Cybersecurity Testing: Integrating QA to Detect and Prevent Data Breaches
Would you trust a company that couldn’t protect your data? Probably not, and neither would most consumers. Studies show that over half of Americans would rather take their business elsewhere than work with an organization that has been a victim of a cyberattack.
Unfortunately, most businesses aren’t aware of whether they are exposed to such attacks. Like many other companies, your organization can be the next victim of cyber threats.
So, how can you protect your businesses from these attacks? The answer lies in cybersecurity testing. This article will guide you on how rigorous quality assurance (QA) practices can expose vulnerabilities before hackers do and prevent your organization from becoming the next victim of digital attacks.
Risks and Potential Impact of Data Breach
Why are data breaches considered so dangerous for an organization? The reason is the aftermath of a cyberattack that companies must face. With that in mind, the following section depicts the impact of a data breach on an organization:
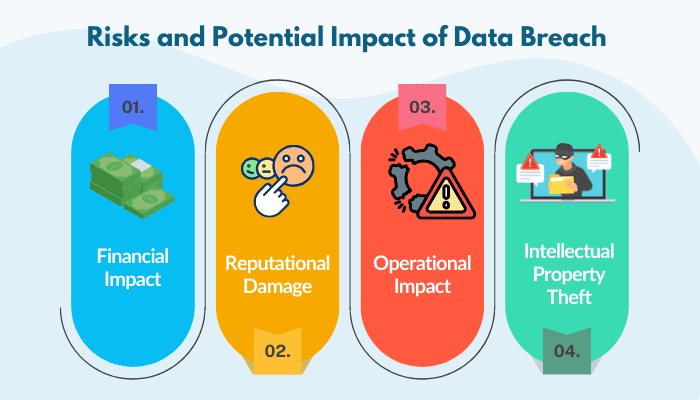
- Financial Impact
In 2017, Equifax faced a massive data breach, exposing 143 million records due to poor security practices. From lawsuits to regulatory fines, the company had to pay $700 million for settlements, impacting its financial standing. - Reputational Damage
Yahoo, a renowned search engine, compromised 3 billion user accounts in a 2013 data breach. Not only that, but the company’s mishandling of the incident delayed its disclosure, damaging its reputation. As a result, Verizon, the company that acquired Yahoo, reduced its acquisition cost by $350 million, illustrating the long-term impact of cybersecurity failure. - Operational Impact
In 2024, Krispy Kreme INC, an American-based doughnut MNC, faced a cyberattack that disrupted its online business. Though customers can order from stores, their online ordering was disrupted. Not only did it hinder digital sales, but their stock price plummeted by 2%. - Intellectual Property Theft
Sony Pictures faced a massive cyberattack allegedly linked to North Korea, resulting in leaked unreleased movies and confidential emails. This breach not only caused financial loss but also exposed sensitive company communications, damaging relationships and revealing strategic business plans to competitors.
How Cybersecurity Testing Protects Against Data Breaches?
Cybercriminals are always on the lookout for vulnerabilities within a system. By proactively identifying and addressing security gaps, cybersecurity testing as part of QA can prevent cyber threats from damaging your organization.
1. Finding Security Vulnerabilities Before Hackers Do
Businesses face data breaches because they fail to realize that their system has vulnerabilities. With prompt identification of security loopholes, you can stay ahead of cyber threats and prevent expensive data breaches.
Key Security Measures:
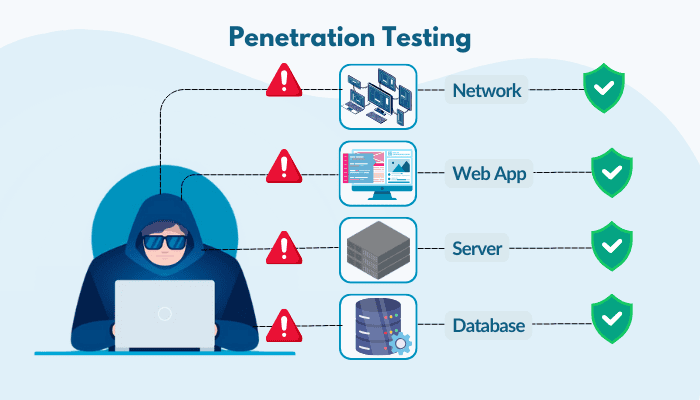
- Penetration Testing: Also referred to as ethical hacking, pen testing involves simulating real attacks on the program to breach security. Cybersecurity experts try to penetrate the security walls of the program to test network security, servers, web apps, and databases and identify potential entry points for the attacker.
- Security Code Reviews: Here, the developers review and test application code to catch security loopholes, such as SQL injection vulnerabilities, that could expose sensitive data.
- Configuration Testing: Standing at number 5 on OWASP Top 10, security misconfigurations have been among the top reasons for data breaches. Configuration testing involves testing the configuration of servers, cloud storage, firewalls, and features to ensure they are set up correctly.
2. Testing with Real-World Scenarios
Finding weaknesses surely helps in making your application security robust, but that’s not enough to prevent an attack. You need to know how your business would behave in the event of an attack. With a strong resilience testing strategy, you can stay prepared for potential threats that may arise.
Key Security Measures:
- Incident Response Testing: Simulating an actual cyberattack on your organization to assess how well your team responds to such an attack is what incident response testing is all about. If employees don’t know how to react on time, an attack could escalate quickly. The goal of this testing is to identify your team's preparedness in case of a legitimate attack.
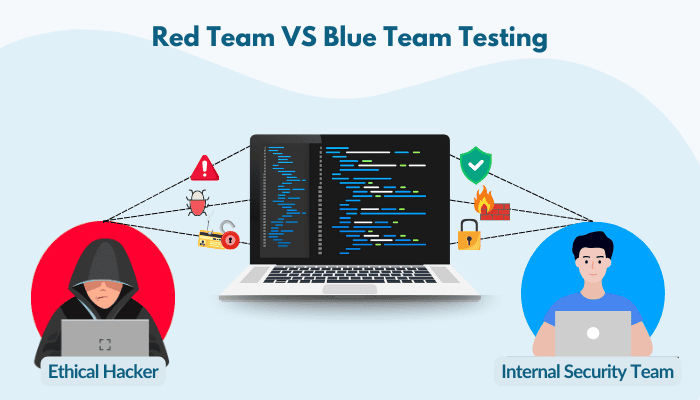
Red Team VS Blue Team Testing: Another approach utilized by cybersecurity experts is performing red team vs. blue team testing. The red team (ethical hackers) tries to break the company systems, whereas the blue team (internal security team) defends the company from such attacks.
3. Meeting Security Standards and Compliance
Many businesses must meet dedicated security standards and compliances to avoid fines and reputational damage and keep organizational data secure. The QA team identifies and aims to comply with the required cybersecurity standards.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission developed the ISO 27000 series to ensure the utmost security from data breaches. It involves a set of standards that the organization should meet:
- ISO 27001: Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) aims to protect sensitive company information to ensure its confidentiality and integrity.
- ISO 27002: Implemented alongside ISO 27001, it offers detailed guidelines and best practices for enhancing an organization's overall security measures.
- ISO 27005: Providing a structured framework for identifying, analyzing, and mitigating risks, ISO 27005 helps in prioritizing security efforts and allocating resources effectively.
- ISO 27017: It is focused on cloud security and provides guidelines specifically tailored for cloud service providers and users to help organizations implement robust security controls to protect data stored and processed in the cloud.
In addition, several compliances should be met to avoid heavy fines and legal issues. Such compliances are:
- PCI Standards: Every organization handling digital payments through debit or credit cards should comply with PCI Standards. Complying with this standard ensures the user that the organization processes and stores the card details securely. Failure to abide by this can result in fines of $5000 to $10,000.
- GDPR: The General Data Protection Regulation mandates that every organization, no matter where it’s based, ensure the privacy, transparency, and user consent of EU residents. Companies that fail to comply with GDPR can expect a fine of up to $20,000 or 4% of the global annual turnover, whichever is higher.
4. Integrating Artificial Intelligence to Prevent Attacks
Cybercriminals are utilizing AI-powered attacks to bypass many traditional security practices. It has been reported that over 70% of professionals experience the consequences of AI-linked cyber threats within their companies. You need AI-enabled cybersecurity, as it can detect, analyze, and stop an attack faster than humans and provide ongoing security.
Key Security Measures:
- AI-Powered Threat Detection: AI is programmed to analyze user behavior and patterns to recognize any anomalous activity that may arise from a cyberattack. AI-enabled tools, such as Darktrace and Cylance, analyze network traffic continuously, 24/7, and can detect unusual traffic.
- Automated Penetration Testing: Pen testing is a vital technique in cybersecurity; however, it does not always need to be performed manually. AI-assisted pen testing can simulate cyber attacks continuously to identify vulnerabilities within the app, servers, and networks. Pentera and HackerAI are the two leading AI-enabled pen testing tools that can aid QA teams in fixing vulnerabilities.
- AI-Enhanced Incident Response: There can be a slight delay between an attack and a response by a professional. This delay can provide attackers with the required time to breach security. AI-powered security platforms such as Cortex XSOAR and IBM QRadar can react to an attack instantaneously by isolating the infected system, blocking malicious traffic, and neutralizing the threats in the initial stage.
5. Protecting Third-Party Integrations
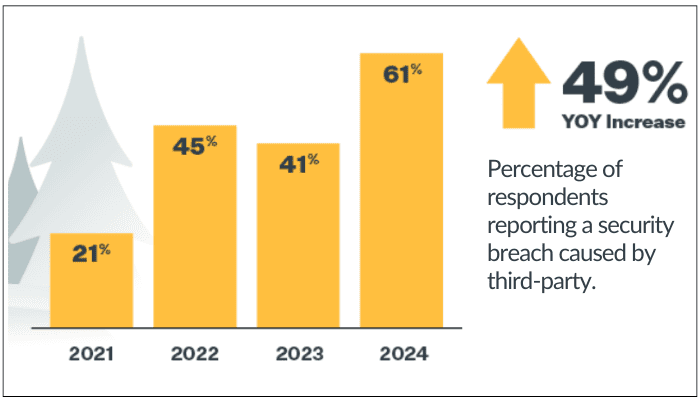
According to a 2024 study by Prevalent, 61% of people have faced a third-party breach in their organization in 2023. Even if you have strong security measures in place within your organization, you could become a victim of cybercrime sooner than expected if you’re not paying attention to the third-party vendors you choose.
Ensuring that third-party integrations are secure is a significant part of cybersecurity testing in QA, helping businesses prevent supply chain attacks, API vulnerabilities, and data breaches.
Key Security Measures:
- Testing Third-Party Vendors or Tools: One of the initial actions the QA team can take is to assist you in evaluating your external partner. An astounding 54% of organizations do not monitor the security and privacy practices of third-party vendors.
QA team will conduct a vendor security review before integrating any third-party solution to review compliance certifications, security policies, incident response capabilities, and how many security breaches have happened in the past. If QA notices anything out of the ordinary, they will flag the vendor. - API Security Testing: Several third-party integrations rely on Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), which can be used as an entry point for attackers if not properly secured. QA will do input validation tests, authentication tests, and token-based access control testing to ensure that APIs do not expose sensitive data or allow unauthorized access.
- Continuous Monitoring: In addition to background checks, it is crucial to monitor their security practices continuously as their security posture changes. CyberGRX and Panorays are the top tools for identifying suspicious activity in third parties. Doing so will allow you to stay updated with their latest security practices and remain confident in the security practices of your vendor or tool.
Identifying Your Cybersecurity Testing Needs
If you’re planning to improve the security of your organization, you need to understand the areas that require security. And that can be achieved by identifying your security testing needs.
- Detect Business-Critical Assets
A business handles various types of data, be it credit card information, names, addresses, inventory, employee records, product designs, and more. As a business, you need to identify the critical data that should be prioritized for protection. - Assess Industry-Specific Threats
Every industry has unique risks that need to be addressed. For instance, the manufacturing industry faced the highest number of cyberattacks in 2023, whereas media and telecommunications faced the least attacks. You need to identify and prepare for the risk as per your industry. - 3. Identify Security Gaps from Past Incidents
If the company has faced a breach in the past, it should consider strengthening its security. Determining factors such as how the breach occurred, which security weaknesses were exploited, what defenses failed, and what the entry point was can help prevent similar attacks in the future. - Third-Party Security Evaluation
One of the most effective ways to identify areas that need attention is to have a third-party service provider evaluate your organization. Some providers offer cyber risk rating services, where they assess your security posture and provide a report detailing vulnerable areas.
How to Assess and Improve the Current Cybersecurity Testing Process?
Step 1: Change Your Mindset
Sometimes, businesses, especially SMEs, believe they are not on cyberattackers' radars simply because they are not big enough, but attackers don’t discriminate based on size. From a small local business to a well-established corporation, cybersecurity is essential to protect your operations.
- Startups and SMEs: Startups and SMEs handling smaller data volumes than large corporations often believe they are too small or that their data is not valuable enough to be targeted. However, such companies are prime targets of cyberattacks because they lack security measures. Cybercriminals exploit weak defenses to steal customer data, intellectual property, or financial information.
- Established Companies: In many cases, well-established companies don’t put focus on updating their existing cybersecurity practices because of the fact that they’ve not been attacked yet. Unlike such companies, cybersecurity threats evolve constantly. Legacy systems, outdated software, and reliance on old security practices create gaps that attackers can exploit.
- Companies Handling Customer Data: Companies such as HIPAA and GDPR protect companies functioning in healthcare and finance to some extent. Even though complying with guidelines is essential, they never guarantee protection. Continuous cybersecurity testing helps these businesses go beyond compliance to actively protect against emerging threats.
- SaaS and Cloud-Based Businesses: Many SaaS companies using cloud infrastructure assume their cloud service provider manages all security risks. Cloud security follows a shared responsibility model, meaning the provider secures the infrastructure, but businesses must secure their own applications and data. Not having cybersecurity in place and relying solely on a cloud provider's security is never advised and acts as an invitation to attackers.
Step 2: Monitor These KPIs If You’re Already Implementing Cybersecurity
The first step towards improving security testing is to understand its current effectiveness, and you can do that by monitoring KPIs.
- False Positive Rate: This metric indicates the frequency at which you’re notified about a threat that later turns out to be a false positive. Having too many such notifications can reduce credibility and lead to alert fatigue.
- Mean Time to Detect: With this metric, you can know the average time taken to detect a vulnerability. A longer MTTD could indicate the slow detection of issues.
- Escaped Defect Rate: Issues that bypass testing and reach production come under the escaped defect rate. A higher rate suggests ineffective security testing, leaving the systems vulnerable.
- Vulnerability Discovery Rate: Using this metric, you can monitor the number of vulnerabilities identified within a specific timeframe or before release. Having a higher vulnerability discovery rate showcases the high efficiency of the security testing process.
- Mean Time to Remediate: In this metric, you’ll get to know the average time consumed to fix a security vulnerability. The higher time depicts an inefficient incident response process.
Step 3: Improve Your Current Cybersecurity Testing Processes
Even businesses with existing security measures must regularly improve their cybersecurity testing strategies to keep up with evolving threats. If you leverage cybersecurity testing, here’s how you can strengthen your current approach:
- Align Security with Business Growth
Growth can occur in various ways, including new locations, expanded customer data types, product launches, and cloud migrations. Sticking to the same security process may not be sufficient to protect all of this, and you need new strategies and processes, such as zero-trust security, continuous security assessments, automated threat detection, strict access controls, data encryption, and DevSecOps integration, that adapt to the evolving risk landscape that comes with a growing business. - Implement Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST)
Unlike traditional testing, IAST continuously analyzes applications in real-time while they are running, detecting live security threats without false alarms. Not just a notification, IAST offers an in-depth report on the ways the vulnerability impacts the overall functionality of the system, ensuring that the reported issue is not a false alert. HCL AppScan or Synopsys Seeker are the top tools that you can use to deploy IAST.
Read More: How to perform security testing on a web application?
- Secure APIs to Prevent Third-Party Breaches
Third-party breaches are among the top contributors to cyberattacks. Weak APIs can allow attackers to penetrate your security layers, compromising sensitive business and customer data. All you have to do is conduct API security testing using Postman Security, OWASP ZAP, Burp Suite, or any other reliable tool. - Integrate Bug Bounty Programs to Discover Unknown Vulnerabilities
A bug bounty program is when a company rewards ethical hackers for finding and reporting security flaws in your system. The reward can be as low as $50, and you’ll be aware of a bug that could lead to a potential data breach.
How Much Does Cybersecurity Testing Cost?
Factors including size, industry, infrastructure complexity, and frequency contribute to cybersecurity testing costs.
You have two options for cybersecurity testing: either establish an in-house team or outsource the testing. Each route comes with a different cost.
Option 1:
In-house Team: Hiring an in-house team requires you to employ a cybersecurity team, including:
| Role | Annual Salary Range (in USD) |
| Security Analyst | 55K to 115K |
| Security Engineer | 75K to 130K |
| SOC Manager | 144K to 173K |
| Chief Information Security Officer | 175K to 260K |
Apart from salaries, you must also bear the cost of tools, including firewalls, antivirus software, two-factor authentication, and other related expenses. The average annual cost of maintaining an in-house team, including salaries, training, and tools, ranges from $750,000 to $2 million.
Option 2:
Outsourcing: On the other hand, you can outsource cybersecurity testing, where an external company will secure your organization. The average cost ranges from $40,000 to $300,000 annually, depending on the size, complexity, number of audits, and other factors.
While some companies may hesitate to spend, the reality is that the financial impact of a data breach exceeds the investment. Cybersecurity testing can help you avoid:
- Reputational damage, legal fees, and, in some cases, ransomware payments.
- Penalties imposed by the government for non-compliance with data protection laws.
- Loss of revenue caused by security incidents interrupting operations.
- Damage to brand credibility, leading to an increase in customer churn.
Rather than viewing cybersecurity testing as an expense, businesses should see it as a tactical investment that avoids financial and reputational losses while ensuring long-term protection.
Essential Steps to Control Damage after a Breach
The best cybersecurity measures surely reduce the probability of an attack, but they certainly never guarantee that your organization is entirely safe. Even with the utmost security, organizations may face cyberattacks. Not just prevention but cybersecurity measures are taken to minimize the damage after an attack.
1. Contain the Damage and Secure Critical Systems
After facing a breach, your primary step should be to limit the impact of the breach immediately. Take necessary actions like restricting access to compromised systems and shutting down affected networks. Furthermore, any unauthorized access should be revoked, and the security team should take control before the situation escalates.
2. Assess the Financial Impact
Getting a clear picture of the breach is important for making informed decisions. It’s essential to pinpoint the areas impacted, the data that may have been exposed, any financial losses incurred, and how the stakeholders are feeling about the situation.
3. Communicate Transparently with Stakeholders and Regulators
Once you have a detailed report on the breach, it should be your responsibility to communicate transparently with affected customers, partners, and regulators. While not revealing it may seem the right choice, communicating correctly helps maintain trust and credibility. Furthermore, regulations such as GDPR mandate the reporting of any breach within 72 hours of identification, and failure to do so can result in severe penalties.
4. Notify Relevant Authorities
After a breach, it’s your responsibility to notify the relevant authorities based on your location and industry regulations. The authorities you may need to contact include:
a) For the USA (Federal and State Level)
- Federal Trade Commission for breaches involving consumer data or electronic personal health records under the Health Breach Notification Rule.
- Department of Homeland Security for critical infrastructure breaches.
- Many states in the US, including California, New York, Texas, and Florida, require companies to report breaches to the state attorney general’s office within a specific timeframe.
b) European Union (EU)
- As part of the GDPR, organizations are required to report breaches within 72 hours to the relevant national data protection authority (DPA).
- National Law Enforcement for breaches that result in criminal activity or large-scale impacts.
5. Connect with Cybersecurity and Legal Experts
Data breaches are more than just a vulnerability, as they involve business and legal complications. You need to start by connecting with renowned cybersecurity experts who will diagnose the entry point of attacks and recommend the right security practices like data encryption, two-factor authentication, and role-based access controls. Additionally, consulting with legal professionals to ensure compliance with data protection laws is recommended.
6. Keep Up with Emerging Threats
Cybersecurity practices are evolving rapidly, and so are digital threats. The only way to stay protected is by staying updated with emerging trends. You need to follow renowned cybersecurity organizations, industry reports, and regulatory updates. Some of the top names where you can find information on the latest security practices, risks, tools, updates, and more are:
- Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
- Krebs on Security
- Dark Reading
For companies without dedicated security teams, partnering with cybersecurity firms that provide regular updates and risk assessments ensures ongoing protection without the need for constant internal training.
Conclusion
Organizations generally do not neglect cybersecurity. However, security threats frequently remain undetected until a major problem emerges. This article highlights the significance of QA-driven security testing in detecting vulnerabilities, safeguarding third-party integrations, and guaranteeing compliance with industry standards, which are essential for preventing breaches before they happen.
But even a great strategy will fail if not executed correctly. Cybersecurity is often not something most businesses want or can do on their own. Aspects such as awareness of new threats, embedding appropriate actions into the existing environment, and testing defenses require more than just intention. They need professional support, which you can get from a renowned cybersecurity testing service provider.
Frequently Asked Questions
Share This Article:



