How Poor Software Testing Costs Your Business and How to Fix It

Did you know that the cost of poor software testing in the US is over $2.4 trillion, as reported in The Cost of Poor Software Quality in the US (2022)? From lost revenue to damaged reputations, the hidden costs of inadequate testing can cripple even the most promising projects. This article will explore these costs, their root causes, and how to prevent them.
Hidden Costs of Poor Software Testing
Poor software testing leads to wasted testing investment and resources. If it remains unchecked, it can hamper the company in many ways. Below is the breakdown of the actual cost of poor software testing:
1. Loss of Reputation Leading to Increase in Marketing and Customer Acquisition Costs
Software glitches that affect the functionality and user experience of the application often lead to social media criticism and loss of credibility. A study by Emplifi revealed that 86% of customers would not hesitate to leave a brand they loved after facing two or three poor experiences. With existing customers leaving, costs like marketing and customer acquisition will increase.
2. Issuing Refunds
Poor testing can lead to refunds and chargebacks, eating into your profits. Take Cyberpunk 2077, an anticipated game by CD Projekt. After its bug-ridden launch, CD Projekt had to refund over 30,000 users directly and countless more through platforms like the PlayStation Store and Microsoft Store. That’s a massive hit to revenue and reputation.
3. Legal Fines and Compliance Issues
In many industries, software must comply with strict regulations, such as GDPR for data protection or HIPAA for healthcare. Neglecting proper testing, especially regarding data security and privacy, can result in non-compliance with industry regulations and hefty fines.
In 2018, Uber faced such a fine when it suffered a data breach affecting 57 million users. However, Uber tried to cover up this incident instead of accepting it by paying the attacker. Uber was fined $148 million, the highest fine at that time, due to violating the state's data breach and notification laws.
4. Loss of Company Valuation

A single software bug can wipe out millions in company value. In 2012, Knight Capital Group lost $440 million in 45 minutes due to a flawed trading algorithm. Their stock dropped 70%, and they were acquired by a competitor the following year. It showcases how a software bug cannot only cause losses but also devalue the company. This is catastrophic for public organizations or private companies seeking funding in exchange for equity.
Must Read: Why Software Bugs Cost Companies Millions?
5. Technical Debt Accumulation Halting Scalability
Technical debt arises when development teams make strategic trade-offs, such as prioritizing speed over thorough software testing, to meet tight deadlines. While this approach can accelerate delivery, it also introduces underlying code inefficiencies that may require future refinement.
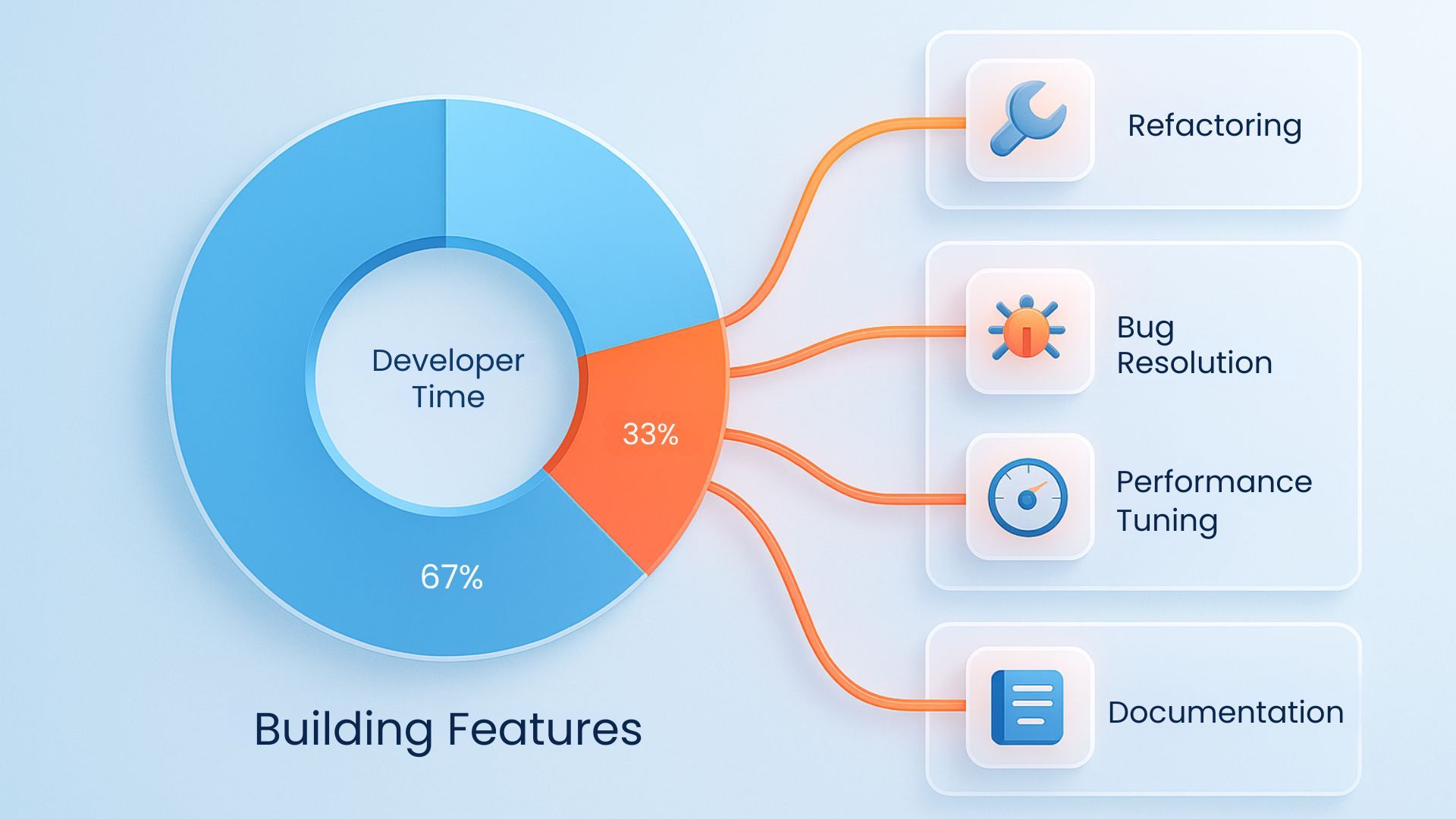
According to Stripe’s Developer Coefficient Report, developers spend 33% of their time addressing technical debt. Over time, technical debt slows development velocity, inflates operational costs, and reduces a product’s scalability.
6. Opportunity Cost
Every moment spent fixing bugs is time lost pursuing growth opportunities. In competitive markets, speed to market is critical. Poor software testing often leads to delays, preventing businesses from launching products or updates on time.
These delays can result in missed revenue opportunities as competitors with reliable and well-tested products seize market share. Furthermore, development teams become bogged down in addressing defects instead of innovating and improving offerings.
Identifying the Root Causes of Poor Testing and Preventing Them
No one deliberately wants poor testing in their organization, but they perform specific actions that lead to it. The following are the top causes of poor testing that you may execute unintentionally.
1. Failure to Vet Software Tools Properly
Organizations often adopt open-source or paid tools without thoroughly evaluating their reliability, security, or compatibility due to time constraints, lack of expertise, or the assumption that widely used tools are inherently safe. However, without proper vetting, these tools can introduce vulnerabilities, compatibility issues, or performance bottlenecks, regardless of whether they are free or paid.
For example, the Log4j vulnerability, an open-source logging library, compromised millions of systems, including those of major companies like Apple and Microsoft.
Even paid tools can pose risks. For instance, SolarWinds Orion, a widely used IT management software, was compromised in a sophisticated supply chain attack in 2020. Many organizations, including government agencies and Fortune 500 companies, were affected because they trusted a well-known vendor without anticipating the possibility of an internal security breach.
What do you need to do?
- Evaluate the Tool: Use vulnerability scanning tools such as Synk or OWASP Dependency Check to identify known security issues. It is an open-source tool that scans project dependencies to identify publicly disclosed vulnerabilities. Moreover, check the tool’s update frequency and community support to ensure it is actively maintained. Also, review the vendor’s security certifications, such as ISO 20071.
- Perform Proof-of-Concept (PoC) Testing: For this, you need to simulate real-world scenarios to identify potential bottlenecks or integration challenges. Ensure they integrate seamlessly with your existing infrastructure and workflows. Document the PoC results to make an informed decision about whether to proceed with adoption or not.
- Monitor and Maintain Tools Continuously: For open-source tools, subscribe to security mailing lists or forums to stay informed about vulnerabilities and updates. For paid tools, ensure timely support and updates. In addition, you can maintain a software bill of materials (SBOM) to track all tools and dependencies, making it easier to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Evaluate Long-Term Viability: Assess whether the tool will likely be maintained and supported in the long term. For open-source tools, check the activity level of the maintainers.
2. Neglecting Third-Party Integrations
Modern applications often rely on third-party APIs and services, but many teams fail to test these integrations thoroughly. This oversight can lead to system failures when external services behave unexpectedly, such as service downtime, API rate limits, or data format mismatches. Without proper testing, these issues can go unnoticed until they cause significant disruptions.
What do you need to do?
- Conduct End-to-End Integration Testing: Test all third-party integrations in real-world scenarios, including edge cases like API rate limits, downtime, and data format mismatches. Ensure that error handling is robust and that the system can recover from third-party failures.
- Implement Monitoring and Fallback Mechanisms: Set up real-time monitoring for third-party services using tools like Datadog or New Relic to track API performance and availability, enabling early detection of failures. Additionally, design fallback mechanisms, such as cached data or alternative services, to ensure continuity during outages. Redis, Kong Gateway, and Hystrix are some of the tools that can help you in this.
- Test Under Real-World Conditions: Perform load testing, failure scenario testing, and data validation testing to simulate service outages, API throttling, and data inconsistencies. Tools like Postman, SoapUI, and JMeter can help automate these tests.
- Document Integration Scenarios: Maintain detailed documentation of all integration scenarios, including expected behaviors, error-handling procedures, and fallback mechanisms. This ensures that your team can quickly troubleshoot issues and effectively onboard new members.
3. Missing Out on Security Testing
According to the Application Security in the DevOps Environment report by HCL Software, 20% of organizations do not test for security vulnerabilities. Some organizations deprioritize security testing due to budget constraints, time pressures, or the misconception that they are unlikely targets.
However, attackers frequently exploit these assumptions, leading to data breaches, unauthorized access, and compliance violations. For instance, Target Corporation’s 2013 data breach, which exposed 40 million credit and debit card records, was traced to inadequate security testing and weak third-party vendor management.
What do you need to do?
- Adopt a Shift-Left Approach: Shift-left integrates security early in the SDLC, allowing you to identify and fix vulnerabilities before they reach production. Combine this with static application security testing (SAST) tools like SonarQube or Checkmarx to analyze code for vulnerabilities during development.
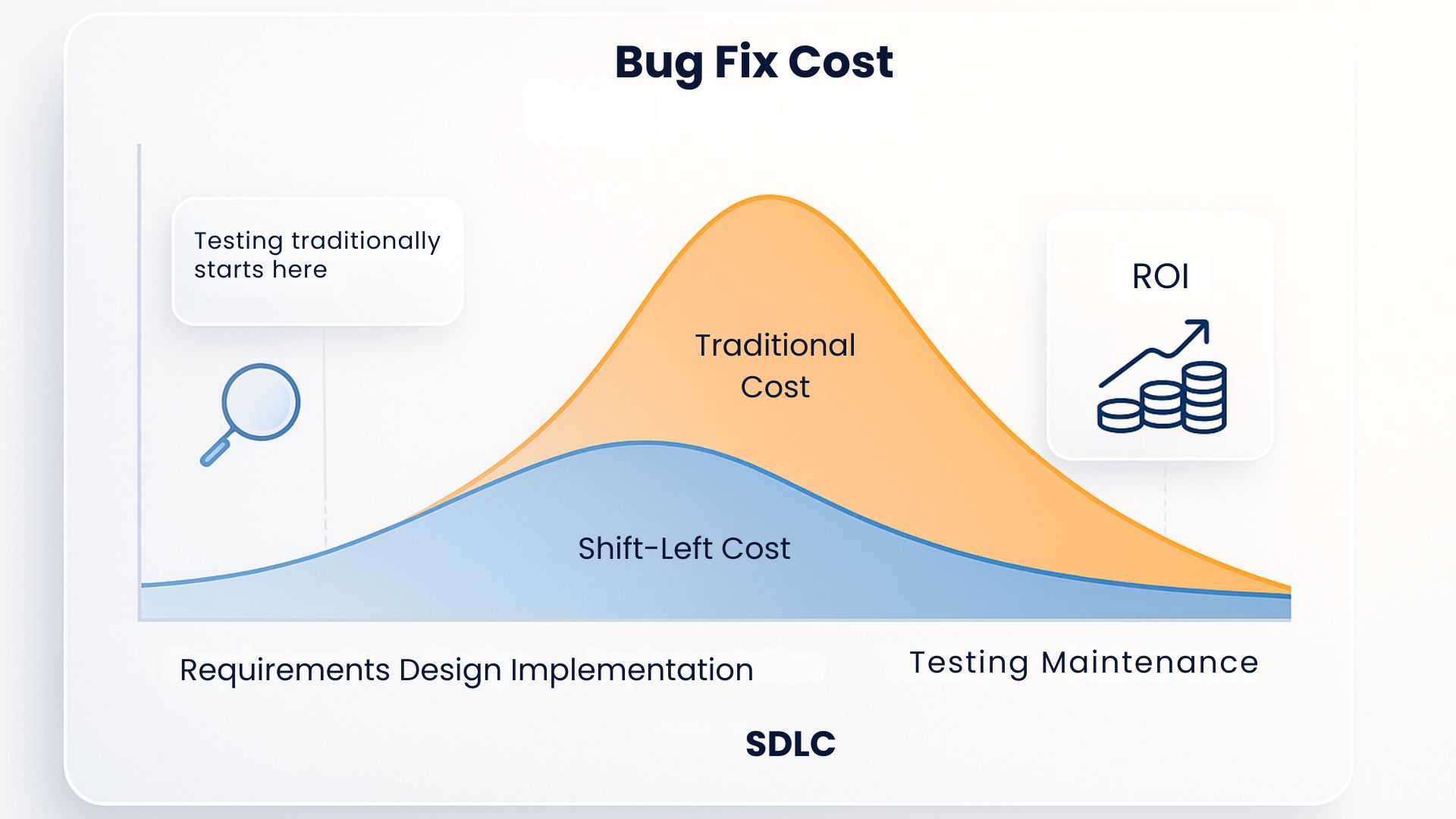
- Conduct Regular Penetration Testing: The best way to conduct a pen test is by hiring skilled ethical hackers to simulate real-world attacks and uncover security weaknesses. Make sure to perform internal and external pen tests to evaluate your system's resistance to attacks.
- Training and Guidance on Secure Practices: Though ensuring security is surely one of the testers' many jobs, they’re not the only ones responsible for it. Everyone involved with the software, from the developer to the marketer, should be trained in the proper security practices and vulnerabilities through third-party or in-house training. You can also include security practices in your in-house magazines or emails.
- Adopt a Zero-Trust Architecture: Design your application with a zero-trust approach, where every user and device is verified before accessing resources. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Create a Cyber Incidence Response Plan: Prepare for potential breaches by creating a structured response plan that includes immediate containment strategies, communication protocols for internal and external stakeholders, roles and responsibilities of response teams, and post-incident analysis and improvements.
4. Insufficient Test Coverage
Insufficient test coverage occurs when critical parts of the application are untested, often due to misaligned testing priorities, lack of resources, or incomplete test cases. Untested areas of the application are more likely to contain bugs, crashes, or security vulnerabilities. For example, if a banking app fails to test its loan calculation module, users may encounter incorrect calculations, leading to financial losses and regulatory penalties.
What do you need to do?
Prioritize Risk-Based Testing: As the software scales, the number of test cases increases. This leads to the need to prioritize test cases based on factors including business impact, frequently updated areas, customer usage patterns, and complexity.
- Use Code Coverage Tools: Tools like JaCoCo, Ncover, Istanbul, and SonarQube can help measure test coverage and identify untested areas. Aim for a balance between unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests to ensure comprehensive coverage. For instance, unit tests can validate individual components, while integration tests ensure that these components work together seamlessly.
- Develop Comprehensive Test Cases: Ensure test cases cover all functional and non-functional requirements, including edge cases and error scenarios. For example, if your application includes a login feature, test for scenarios like incorrect passwords, expired sessions, and account lockouts. Regularly review and update test cases to reflect changes in the application.
5. Inadequate Automation in Testing
Many organizations either struggle with inadequate automation due to a lack of clear strategy, or they believe that manual testing is their need of the hour. This results in over-reliance on manual testing, which is time-consuming, error-prone, and difficult to scale.
Without proper automation, testing becomes a bottleneck in the development process. Teams struggle to keep up with frequent releases, leading to rushed testing, overlooked bugs, and poor-quality software.
What do you need to do?
- Develop a Clear Automation Strategy: Developing a clear automation strategy starts with identifying which tests to automate and which to run manually. Focus on automating repetitive, high-risk tests like regression and smoke testing using tools like Selenium or Cypress. For tests that require human intuition, such as exploratory or usability testing, stick to manual execution. Begin with critical workflows, monitor results, and gradually expand automation based on coverage gaps, business impact, and ROI.
- Adopt Behavior-Driven Development (BDD): Use BDD frameworks like Cucumber or SpecFlow to create tests that are easily understandable by both technical and non-technical stakeholders. This ensures that everyone is on the same page regarding the application’s expected behavior.
- Leverage AI-powered testing Tools: Use AI-driven tools like Testim or Applitools to automate complex test scenarios and improve test accuracy. These tools can also help identify patterns in test failures, making it easier to address underlying issues.
- Monitor and Optimize Test Scripts: Regularly review and optimize your test scripts to ensure they remain effective as the application evolves. Make sure to remove redundant tests and update scripts to reflect changes in the application.
6. Lack of Resources and Expertise
Poor software testing often stems from a lack of skilled personnel, budget, time, or infrastructure. Without adequate resources, companies struggle to identify and fix hidden bugs, leading to inefficient processes and subpar product quality.
For example, a small startup may lack the budget to hire experienced testers, which can lead to frequent crashes and negative reviews.
What do you need to do?
- Accurate Estimation of Needed Resources: Conduct a thorough assessment of testing requirements, including scope, complexity, and risks, to determine the necessary tools, infrastructure, and personnel. Tools like Jira and Asana streamline tracking, ensuring no task or bug goes unnoticed.
- Leverage Cloud-Based Testing Platforms: According to MarketsandMarkets, the cloud testing market is expected to grow by 15% annually, highlighting its effectiveness. Cloud platforms like BrowserStack or Sauce Labs offer access to diverse devices, browsers, and environments without hefty infrastructure costs. This ensures scalability and comprehensive test coverage. You can also use analytics tools to monitor results and generate actionable insights.
- Outsource Testing to Experts: Partnering with specialized testing firms gives you access to skilled professionals, advanced tools, and industry best practices without heavy in-house investment. Start by identifying your security or performance testing needs and researching reputable firms with proven track records. Clearly define goals, timelines, and deliverables in a contract, and maintain regular communication to ensure alignment.
Conclusion
Effective software testing is critical for delivering high-quality, reliable applications, yet many organizations struggle with challenges like inadequate resources, lack of expertise, and insufficient automation. However, navigating these challenges alone can be risky.
Professional assistance brings the expertise and resources needed to tailor testing strategies to your business needs, ensuring optimal performance and customer satisfaction. The right professional support isn't just beneficial for your business but also essential for delivering reliable, scalable, and high-quality products.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Share This Article:



