks for efficient regression testing
- Bug tracking systems for defect management
- Performance testing tools for scalability validation
Industry experts have expressed their opinions on this challenge. Lisa Crispin, an Agile Testing expert, advocates for early QA integration in the development process to prevent costly defects.
How can companies measure their QA investment returns? The answer lies in tracking specific metrics:
- Monitoring pre and post-release defect trends
- Analyzing the cost differences between early and late-stage bug fixes
- Evaluating customer satisfaction metrics and support ticket patterns
Smart QA implementation doesn't require massive spending. Take Pfizer's example: Within six months, their QA framework cut core regression testing time by 80%. Business testers performed test automation without deep programming knowledge, which sped up testing and improved accuracy. Pfizer expanded web portals, added new features, and reduced production defects. Their QA framework improved testing efficiency across 64+ applications.
8. Choosing Incorrect Test Types
Now let us show you why relying on a single testing technique is one of the biggest mistakes in quality assurance.
Depending solely on one testing method can leave critical defects undiscovered in your software. A comprehensive testing strategy combines different approaches to ensure thorough coverage.
Here's how different testing techniques work together to create an effective testing strategy.
- Manual testing spots user interface issues and usability concerns.
- Automated testing handles repetitive tasks with precision.
- Performance testing evaluates system behavior under various loads.
- Exploratory testing uncovers unexpected issues that structured testing often misses.
But how should you distribute your testing efforts?
Data shows successful teams typically use: 40% automated testing for regression and repetitive tasks, 30% manual testing for new features and complex scenarios, 20% exploratory testing to find unforeseen issues, and 10% performance testing to verify application stability.
This distribution varies by project needs. Small projects often need more manual and exploratory testing due to resources, while large applications require more automation for extensive regression testing. Finance and healthcare applications demand thorough testing across all types to maintain compliance and reliability.
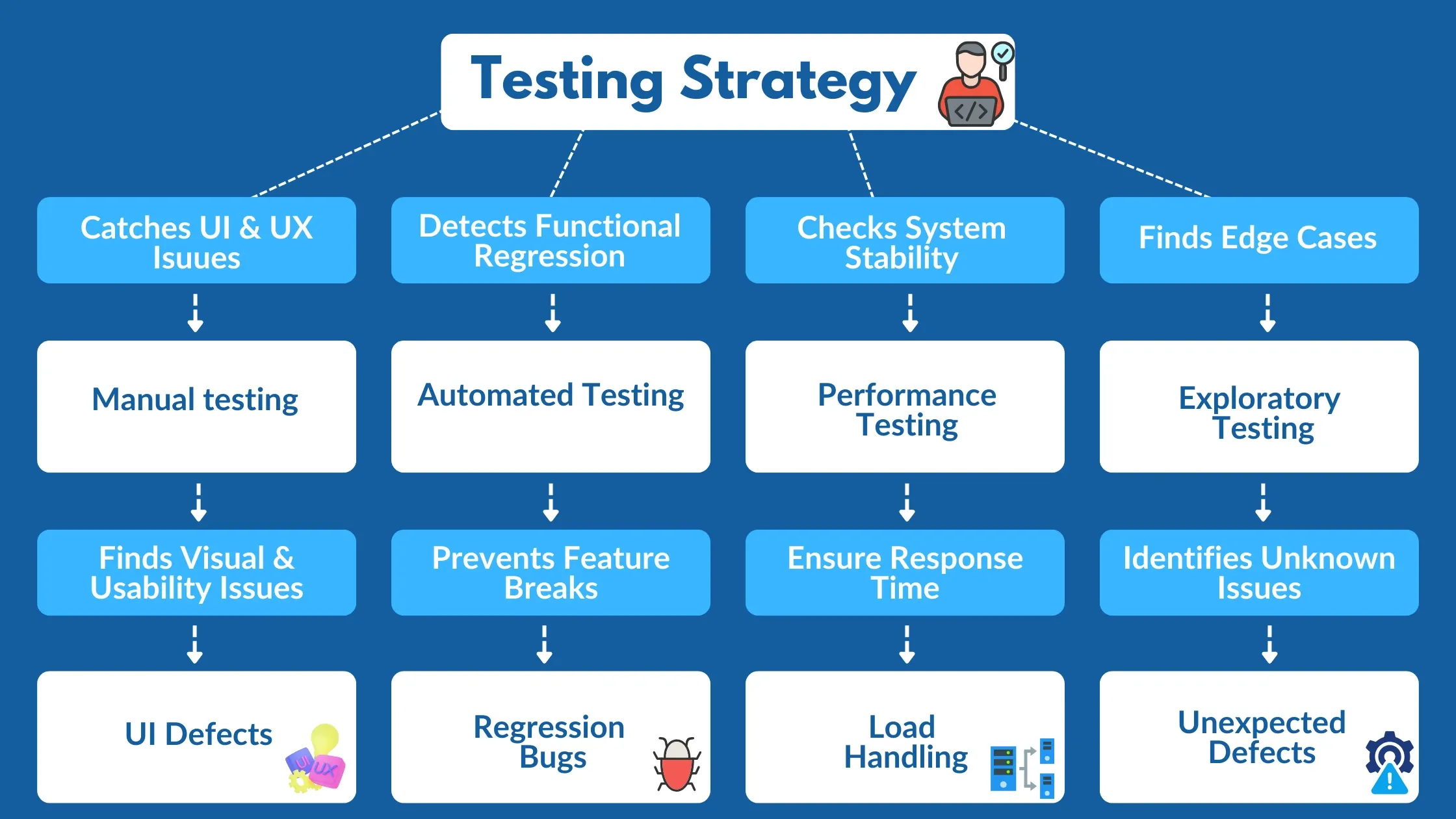
Each testing type targets specific defects:
- Manual Testing: Catches visual discrepancies, alignment issues, and user experience flaws
- Automated Testing: Identifies functional regressions and ensures new code changes don't break existing features
- Performance Testing: Uncovers issues with response times, throughput, and stability under varying loads
- Exploratory Testing: Reveals defects in areas not covered by predefined test cases, including edge cases
While implementing multiple testing techniques may require a significant initial investment, particularly in automation tools, the long-term benefits are substantial. Organizations report reduced time-to-market, lower maintenance costs, and improved product quality leading to higher customer satisfaction.
The Attlassian Code Coverage recommendation is 80%, but achieving 100% coverage is not a guarantee of defect-free software. The most important thing is to focus on critical code paths and functionalities.
9. Not Defining Metrics and KPIs
Now we'll explore one of the most critical aspects of software testing that teams often overlook - metrics and KPIs.
Testing teams need meaningful metrics and KPIs to understand their progress and impact.
Without them, teams can't effectively measure quality or make data-driven improvements.
What makes a metric truly valuable in the testing process?
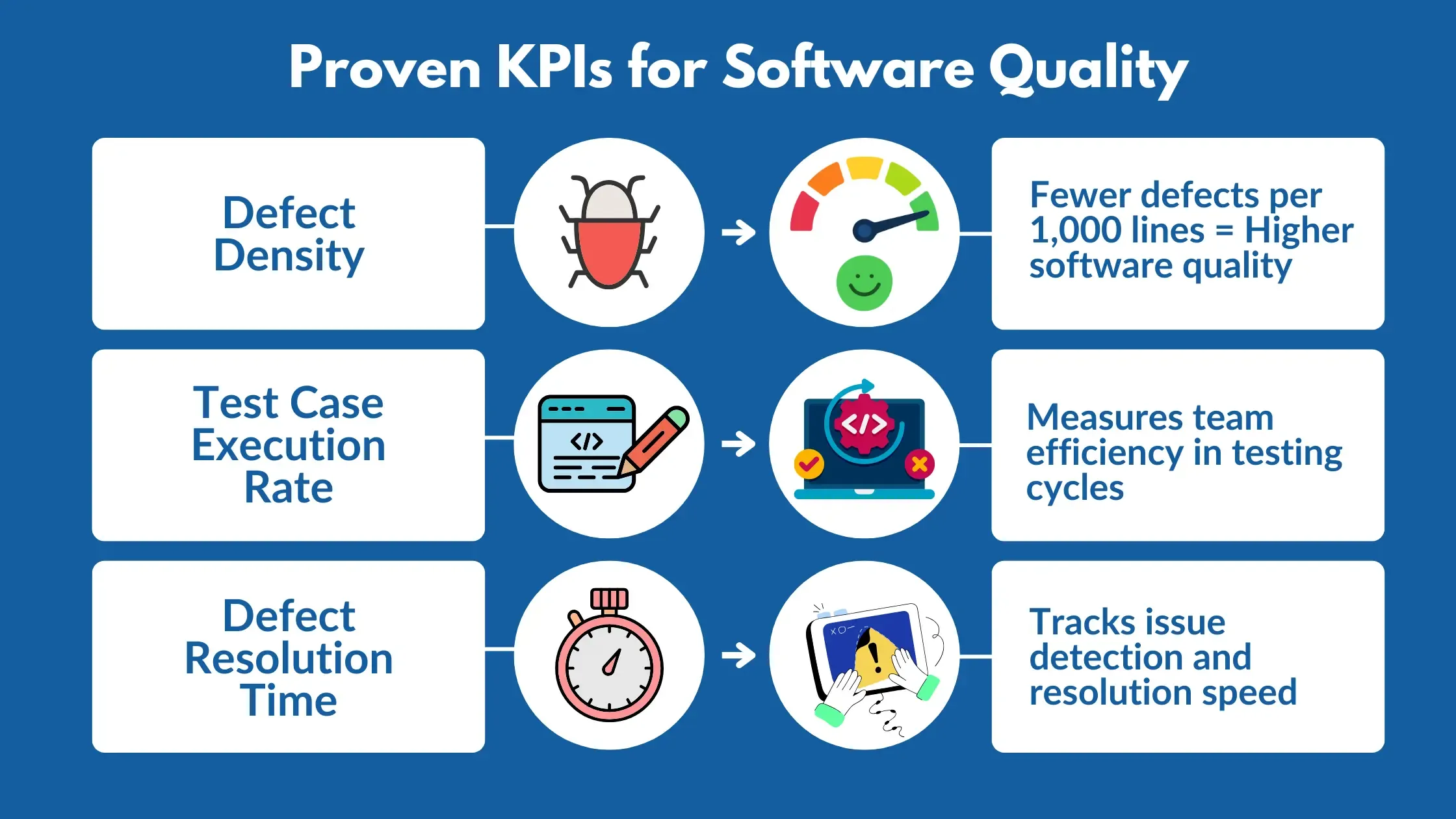
Let's examine proven KPIs that are crucial:
- Defect Density measures the number of defects per 1,000 lines of code. A lower number signals better software quality.
- Test Case Execution Rate shows you exactly how efficiently your team moves through testing cycles.
- Defect Resolution Time reveals how quickly teams identify, address and resolve issues.
Organizations need a structured approach to implement these metrics. Start by defining objectives that connect to business goals, then select metrics providing clear insights. Focus on reliable data collection methods and realistic benchmarks.
The data on industry standards is clear: The average defect density is around 0.5 defects per 1,000 lines of code. Use this as a starting point when evaluating your testing processes.
There are several tools that help teams track these metrics effectively:
Testsigma provides real-time testing performance data
ACCELQ measures team productivity comprehensively
Functionize specializes in process metrics
Implementing these metrics creates accountability and pushes teams toward excellence in testing. Regular monitoring enables better decision-making and improved testing outcomes.
Conclusion
This article has explored these key issues in depth and provided solutions. By adopting these best practices, your team can improve testing efficiency, reduce defects, and accelerate software delivery.
This also gives you a chance of staying ahead of industry trends and continuously refining your testing strategies, and meet evolving user expectations with confidence.
If your organization is struggling with any QA challenges or inefficient testing workflows, then consult ThinkSys to address your concerns about software quality and process optimization.
Frequently Asked Questions
Share This Article:



