Multi-tenant Architecture For Cloud Apps
Cloud Computing is now an essential technology with more benefits continuously emerging and driving up usage with every passing day. By some estimates, the cloud market is worth over 300 billion USD, with SaaS offerings being at the top of the charts, followed by IaaS and PaaS solutions, respectively.
As users grow, use cases surge, and usage rises, optimal and effective resource sharing becomes critical to effectively serving users on cloud apps and services.
Multi-tenant architecture makes that possible by enabling them to effectively get the resources they need.
But what exactly is MTA, and why is it so important for cloud applications?
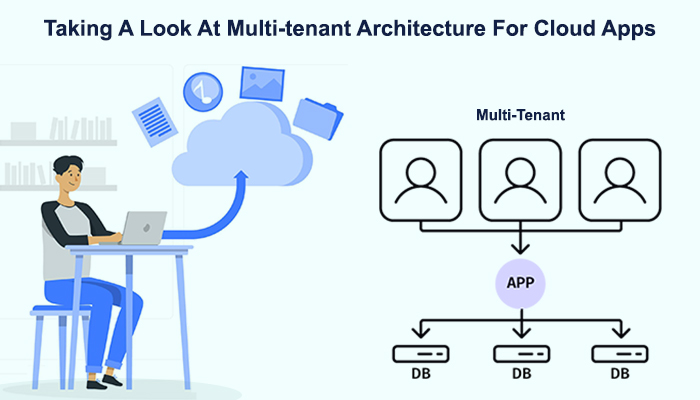
What is Multi-tenant Architecture?
Multi-Tenant Architecture is a software architecture model where a single instance of the software serves multiple customers or "tenants." Each tenant's data and configuration are isolated, ensuring privacy and security, but the underlying infrastructure and application code are shared. This architecture is akin to an apartment building, where each tenant has their own private space but shares the overall structure and utilities.
For example, consider a cloud-based email service provider like Gmail. Millions of users access the same application, but each user's inbox and settings are kept separate and secure. This is an instance of multi-tenant architecture, where a single application instance (Gmail) serves multiple tenants (users).
MTA plays a crucial role in cloud computing due to its inherent efficiency and scalability. It allows cloud service providers to serve a large number of customers with a single application instance, reducing hardware and software costs. Moreover, MTA simplifies updates and maintenance, as changes can be made centrally and instantly benefit all tenants. This efficiency makes MTA a cornerstone of Software as a Service (SaaS) models, where software is delivered over the internet on a subscription basis.
Key Characteristics of MTA
- Resource Sharing: Tenants share the same infrastructure and application, leading to efficient resource utilization.
- Isolation: Despite sharing resources, each tenant's data and configuration are kept separate and secure.
- Scalability: The architecture can easily scale to accommodate more tenants without significant changes to the application.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduced operational and hardware costs due to shared resources.
How MTA Differs from Single-Tenant Architecture?
In a single-tenant architecture, each customer has their own dedicated instance of the application and infrastructure. This approach offers complete isolation and customization but at a higher cost and complexity. In contrast, multi-tenant architecture optimizes resource usage and cost by sharing infrastructure among multiple tenants while maintaining isolation. This makes MTA a preferred choice for cloud applications and services where scalability and cost-efficiency are key considerations.
Types of Multi-tenant Architecture for Cloud Apps
End-users may have different priorities for a cloud app depending on the type of application, information categories, user types, and interfaces. Multi-tenant architecture comes with the following two options to suit these customer requirements and priorities.
Type #1: One App Instance, One Database -
In this multi-tenant architecture, a single instance of the cloud application supports one database. The users accessing the application have their data present in the same database. With the increase in the number of users, the multi-tenant architecture enhances the resources and capacity to offer better scalability. The costs also come down due to the concept of resource sharing.
However, this option has a few drawbacks. The primary drawback is the noisy neighbor effect. In such a case, network performance issues may emerge for one or more tenants due to the other tenant using a majority of the available resources.
Type #2: One App Instance, Several Databases:
This is the multi-tenant architecture that includes one instance of the cloud application and supports multiple databases. There is a mapping of a dedicated database for each of the tenants. The maintenance and management of these database instances are also independent of one another. This brings down the overall complexity levels and also introduces ease of management. The drawback around the noisy neighbor effect in one app instance, one database option, is also not present in this case. However, the option has lower scalability and higher costs. It can be expensive to have a separate data storage space. To promote scalability, additional database nodes can also have adverse implications on the costs.
Multi-tenant Architecture Benefits for Cloud Apps
Multi-tenant architecture offers numerous advantages for cloud applications. These benefits make it an appealing choice for businesses seeking to leverage the power of cloud computing while optimizing their IT investments.
- Better Flexibility and Scalability: As the number of users or tenants increases, the system can easily scale to accommodate this growth without the need for major infrastructure changes. This is particularly beneficial for cloud applications that experience fluctuating demand, as resources can be dynamically allocated and de-allocated based on current needs. This flexibility ensures that businesses can efficiently manage their resources and maintain optimal performance even as their user base expands.
- Cost-Savings:There is a positive impact on costs. The server cloud needs for applications with multi-tenant architecture are proportionally lesser than for single-tenant architecture. As a result, cost savings are possible for the cloud providers as well as the customers. Businesses enjoy lower operational and capital expenses, making it an attractive option for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) as well as larger organizations looking to optimize their IT spending.
- Optimal Resource Usage: his is one of the primary benefits of using multi-tenant architecture for cloud applications. With these architectures, you can utilize the same infrastructure and resources to address multiple needs. The data centers also do not require individual increments for every single customer. This allows providers to utilize every bit of the considerable computing power the servers and other devices in the ecosystem command. All of this brings down the performance overheads while maximizing resource usage.
- Maintenance and Updates: In a multi-tenant architecture, maintenance and updates are managed centrally, which simplifies the process and reduces the workload for IT teams. Since all tenants share the same application instance, updates and patches can be applied once and immediately become available to all users. This not only streamlines the update process but also ensures that all tenants have access to the latest features and security enhancements, contributing to a more consistent and reliable user experience.
- Security: While security is often cited as a concern in shared environments, multi-tenant architectures are designed with robust isolation and data protection mechanisms to safeguard tenant data. Techniques such as data encryption, access controls, and tenant-specific security policies help ensure that each tenant's data remains private and secure. Additionally, the centralized nature of multi-tenant systems allows for more efficient monitoring and response to potential security threats, further enhancing the overall security posture of the application.
Things to Consider If You Want to Build a Multi-Tenant Architecture for Your Users
In this section, we'll dive deeper into the challenges and considerations that businesses need to keep in mind when adopting multi-tenant architecture for cloud apps. Understanding these aspects is crucial for ensuring a successful and secure implementation.
1. Data Security and Privacy
One of the primary concerns in multi-tenant architecture is the security and privacy of tenant data. Since multiple tenants share the same infrastructure and resources, it's essential to implement robust isolation mechanisms. This involves segregating data at the storage, application, and network levels to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Employing encryption, access controls, and regular security audits can further enhance data security and privacy.
2. Performance
In a multi-tenant environment, resource allocation and contention can significantly impact performance. It's vital to have an efficient resource management strategy that ensures fair distribution and prevents any tenant from monopolizing resources. Techniques like load balancing, resource quotas, and auto-scaling can help maintain optimal performance levels for all tenants, even during peak usage times.
3. Customization
Customization is another challenge in multi-tenant architecture. While tenants may require personalized features and configurations, maintaining a standardized environment is essential for efficiency and scalability. Striking the right balance involves providing configurable options and templates that allow tenants to tailor the application to their needs without compromising the underlying architecture's integrity.
4. Compliance
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is critical in multi-tenant architecture, especially for businesses handling sensitive data. Ensuring compliance involves implementing security measures, data protection policies, and regular compliance audits. It's important to stay updated with regulatory changes and adjust the architecture and processes accordingly to maintain compliance.
Implementing Multi-Tenant Architecture
Multi-Tenant Architecture seems useful. That's why most businesses want to adopt it. However, without a proper strategy, planning, and expertise, all your efforts can go in vain. Hence, first understand how you can implement it in your organization successfully.
Key Steps in Developing a Multi-Tenant Cloud App
- Define Requirements: Understand the specific needs of your target audience and the functionality required for your multi-tenant application.
- Select a Cloud Platform: Choose a cloud platform that supports multi-tenancy and offers scalability, reliability, and security features.
- Design the Architecture: Decide on an architectural pattern (e.g., database per tenant or shared database) that aligns with your application's requirements and scalability needs.
- Develop the Application: Build the application with multi-tenancy in mind, ensuring that each tenant's data and configurations are isolated.
- Implement Security Measures: Incorporate robust security mechanisms to protect tenant data and ensure privacy.
- Test Thoroughly: Conduct extensive testing to identify and address any issues related to multi-tenancy, performance, and security.
- Deploy and Monitor: Launch the application and continuously monitor its performance and security to ensure a seamless experience for all tenants.
Choosing the Right Cloud Platform and Tools
When selecting a cloud platform for your multi-tenant application, consider the following factors:
- Scalability: The platform should easily scale to accommodate the growth of tenants and their resource demands.
- Security: Look for platforms with strong security features to protect tenant data and ensure compliance with regulations.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Evaluate the pricing models of different platforms to find one that fits your budget and offers good value for the features provided.
- Developer Ecosystem: Choose a platform with a rich ecosystem of tools and services that can simplify development and deployment processes.
Architectural Patterns: Database per Tenant vs Shared Database
- Database per Tenant: In this pattern, each tenant has its own database, providing strong data isolation and easier customization. However, it can lead to higher resource consumption and management complexity.
- Shared Database: In a shared database pattern, multiple tenants share a single database, with data separated by schemas or other mechanisms. This approach offers better resource utilization but requires careful design to ensure data isolation and security.
Tenant Isolation Strategies
Ensuring tenant isolation is crucial in a multi-tenant architecture. Some common strategies include:
- Data Isolation: Use separate databases or schemas to isolate tenant data, preventing one tenant from accessing another's data.
- Resource Isolation: Implement resource quotas and limits to prevent one tenant from monopolizing shared resources.
- Security Isolation: Use role-based access control (RBAC) and tenant-specific security policies to ensure that tenants can only access their own data and resources.
- Network Isolation: Employ network segmentation and virtual private networks (VPNs) to isolate tenant network traffic.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies of Multi-Tenant Architecture
Multi-tenant architecture has revolutionized the way cloud apps are developed, deployed, and managed, offering significant benefits across various industries. In this section, we'll explore some real-world applications and case studies to understand the impact of multi-tenant architecture.
Examples of Successful Multi-Tenant Cloud Apps
- Salesforce: A pioneer in multi-tenant cloud applications, Salesforce provides a comprehensive suite of CRM tools and services. By leveraging multi-tenant architecture, Salesforce can efficiently serve millions of users across various organizations, ensuring data isolation while sharing underlying resources.
- Microsoft Office 365: This popular suite of productivity tools employs multi-tenant architecture to offer scalable and secure services to businesses of all sizes. Users can access shared resources like servers and databases, reducing costs and enhancing collaboration.
- Shopify: An e-commerce platform that enables businesses to create online stores, Shopify uses multi-tenant architecture to host thousands of stores on a single infrastructure. This approach allows for cost-effective scaling and simplified maintenance.
- Zendesk: A customer service platform that uses multi-tenant architecture to provide support and ticketing solutions. By sharing resources, Zendesk can offer a reliable and scalable service to a large number of businesses.
- Slack: A communication platform for teams that allows organizations to create a network of channels for messaging, file sharing, and collaboration. Slack's multi-tenant setup ensures data isolation while serving millions of users globally.
- Zoom: A video conferencing tool that became especially popular for its ability to connect people during the COVID-19 pandemic. Its multi-tenant cloud infrastructure supports millions of concurrent video calls, making it a reliable solution for businesses, schools, and personal use.
- AWS Multi-Tenant Hosting: Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers multi-tenant hosting services that allow developers to build and deploy scalable applications in the cloud. AWS's infrastructure is used by a wide range of applications, from startups to large enterprises, to achieve cost-efficiency and scalability.
- Google Workspace (formerly G Suite): Google's suite of productivity and collaboration tools, including Gmail, Docs, Drive, and Calendar, operates on a multi-tenant cloud architecture. This enables seamless collaboration and communication for businesses and educational institutions.
Impact on Different Industries
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Multi-tenant architecture is a cornerstone of the SaaS industry, enabling providers to offer scalable, cost-effective solutions. Businesses can access a range of software applications without the need for on-premise installations or dedicated infrastructure.
- E-commerce: In the e-commerce sector, multi-tenant architecture allows platforms like Shopify to host multiple online stores, providing a unified and scalable infrastructure. This helps small and medium-sized businesses compete in the digital marketplace without significant investment in IT infrastructure.
- Healthcare: Cloud-based healthcare applications leveraging multi-tenant architecture can provide secure and scalable solutions for electronic medical records, telemedicine, and patient management. This architecture ensures compliance with stringent data protection regulations while offering flexibility and cost savings.
- Education: Educational institutions and e-learning platforms benefit from multi-tenant architecture by offering accessible and scalable learning management systems. This approach supports a large number of users and courses, enabling personalized learning experiences.
- Financial Services: Multi-tenant cloud apps in the financial sector, such as banking and investment platforms, provide secure and scalable solutions for managing transactions, portfolios, and customer data. This architecture allows for rapid deployment of new services and regulatory compliance.
Best Practices for Multi-Tenant Architecture
If you want to build an application based on Multi-Tenant Architecture, you need to follow certain best practices, which are given below:
1.Security Measures
Security is a paramount concern in multi-tenant architecture, as multiple tenants share the same infrastructure and resources. To ensure robust security:
- Encryption: Encrypt tenant data at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access. This includes encrypting databases, backups, and network traffic.
- Access Control: Implement strict access control measures to ensure that tenants can only access their own data. Use role-based access control (RBAC) to define permissions based on user roles.
- Audits: Regularly conduct security audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security policies. This includes reviewing access logs, system configurations, and user activities.
2. Scalability Techniques
Scalability is crucial for accommodating the varying demands of tenants. To achieve seamless scalability:
- Load Balancing: Distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers to ensure optimal performance and availability. This helps in managing spikes in user demand without affecting the overall system performance.
- Auto-Scaling: Implement auto-scaling mechanisms that automatically adjust resources based on the current workload. This ensures that the system can handle increased demand without manual intervention.
3.Monitoring and Management
Effective monitoring and management are essential for maintaining the health and performance of a multi-tenant architecture:
- Performance Tracking: Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as response times, throughput, and resource utilization. This helps in identifying performance bottlenecks and optimizing resource allocation.
- Tenant Management: Implement tools for managing tenant lifecycle, from provisioning to de-provisioning. This includes managing tenant subscriptions, resource quotas, and billing.
Future Trends in Multi-Tenant Architecture
Multi-tenant architecture (MTA) continues to evolve, driven by advancements in technology and shifts in the cloud computing landscape. As businesses increasingly adopt cloud-based solutions, understanding the future trends in MTA is crucial for staying competitive and innovative. Here are some key developments to watch:
1. Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms can analyze tenant data to predict future trends, enabling more proactive resource allocation and service customization.
- Automated Security: AI-powered security systems can monitor tenant activities and detect anomalies in real time, enhancing data protection in multi-tenant environments.
- Enhanced User Experience: AI can personalize user interfaces and functionalities for each tenant, improving user engagement and satisfaction.
2.The Rise of the Internet of Things (IoT)
- IoT-Enabled Services: Multi-tenant platforms can offer IoT services, allowing tenants to easily integrate and manage their IoT devices. This can open up new possibilities for smart homes, industrial automation, and more.
- Data Management: The influx of data from IoT devices requires robust data processing and storage solutions. MTA can provide the scalability and flexibility needed to handle this data efficiently.
- Edge Computing: As IoT devices generate vast amounts of data, edge computing becomes essential for processing data closer to the source. Multi-tenant architectures will need to adapt to support edge computing requirements.
3.Evolution of Cloud Computing
- Serverless Computing: The shift towards serverless architectures reduces the need for tenants to manage servers, making MTA even more cost-effective and scalable.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies: Businesses are increasingly adopting hybrid and multi-cloud approaches. Multi-tenant architectures will need to accommodate seamless integration across different cloud environments.
- Sustainability: As environmental concerns grow, cloud providers and tenants are focusing on sustainability. Future multi-tenant architectures will likely incorporate energy-efficient technologies and practices.
To Sum Up Multi-tenant Architecture:
The adoption of multi-tenant architecture (MTA) for cloud apps presents a transformative opportunity for businesses seeking to harness the power of cloud computing. By allowing multiple tenants to share the same infrastructure, applications, and databases, MTA offers a cost-effective, scalable, and flexible solution that can accommodate the evolving needs of a diverse user base.
As cloud technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated security measures to emerge, further enhancing the appeal of multi-tenant architecture.
The adoption of multi-tenant architecture for cloud apps represents a strategic move for businesses aiming to stay competitive in the digital age. It offers a pathway to increased efficiency, agility, and innovation, enabling organizations to deliver high-quality services while maintaining control over their costs and resources.
Share This Article:







