Choose the Right Type of Web Application for Your Business
This guide is designed for business leaders, project managers, and entrepreneurs considering building a web application. It walks you through essential steps, breaking down key factors to evaluate before you start. You'll see how companies like Instagram, Google, and Microsoft built their web applications to align with their goals and engage their users.
With this guide, you’ll get a clear roadmap for creating a type of web application that matches your business needs and captures your audience's interest. Let’s begin.
1. Identify Your Business Needs and Objectives:
Before choosing a web application type, take a moment to understand your current digital setup, the hurdles you’re facing, and your goals. This step ensures you make informed decisions tailored to your business.
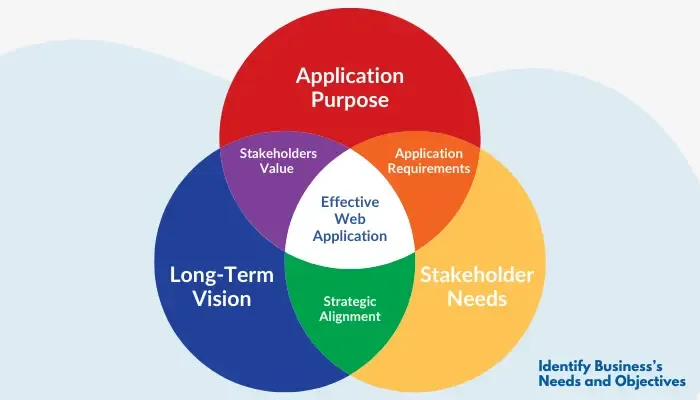
- Identify Your Business Challenges: Pinpoint the issues your web app will solve. Are you dealing with workflow bottlenecks, weak customer engagement, or scaling struggles? Clarifying these pain points defines your application’s purpose.
- Know Stakeholders and User Needs: Identify who will use the app and who it will impact. Engage stakeholders early to gather insights and guide your web application’s features and functionalities.
- Define Application Needs with Long-Term Goals: Align your web app’s type with your broader vision, whether it’s expanding market reach, enhancing customer experience, or improving operational efficiency.
- Set Up Performance and ROI Benchmarks: Outline metrics to measure your app’s success, such as cost savings, user engagement, or productivity gains. Clear benchmarks guide development and provide a standard for success.
Clarifying these elements positions your business to make choices that align with growth and adaptability.
2. Exploring Web Application Types That Suit Your Business Goals:
Choosing the right type of web application can make a big difference. Whether it’s the immersive experience of a native app, the flexibility of a web app, the blend of both in a hybrid or the reach of a PWA, each type offers distinct advantages. Here’s what you need to know about each option:
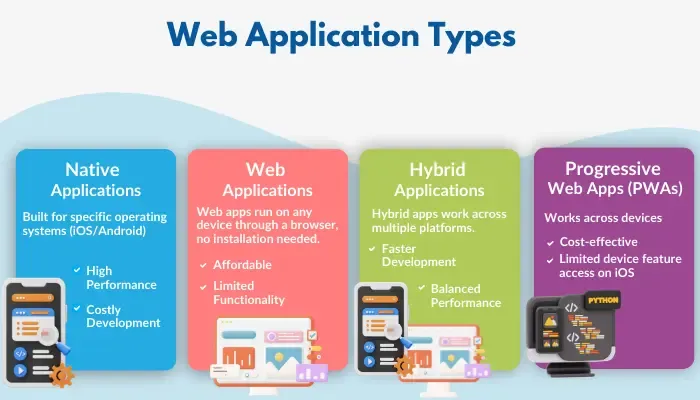
- Native Applications: Native apps are built for specific operating systems like iOS or Android. They deliver high performance and can use a device’s features like camera, GPS, and offline functionality. This makes them ideal for high-resource tasks.
For instance, the gaming industry often relies on native apps to leverage device-specific capabilities and give users an optimal experience. But they’re costly since each platform needs its own version.- Pros:
- Smooth performance.
- Offline accessibility.
- Immersive experience.
- Cons:
- High development costs.
- Limited to one platform per version.
- Pros:
- Web Applications: Web apps run on browsers and are accessible across devices without installation. They’re budget-friendly but rely on internet connectivity. Examples: Google Docs for real-time collaboration.
- Pros:
- Cross-platform accessibility.
- Easy maintenance.
- Affordable development.
- Cons:
- Limited offline functionality.
- Internet-dependent.
- Pros:
- Hybrid Applications: Hybrid apps combine native and web features, working across platforms with faster development cycles. Examples: Instagram’s hybrid model for broader reach.
- Pros:
- Faster development.
- Supports multiple platforms.
- Cons:
- Limited access to device features.
- Slower performance.
- Pros:
- Progressive Web Apps (PWAs):PWAs bridge the gap between apps and websites, delivering an app-like feel on any device. They load quickly, support offline use, and offer push notifications, making them a cost-effective way to provide broad accessibility. Starbucks, for example, uses PWAs to keep its app lightweight, which improved order diversity by 23%. Even during peak times, users could locate nearby stores without issues.
- Pros:
- Broad accessibility.
- Cost-effective.
- Cons:
- Limited device feature access.
- Requires up-to-date browsers.
- Pros:
3. The Role of Scalability in Web Applications:
An application built to scale can handle spikes in user traffic, expanding data, and additional features without slowing down or compromising the user experience. Building with scalability in mind keeps your app ready for growth, reducing the need for disruptive overhauls.
- Choose Technologies with Staying Power: Opt for flexible, widely adopted technologies like React, Node.js, and cloud-native platforms such as AWS or Azure. Developer-friendly languages like JavaScript or Python not only improve support options but also provide access to a larger talent pool, making it easier to find long-term support.
Recently, Statista surveyed developers about their preferred programming language and found JavaScript, HTML/CSS, and Python as top choices. But there are a lot of other languages as well which you can find below.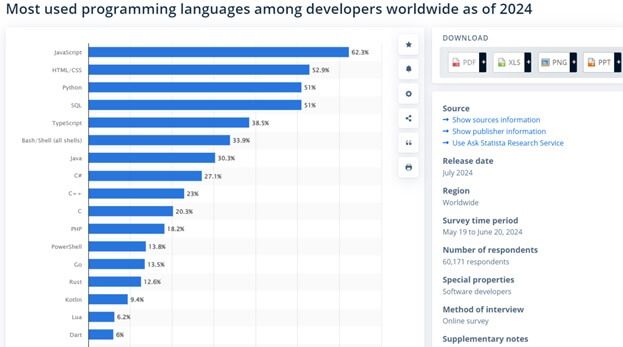
- Future-Proofing Techniques to Meet Evolving Demands: To ensure resilience and adaptability, consider these future-proofing techniques:
- Modular Design: Use a modular structure that allows updates in small increments rather than full-scale overhauls. A modular setup makes it easier to adapt to new technologies as they emerge without major disruptions.
- Cloud Infrastructure: Platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer the flexibility to scale up or down as needed. According to a report by O'Reilly, over 90% of organizations rely on cloud infrastructure, primarily because it reduces downtime and improves data management.
- API-First Development: Building with an API-first approach ensures your app integrates easily with new tools and services, keeping it compatible with changing technologies.
With rising cyber threats and tighter data regulations, keeping your application secure and compliant is essential. Here’s a breakdown of key protocols, standards, and best practices to protect your users and build trust.
4. Prioritizing Security and Compliance:
Embedding security into your web application safeguards user trust and complies with regulations. Here are some key things to protect your web applications. 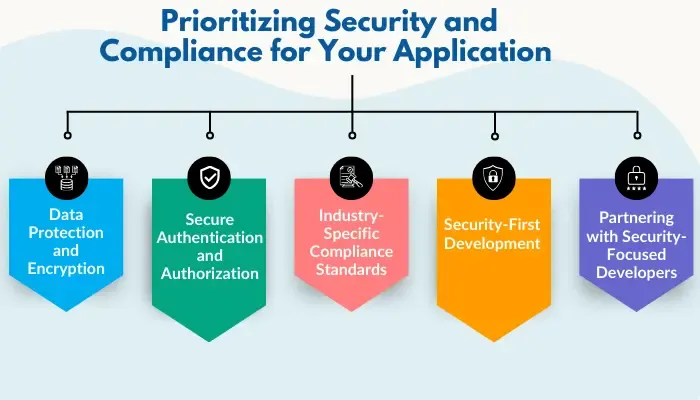
- Data Protection and Encryption: End-to-end encryption safeguards data at rest and in transit, reducing breach risks. Techniques like data masking and anonymization provide extra protection for personally identifiable information (PII), limiting unauthorized access and enhancing user privacy.
- Secure Authentication and Authorization: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and OAuth 2.0 protocols are critical. Proper authorization restricts access, reducing data exposure risks and supporting compliance efforts.
- Industry-Specific Compliance Standards: Some industries have specific data handling standards:
- Healthcare (HIPAA): Protects patient health information in the U.S.
- Data Protection (GDPR): Governs personal data use across the EU, with penalties of up to €20 million for violations.
- Payment (PCI-DSS): Sets standards for handling payment data, which is essential for apps processing transactions. Planning for these standards early can prevent heavy fines and protect your reputation.
- Security-First Development: Embedding security into every stage of development—often called DevSecOps—ensures security is central throughout. Regular security testing, like penetration tests and vulnerability assessments, helps maintain this standard. Tools like the OWASP Top 10 identify common risks and have become standard in secure development.
- Partnering with Security-Focused Developers: If outsourcing, choose a development partner who values security. Seek teams skilled in secure coding, regulatory compliance, and ongoing monitoring.
5.Integration with Existing Systems:
When businesses adopt new web applications, making them work with existing systems can be challenging. Seamless integration is essential to maintain productivity and avoid disruptions. Here’s how to ensure your new application integrates smoothly.
- Evaluate Current Systems for Compatibility: Start by assessing your existing systems. Check their core functionalities, data structures, and any limitations. This helps you identify potential issues early and ensures alignment between the new application and your current tech setup.
- Choose Integration-Friendly Development Platforms:
Opt for platforms designed with integration in mind. Many modern web applications come with tools and connectors that easily work with common software like ERP and CRM systems. Choosing the right platform can save time and reduce potential complications. - Use API-First Development for Flexible Integrations: An API-first approach allows data to flow freely between systems with minimal custom coding. Open APIs provide a flexible way to connect both new and legacy systems, making future integrations easier.
- Address Legacy System Challenges: Older systems often have outdated technology and rigid structures that make integration more complex. Middleware solutions or API gateways can act as connectors, allowing smoother data exchanges between systems.
6.Balancing Customization vs. Off-the-Shelf Solutions:
Choosing between a custom-built web application and an off-the-shelf solution is a strategic decision that impacts costs, timelines, and flexibility. This section provides a framework for evaluating both options, helping you make the best choice based on your business’s specific needs.
- Benefits and Limitations of Custom-Built Solutions: Custom-built applications offer tailored functionality designed to align closely with your business processes. They provide unique features and flexibility that off-the-shelf solutions often lack. However, they typically require more time and a larger budget due to the complexity and resources involved in development and testing.
- Pros:
- Tailored functionality.
- Scalability.
- Competitive differentiation.
- Cons:
- Higher development cost.
- Longer timeline.
- Potential maintenance challenges.
- Pros:
- Benefits and Limitations of Off-the-Shelf Solutions: Ready-made solutions are ideal if you want a faster setup with a lower initial investment. They include vendor support and typically have shorter deployment times. However, these solutions may not fully match your specific needs and can limit flexibility as your business grows.
Many small businesses opt for off-the-shelf CRMs, like HubSpot or Zoho, which cover essential needs at a reasonable cost, though they may require future upgrades as the business scales.- Cons:
- Cost-effective.
- Quick deployment.
- Vendor support.
- Pros:
- Limited customization.
- Feature gaps.
- Potential scalability issues.
- Cons:
- When Customization Becomes Essential: Consider customization if your business requires specialized features that align with specific workflows, compliance standards, or client demands. In industries like healthcare or finance, where unique processes and strict standards are critical, custom applications often become indispensable.
- Budget and Future Flexibility: A custom app involves a higher initial investment but can adapt as your business grows. Off-the-shelf options, though cheaper initially, may incur extra costs as your business scales and requires integrations. A popular trend is the hybrid approach, where companies start with off-the-shelf software and add custom modules as they grow, balancing flexibility and cost efficiency.
7. Building a Good UX for Customer Satisfaction:
The strength of a web application lies in delivering a smooth, engaging user experience. Prioritizing usability, accessibility, and intuitive design meets the expectations of both customers and internal users. Here’s how to build a UX that truly serves your users.
- Understand User Needs and Behavior: Start by researching user behavior to identify pain points. Build features that address real needs to keep users coming back. For example, Amazon continually analyzes how users interact with its platform, creating personalized experiences that improve customer retention.
- Implement Core UX Principles for Web Applications: A strong UX depends on simplicity, consistency, and responsiveness. Keeping the design clean helps users focus without distractions. Streamlined navigation, clear visual hierarchies, and quick feedback for user actions make the experience intuitive and seamless.
- Accessibility Across Devices and Platforms: Accessibility makes web applications more inclusive. Design with accessibility in mind to meet standards like WCAG. Features such as keyboard navigation, adaptable layouts, and screen reader compatibility open the application to a broader audience.
BBC News, for instance, includes text resizing, color contrast settings, and comprehensive screen reader support to meet WCAG 2.1 standards, improving access for all.
8. Key Factors Influencing Development Costs:
The cost of web application development depends largely on the complexity, features, and platform requirements. Applications with extensive customization or complex backend integrations are generally more expensive because they require specialized skills and time.
Developing a mid-level web application typically costs between $60,000 and $150,000, with custom applications often landing on the higher end of that range.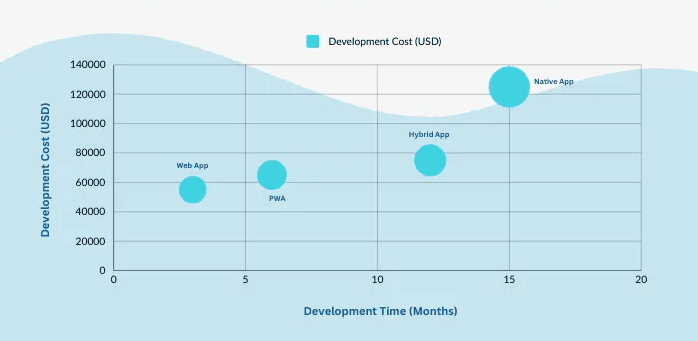
- Cost Breakdown by Application Type: Each type of web application has its own cost structure. Here’s a quick look:
- Native Apps: These are the most expensive since they need separate builds for platforms like iOS and Android.
- Web Apps & PWAs: More budget-friendly, compatible across devices, and accessible via browsers.
- Hybrid Apps: A middle-ground option, typically priced between $50,000 and $100,000, offering broader compatibility with some native-like features.
- Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): Known for saving on costs while delivering near-native performance.
- Example Costs:
- Native: $100,000+ (iOS and Android separate builds)
- Web App: $30,000 - $80,000
- Hybrid: $50,000 - $100,000
- PWA: $40,000 - $90,000
- Estimating Timelines and Setting Milestones: Development timelines vary by app type and feature set. Native applications generally take longer due to platform-specific requirements, while PWAs and web applications often have shorter timelines.
The average timeline for developing a PWA is around 3-6 months, while native applications can take 6-12 months.
9. Choosing the Right Development Partner:
This step is crucial if you don’t want to build a web development team. In that case, partnering with a development team is the right choice. Here’s how to choose wisely and find the right development partner.
- What to Look For: Choose a team that’s experienced in your industry. Specialists understand the unique needs you face. For instance, at ThinkSys, we’ve successfully delivered projects for clients who are highly skilled technically but may struggle to articulate their exact needs or the best approach. Despite that, our experts work to understand their requirements and deliver solutions that genuinely work for them.
- Checklist to Hire a Development Partner:
- Projects similar to what you need.
- Verified client testimonials.
- Familiarity with compliance standards (e.g., HIPAA, PCI-DSS).
- Technical Know-How and Problem-Solving: Technical skills alone aren’t enough. Look for partners who think strategically, too. Review their past work to see if they’ve solved complex issues.
- Clear Contracts and Expectations: When it comes to contracts, clarity is essential. Define timelines, deliverables, and costs upfront. Also, confirm the support they offer post-launch. A partner committed to ongoing updates and security patches can save you from future headaches.
- Best Practices:
- Transparent Contracts: Cover timelines, costs, and potential changes.
- Long-Term Support: Confirm they provide updates and security assistance after launch.
- Collaborate for Real Results: Effective communication makes all the difference. Look for a partner who values transparency and regular updates. Weekly check-ins help improve project timelines and reduce revisions. A good partner will ensure you’re involved in key decisions to keep the project aligned with your goals.
Conclusion:
Building the right type of web application involves strategic planning and collaboration. This guide has taken you through essential steps, from identifying your business’s specific needs and selecting the appropriate app type to focusing on scalability, security, and user experience.
If you're facing challenges with scalability or secure integrations, partnering with ThinkSys can resolve those issues and guide you in building a tailored solution designed for long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Share This Article:








