Cloud-Native App Development
Cloud-native refers to an approach to develop and run applications to take benefit of the many powerful cloud computing models out there. The development approach is apt for public as well as private cloud options. Cloud-native app development also folds in many of the latest development concepts and approaches like DevOps, Microservices architecture, containers, and continuous integration & delivery.

To further examine the process of cloud-native app development, the following table highlights the key differences of this approach from the traditional enterprise app development.
|
Parameter |
Cloud-native App Development |
Traditional Enterprise Apps |
|
Delivery and Development Model/Approach |
Continuous development, integration, and delivery |
Waterfall (rigid) development earlier, now Agile |
|
Scalability |
Automated scaling |
Manual Scaling |
|
Recovery Rate |
Rapid |
Slow |
|
Capacity |
Right-sized |
Over-sized |
|
Architecture |
Microservices |
Monolithic |
|
Level of Abstraction |
High |
Low — OS dependent |
The following figure from Microsoft illustrates cloud-native design quite beautifully.
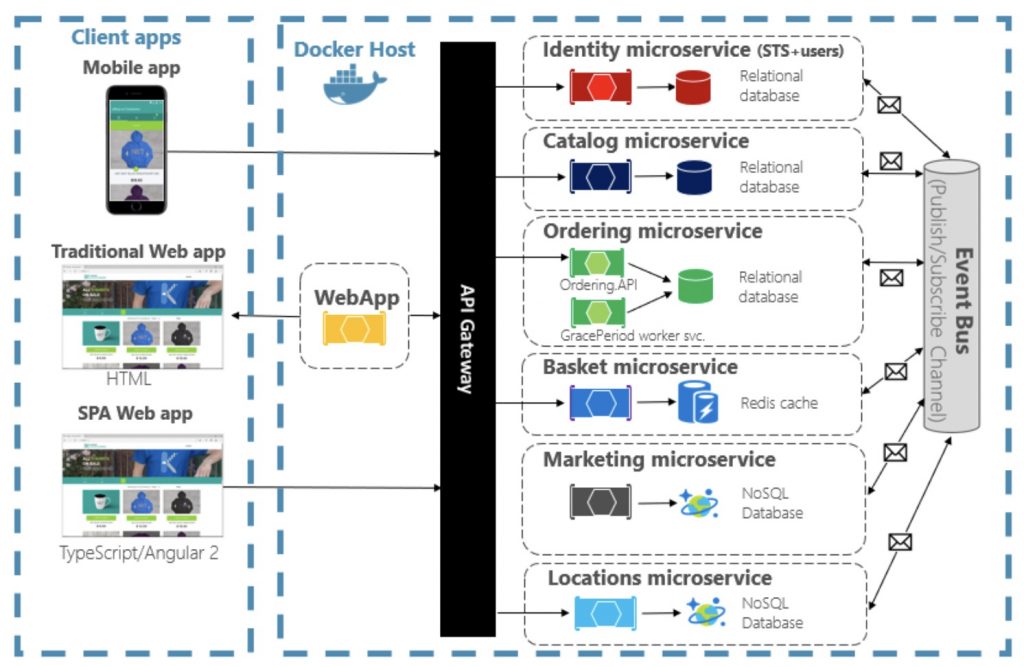
Interesting Read:- How to boost cloud-native security?
Building Cloud-native Apps
Cloud-native apps often comprise small and independent services to provide required business value with continuous delivery and improvement. The approach enhances the speed of development and connects new apps with existing ones.
Several elements and components are significant in cloud-native app development. While well-known concepts in themselves, it's worth touching on them to establish the concept.
- DevOps is one such element and it refers to the continuous collaboration of development and IT operations. The primary objective of the DevOps approach is to continuously improve the quality of the software applications while simultaneously resolving customer/user concerns. It leads to the formation of a cohesive environment to build, test, and release the apps consistently.
- Microservices are integral components in the cloud-native app development lifecycle. It refers to an architectural approach comprising a collection of small services that are developed independently of each other.
Each service in a microservices architecture is independent and can run in its process. The services can also be deployed, scaled, and restarted without involving any other service due to their loosely coupled nature. The involvement of the microservices architecture facilitates regular updates of the live applications without causing any adverse implications on app continuity, availability, or customer requirements. - Containers in cloud-native app development provide supreme efficiency and higher speeds in comparison with Virtual Machines (VMs). The involvement of OS-level virtualization leads to the dynamic division of a single OS instance in one or multiple isolated containers. These containers have a unique writable file system along with a resource quota.
Two properties have relevant value for using containers in cloud-native app development. These are low overhead and high packing density qualifying containers to be an ideal choice to deploy the microservices.One of the essential properties that distinguish cloud-native app development from the traditional process is continuous delivery and integration.
Agile development processes come into the picture to ensure continuous delivery. The development process includes incremental changes in the software with parallel testing and continuous delivery. Constant collaboration and feedback from the end-users add to the empowered enhancement of software and application quality. - Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) help integrate the data sets, apps, and devices for seamless delivery. Agile integration is used in cloud-native app development to offer higher scalability and flexibility with well-managed endpoints.
Cloud-Native App Developer Tools:
Information security and privacy risks on the systems and applications are at an all-time high. Cloud-native security offers a transformative mechanism to bring down the risks. This is because repairs and patches are installed as soon as the updates are available. The applications also constantly repave the services and rotate user credentials often to reduce the attack surface and attack window.
Kubernetes makes the deployment and management of container applications easy by allowing easy and robust orchestration. It has also come up with several abstractions in the app development workflows. Some of the tools listed below can be effective in cloud-native app development and bringing down the management overhead for the developers.
1. Draft:
Draft is a tool that provides two primary features to cloud-native app developers. It can automatically spin up the artifacts required to run Kubernetes apps. It also builds container images from the code and can deploy them to a Kubernetes cluster.
2. Skaffold:
It is a tool to iterate on application codes locally. The tool also includes features to build container images and deploy the same to local/remote clusters. The tool also offers features to manage and maintain continuous integration and delivery pipeline.
3. Telepresence:
The tool allows advanced application development by enabling cloud-native app developers to develop services locally. They can also sync and connect these services to the remote clusters and generate automatic updates based on the changes.
4. Okteto:
The tool enables the developers to determine local code changes and also has the feature to synchronize changes in a remote development environment. Such features allow the cloud-native app developers to work with their preferred tools and also speeds up the overall development lifecycle.
To Sum it Up
Cloud-native app development leverages the power of the cloud as an engine for business growth. Development teams can look to improve resilience and achieve higher scalability and flexibility with this approach. It is a great way to develop and run fault-tolerant apps irrespective of the cloud models involved.
Share This Article:







